Analyzer of phantom and generator of marks them to microwaves
Analyzer of phantom
1) Outline of a phantom analyzer superheterodyne:
It marks them RF is sended through a filter lowpass to the mixer which it introduces an isolation IF-RF not infinitely therefore prefers to have a greater IF of the fixed RF and to one determined frequency so as to to simplify the plan of the successes to you filters bandpass many straits which precede the envelope detector. A generator of rampa sendes the same one marks them is to the horizontal channel of the CRT that to the local oscillator which therefore the e variesf corresponding having to remain fixed fthe IF is gone to analyze one different fRF .
The lowpass in income it has the task to cut via the which had contribution to the frequency image that is speculating of fthe RF regarding the local oscillator.
2) Criteria in order to resolve two mark them many neighbors in frequency:
A phantom analyzer that has a tone in income always represents it in escape by means of a Gaussian bell that corresponds to the answer of selected filter RBW, that means that if we have two he marks them many neighbors in frequency their bells will be overlapped, achieves some that if the two tones have the same amplitude he is sufficient to set up for the RBW an opportune band to â?"3dB while if the amplitude of one of the tones is much greater one regarding the amplitude of the other tone is necessary to be able to vary also the selettività of filter RBW that is the relationship between the bandwidth to â?"60dB and the bandwidth to â?"3dB.
3) Skirt:
Draft of the value of attenuation of the filter for an offset data regarding the frequency centers them, is important in how much concurs to select an opportune RBW to the aim to visualize two marks them of which one it has an inferior level of NdB regarding the other.
4) Characteristics of the local oscillator:
It is an oscillator to variable frequency based on YIG spheres, it introduces a residual FM of approximately 1kHz due to the connection between the tooth of saws that it polarizes the YIG and the present active device in the oscillator, the effect is made obvious diminishing of the RBW, in particular when this is of the same order of magnitude of the band due to the residual FM is looked at of the frastagliature on the bell that it describes marks them of income.
The local oscillator introduces moreover instability is in amplitude that in phase, before can be eliminated by means of a limiter while the second one is due to manifest the active element and its effects in correspondence of the noise of bottom of the system, in particular has contributions 1/f, 1/f2 , 1/f3 , 1/f4 that assume have had to beats with if same of the noise 1/f.
5) Sweep Time:
It is the time necessary to the local oscillator in order
to execute brushing of the interval of frequencies, such time
increases to increasing of the resolution that is diminishing of the
RBW, it is had in fact that the 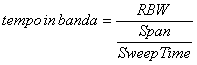 time that marks
them remains to the inside of the RBW must be greater of
time that marks
them remains to the inside of the RBW must be greater of ![]() the of the resolution filter being k one constant that
holds account of the fact if we estimate 80% or 90% of the asymptotic
value in order to estimate the time of answer of the filter.
Replacing the inequality is obtained
the of the resolution filter being k one constant that
holds account of the fact if we estimate 80% or 90% of the asymptotic
value in order to estimate the time of answer of the filter.
Replacing the inequality is obtained ![]() that
it evidences as to diminishing of the RBW the Sweep Time increases
quadratic, in order to avoid excessive long times of scansion can be
reduced the span in the case use RBW many small but in this case the
dependency is linear solo.
that
it evidences as to diminishing of the RBW the Sweep Time increases
quadratic, in order to avoid excessive long times of scansion can be
reduced the span in the case use RBW many small but in this case the
dependency is linear solo.
6) Characteristics of the envelope detector:
The frequency del marks them of income is desumibile gives it to frequency della oscillating premises therefore only interests to determine the associated amplitude to us to every frequency, to such aim uses a detector of envelope constituted from a diode valve followed from un parallel RC whose constant of time must is such to follow the peaks del marks them IF. It is observed that if the local oscillator comes made to work then to a fixed frequency to the escape of the detector we have the demodularred one.
7) Filtering video:
It is possible to eliminate the ripple overlapping to
marks demodularred them simply posponendo to the envelope detector a
filter video low-pass filter that it precedes the CRT, in the case
that is VBW < RBW is had that the VBW concurs to the determination
of the minimum Sweep Time, in particular is had ![]() .
