Guiding structures
Lines of transmission
1) Equations of the telegraphers:
Part considering itself a feature of having line
infinitesimal length dz, it will introduce R, L, C, G to length unit
and the two equations e ![]() from
from ![]() which will be able therefore to be written becoming simpler
obtain
which will be able therefore to be written becoming simpler
obtain ![]() e
e ![]() from
which can be obtained the equations of telegraphers
from
which can be obtained the equations of telegraphers ![]() e
e ![]() dove
dove ![]() are the constant of propagation of the line.
are the constant of propagation of the line.
![]()
2) primary and secondary Constants:
the primary constants are R, L, C, G while the secondary
constants are the propagation constant g and the characteristic stiffness ![]() it is
gained before writing the generic solutions of the equations of
telegraphers
it is
gained before writing the generic solutions of the equations of
telegraphers ![]() that is e
that is e ![]() and replacing in
and replacing in ![]() the
, obtain an expression that I(z) alloy to V(z) by means of the
characteristic stiffness.
the
, obtain an expression that I(z) alloy to V(z) by means of the
characteristic stiffness.
3) Wavelength and speed of phase:
The direct wave and that one reflected propagano along the
line, the points in which ciascuna of they assume the same phase are
found between they to multiple distances of the wavelength ![]() , the equiphase points move along the line with one
speed
, the equiphase points move along the line with one
speed ![]() .
.
4) Concept of pupinizzazione:
In order to vary the propagative characteristics of a line how much must be acted as well as on geometry inserting of the elements does not concentrate to you, inductances or ability, opportunely distanced.
5) Coefficient of reflection on the cargo:
Considering a system of coordinated in which the cargo ZL it is found in z = 0 and to its
left it has the line having length â?"l, and remembering the
expression of tension and current to the coordinate z cioè ![]() e
e ![]() ha
ha ![]() from which pu² writing
from which pu² writing 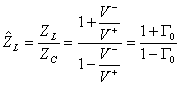 where
where 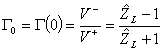 is the reflection coefficient on the cargo
e
is the reflection coefficient on the cargo
e ![]() the standardized stiffness.
the standardized stiffness.
6) Stiffness of Z incomein of one long line l sluice on a cargo ZL with and without losses:
![]() from which
from which 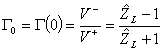 is replaced and
coupling the esponenziali opportunely reaches the
is replaced and
coupling the esponenziali opportunely reaches the 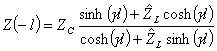 expression then supposing that the line is lacking in
losses the equation is reduced to
expression then supposing that the line is lacking in
losses the equation is reduced to ![]() .
.
7) Characteristics of the Zin in function of the length of the line:
From ![]() the it is obvious that for
multiples of l/2 Z in= Z Lis
had while for uneven multiples of l/4 is had
the it is obvious that for
multiples of l/2 Z in= Z Lis
had while for uneven multiples of l/4 is had ![]() . If
the cargo then is in short that is ZL= 0 it has that the stiffness is pure reactive and has the
course of the tangent while in the case the cargo is an open circuit
the stiffness is still pure reactive but the course is that one of the
cotangent. Finally if ZL =
ZC then Zin = everyZ C
for l that is the line is adapted.
. If
the cargo then is in short that is ZL= 0 it has that the stiffness is pure reactive and has the
course of the tangent while in the case the cargo is an open circuit
the stiffness is still pure reactive but the course is that one of the
cotangent. Finally if ZL =
ZC then Zin = everyZ C
for l that is the line is adapted.
8) Coefficient of long reflection one line without losses:
![]()
that is the module of the reflection coefficient is constant along the line while its phase varies.
9) VSWR:
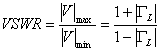
Paper of Smith
10) Mapping of the flat Z in the flat G :
It is based on the relation ![]() from
which for reversal
from
which for reversal ![]() is obtained the points to
constant R comes mappati in circumferences that in the case of R>0 are
comprised in the circle to unitary module that calls Paper of Smith
and passes all for the point GR = 1 the points to constant reattanza comes
instead mappati in circumferences also they passing for the point GR = 1 but
stavolta they do not intersect the real axis, to the inductive
reattanze correspond circles in the advanced semiplan while to the
capacitive reattanze circles in the downstairs correspond. The
paper of Smith of the admittances simply obtains for symmetry of the
paper of Smith of the stiffnesses regarding the origin, to notice that
the capacitive admittances are in the advanced semiplan while those
inductive ones in the downstairs while the adaptation and points
c.a., c.c. remain fixed.
is obtained the points to
constant R comes mappati in circumferences that in the case of R>0 are
comprised in the circle to unitary module that calls Paper of Smith
and passes all for the point GR = 1 the points to constant reattanza comes
instead mappati in circumferences also they passing for the point GR = 1 but
stavolta they do not intersect the real axis, to the inductive
reattanze correspond circles in the advanced semiplan while to the
capacitive reattanze circles in the downstairs correspond. The
paper of Smith of the admittances simply obtains for symmetry of the
paper of Smith of the stiffnesses regarding the origin, to notice that
the capacitive admittances are in the advanced semiplan while those
inductive ones in the downstairs while the adaptation and points
c.a., c.c. remain fixed.
11) Paper of Smith of one line with and without losses:
From ![]() the but considering positive
distances crescents approaching itself the cargo
the but considering positive
distances crescents approaching itself the cargo ![]() is had that in the case of line with losses becomes
is had that in the case of line with losses becomes ![]()
Representation of linear nets by means of spread parameters
12) Matrix of the admittances short circuit:
One obtains considering the tensions as applied largenesses and the currents like turning out largenesses:
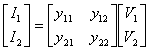
it comes said matrix of the admittances in short circuit in how much in order to determine the parameters y is necessary to place one of the two tensions to zero that is is necessary cortocircuitarla.
13) Matrix of the stiffnesses to empty:
One obtains considering the currents as applied largenesses and the tensions like turning out largenesses:
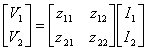
it comes said matrix of the stiffnesses to vuoto in how much in order determining the parameters z is necessary to place one of the two currents to zero that is open circuit.
14) Matrix of transmission and its property:
It is obtained considering applied to the largenesses to the second door and turning out the largenesses to the first door
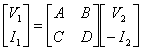
in order to gain parameters ABCD it is evidently necessary to cancel the just largeness to the second door.
Much profit in how much is a matrix the matrix turning out from the cascade of nets 2-doors is simply the product of the matrices of transmission of the single doors.
For a symmetrical net it is had To = D while for a mutual net AD-BC=1 is had, finally for a circuit without losses To and D is real while B and C are imaginary. One important property is that matrix ABCD exists for every net while this is not true for the other typology of matrices.
15) Matrix of transmission of a having feature of long line without losses l and characteristic stiffness ZC :
Part from the expressions ![]() e
e ![]() writing themselves the complex exponential in
terms of breast and cosine and replacing the closing condition on the
cargo that is
writing themselves the complex exponential in
terms of breast and cosine and replacing the closing condition on the
cargo that is ![]() can immediately be identified the
coefficients of the transmission matrix, is had:
can immediately be identified the
coefficients of the transmission matrix, is had:
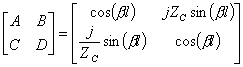
16) Coefficient of reflection in terms of waves and matrix of Scattering:
Reflected wave incident and can be expressed in the shape ![]() e
e ![]() follows some
that the reflection coefficient that is the relationship between wave
incident and reflected wave assumes the shape
follows some
that the reflection coefficient that is the relationship between wave
incident and reflected wave assumes the shape ![]() .
.
Extending the concept to a net 2-doors the matrix of dispersion can be introduced or scattering
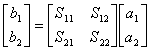
it is observed that in order to obtain the parameters of scattering will be necessary to cancel the wave directed to the income door or to that one of escape that it is possible by means of the adaptation but the this demands the acquaintance of the stiffness of normalization Z0 . For a mutual net it is had that the elements on the inverse diagonal are equal and in the case of passive net evidently the module of all the parameters of scattering is inferior to 1 finally in the case of a mutual net and without losses is had that the sum of the squares of the parameters of scattering is worth 1.
Coaxial cable
17) Description of the coaxial cable:
It is constituted from two coaxial conductors, one of beam r situated to the inside of the having other beam r0. The propagation of ways TEM concurs and they do not have frequency of inferior cut, the maximum frequency instead is marked from the beginning of the operativity of ways TM and YOU.
18) characteristic Stiffness:
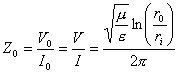
19) primary Constants:
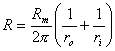 from it is deduced that the much more inner conductor
is small, much more is heavy the ohmic losses, in the expression ha
from it is deduced that the much more inner conductor
is small, much more is heavy the ohmic losses, in the expression ha ![]() that holds account of the losses of the
conductors essendo
that holds account of the losses of the
conductors essendo 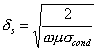 the
depth of penetration that diminishes to growing of the frequency
making to increase the losses.
the
depth of penetration that diminishes to growing of the frequency
making to increase the losses.
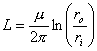 from which remembering the expression of Z0 it is had that elevatedZ 0 implies high L moreover is
from observing that it is dependent only from the geometric
characteristics and not of the line and not of the dielectric and the
metal.
from which remembering the expression of Z0 it is had that elevatedZ 0 implies high L moreover is
from observing that it is dependent only from the geometric
characteristics and not of the line and not of the dielectric and the
metal.
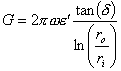 dove
dove ![]() essendo d the loss angle of the
dielectric.
essendo d the loss angle of the
dielectric.
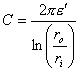 .
.
20) the maximum Frequency of I use of the coaxial cable:
It is the frequency beyond which ways not TEM take part
also, ![]() naturally dominates ror that how much the more it is small
much more concurs with the cable to work to vhf of the rest but to
growing of f we have seen increase also the losses for via of the
effect skin and in kind the limitation is this that takes part before.
naturally dominates ror that how much the more it is small
much more concurs with the cable to work to vhf of the rest but to
growing of f we have seen increase also the losses for via of the
effect skin and in kind the limitation is this that takes part before.
21) manipulable Power:
It is the amount of power RF that the cable can sopportare above all in terms of temperature.
22) Maximum tension of use:
It is the maximum potential difference them bearable
between centers them and the stocking, does not correspond to the
dielectric rigidity towards which the relation is had
indeed ![]() , for advanced tensions they are had arches in the
dielectric that gives to place to noise and damaging of the
dielectric.
, for advanced tensions they are had arches in the
dielectric that gives to place to noise and damaging of the
dielectric.
23) Attenuation:
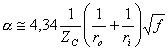 db/100piedi
db/100piedi
24) Isolation:
The schermaggio of the inner electric field agrees to the cable regarding the external electric fields, depends on the stocking which can be to single mesh, double mesh, to strip, solid.
Rectangular waveguide
25) Structure of the waveguides:
Draft of a pierced conductor to on one side greater characterized rectangular section R-at and from a smaller side b. Evidentemente previews a frequency of inferior cut in how much well-known the continuous one needs of two conductors.
26) Frequency of cut-off:
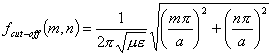
therefore in any case having indices (m,n) are associated a frequency of cut-off and propaga only for advanced frequencies to it.
27) dominant Way:
It is the way that possesses the frequency of cut-off more lowland, in a guide is always YOU1,0 while for ways TM the first valid way is TM1.1 which elevated frequency of cut-off more possesses one.
28) Lines of force of and and H in a rectangular waveguide:
The electric field turns out maximum to the center of the long side and therefore the lines of force more are thickened here and directed orthogonally to such side. The magnetic field instead turns out maximum also it to the center of the side along but the lines of force are parallels to such side while the member along the propagation direction is null to the center of the long side.
29) Cause of the losses in the waveguides:
The currents are distributed on an ended thickness of the metal in how much the conductivity of the metal are not infinite as it would have ideally to be, also the dielectric then introduces one very rappresentabile not null conductivity with one constant complex dielectric or the tangent of the loss angle.
30) passing Band of the waveguide:
The formed guide being from a single conductor behaves itself as a pass-high filter however has been interested to the monomodale behavior in how much the ways introduces between they various speed of phase and therefore it gives place to dispersion in the case that is concurred that they are operated to you more of one. Choosing to = 2b it makes so that the way YOU1,0 is operating alone for one eighth of frequency. The presence of losses of the rest door to an extension towards the bottom of the ways, that in truth reduces the passing band of the guide in as far as vlves cannot be used dates the strong losses while to other frequencies even though with remarkable losses the advanced way is introduced.
31) salienti Characteristics of the waveguides in use:
Two norms are had, the valid EIA only for the guides and the valid JAN for all means transmitted to you. To vlf the guide is large therefore prefers the aluminum that he is a light conductor mentre to growing of the frequency to the aim to limit the losses come uses you metals with one lower resistività like the brass and silver.
There are then guides in which the long side is more of the double quantity of the short side, the reason is from searching itself in the best performances in the comparisons of the losses introduced from this geometry.
Microstriscia
32) physical Structure of the microstrip:
A dielectric substrate is had high h and with dielectric constant andr, to of under a metallic plan of mass is had and to of over one wide metalization high W and t. The substrate can be is of type âSoftâ?, like the Duroid that can be flexed and that to second of the composition wide variation introduces one of andr, than of type âHardâ? in kind alumina.
33) nearly static Approximation of the microstrip:
Not being a homogenous structure, the propagation of ways
TEM does not concur but only ways âquasi-TEMâ?. The 00
abilities to unit of length of such structure are a structure
difficult to analyze ![]() from an electromagnetic point
of view however the characteristic stiffness canbe determined imagining to replace the
dielectric with air being C.
from an electromagnetic point
of view however the characteristic stiffness canbe determined imagining to replace the
dielectric with air being C.
34) characteristic Stiffness of the microstrip with dielectric and its value in function of the W/h relationship:
Draft of expressions empiricists who once fixed the W/h
relationship and the dielectric constant andr concur to determine the
characteristic stiffness of the microstrip, in particular for tight
microstrips that is that they introduce W/h < 3.3 has 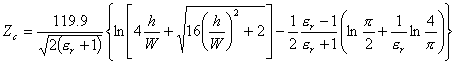 while for wide microstrips it is had
while for wide microstrips it is had 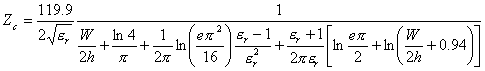
35) effective dielectric Constant:
It holds account of the fact that the microstrip is
formed from two various dielectrics that is the dielectric of the
substrate and the air, in order to hold account of both has 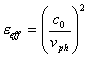 it is greater of andr , that is the value that would have
in the case of a line the many wide in which the all lines of force
crosses the dielectric, and minor of
it is greater of andr , that is the value that would have
in the case of a line the many wide in which the all lines of force
crosses the dielectric, and minor of ![]() that is
the value that would have in the case of a line much grip for which
the lines of force are half in air and half in the substrate.
that is
the value that would have in the case of a line much grip for which
the lines of force are half in air and half in the substrate.
36) Phenomena do not consider in the expressions analytics you of the microstrips:
to) the microstrip it is dispersive in how much andEFF is function of the frequency
b) it is the metal that the dielectric introduces of the losses
c) in the practical applications the structure goes considered of ended dimensions and inscatolata
Discontinuity of the guiding structures
37) Discontinuity:
The discontinuity excites locally of the ways that in normal conditions would not come excite to you and that they come attenuates to you esponenzialmente going away from the discontinuity. Two near discontinuities can moreover give place to of the zeroes of transmission.
38) Discontinuity in coaxial cable:
to) gap it enables to you that is of the microinterruptions of centers them that they prevent the passage of the continuous one and can also be used like filters pass-band if spaced out from features of line of opportune length
b) it knows you of stiffness obtain with one variation of the beam of the inner conductor and/or that outside
c) capacitive windows with of the local variations of the diameter of one of the two conductors
d) splices to T that concur the insertion of Stub in parallel with the line
39) Discontinuity in rectangular waveguide:
to) post that is of the cilindretti metallic that they are placed along the cross-sectional section to the direction of propagation, a post is had post inductive if the cilindretto it is high b, resonant if it is high L<b or a post capacitivo if it is high to and it is placed in parallel with the long side of the guide
b) metallic strips that can are placed parallel or orthogonally to the propagation direction.
c) diaphragms that is narrowing localizes you of the guide or in the plan and or the flat H
d) curving (bends) to 90° that they can happen is in the plan and that in the flat H
and) splices to T, joining some two the magical T is obtained
40) Discontinuity in microstrip:
to) open circuit
b) gap
c) stiffness jump
d) splice to T and cross