.
8) Medium video:
Draft of a filtering that more consists in carrying out one medium of the values obtained on two or brushed of the interval of frequencies in examination, in such a way comes remarkablly reduced the fluctuations.
9) Methods of visualization:
The visualization directed on CRT introduces problems of persistence in the case of long Sweep Time, is preferred therefore to resort to display numerical, for they is had that the Span comes subdivided in a number of not advanced cells to 1000 to ognuna di.le which is associated a memory lease, the modalities of assignment of a value to a cell is the three following:
to) Sample Mode
championship comes and visualized it always marks them present in one determined position of the cell, as an example to the center or on an edge
b) Pos Peak and Neg Peak
with detector the Pos Peak it comes visualized the present value of the maximum amplitude in the cell while with the Neg Peak it comes visualized the minimum
c) Rosenfell
In the noise case they will come shown for every cell is the maximum value that the minimum while in the case of it marks them will come only shown the maximum value
10) absolute and relative Uncertainty:
The absolute uncertainty is function of the procedure of calibration of the instrument that consists in sending in income marks them of which they are notes frequency and power so as to to correct the errors arranged to us. The relative uncertainty holds account of the fact that marks them in income to the analyzer has various frequency and amplitude regarding those of marks them of calibration.
11) Sensibility of the phantom analyzer:
The ability to find marks having them level much bottom is inficiata from the noise generated from the circuitry of the phantom analyzer and in particular from amplifier IF. Leaving the income opened on the display the sum of the external noise is had and of the inner generated noise, the figure of noise of the system is much elevating, for ridurla an preamplifier is used which but it reduces also the dynamic range therefore is necessary to insert also a suppressor which diminishing the level of it marks them but leaving the noise unchanged it gets worse relationship S/N and therefore the noise figure. An improvement of the sensibility is obtained shrinking the RBW, in such a way in fact can be cut via more noise.
12) Cifra of noise of the phantom analyzer:
Since the analyzer has unitary gain, he is had that the
noise factor is ![]() therefore the noise figure is
therefore the noise figure is ![]() in which I replace
in which I replace ![]() which for
B=1Hz is worth â?"174dBm while for B=10kHz it is worth analogous
â?"110dBm has
which for
B=1Hz is worth â?"174dBm while for B=10kHz it is worth analogous
â?"110dBm has ![]() therefore replacing, simplifying B
and making to appear RBW in an expression it is had
therefore replacing, simplifying B
and making to appear RBW in an expression it is had ![]() that considering an equal RBW to 10kHz it is worth
approximately 24dB which much high is a value but account must be held
that the phantom analyzer is one instrument to general character and
not a simple receiver.
that considering an equal RBW to 10kHz it is worth
approximately 24dB which much high is a value but account must be held
that the phantom analyzer is one instrument to general character and
not a simple receiver.
13) Measure of noise:
The analyzer of phantom in kind introduces a level of inferior noise of 2,5dB to the effective value, that has had to the fact that the distribution of income is normally Gaussian but to the escape of the detector we have the envelope that, in the case of a linear scale, is distributed according to Rayleigh that determines a correction of 1,05dB to which they must themselves be added 1,45dB in the case of logaritmica scale therefore altogether has an equal systematic error to 2,5dB that it can be corrected in automatic way.
14) Cifra of noise of a system composed from phantom analyzer and preamplificatore:
The factor of noise of the system is 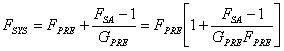 therefore observing that the factor of noise of the analyzer is
comprised between 100 and 1000 we can neglect 1 regarding FKNOWS therefore the figure of noise of
the system is
therefore observing that the factor of noise of the analyzer is
comprised between 100 and 1000 we can neglect 1 regarding FKNOWS therefore the figure of noise of
the system is 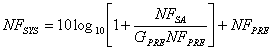 that can be represented on the
formers of a diagram having in
that can be represented on the
formers of a diagram having in ![]() abscissa,
evidently when this last largeness is worth 0 we have
abscissa,
evidently when this last largeness is worth 0 we have ![]() while asymptotically we have is to dx that to
sx
while asymptotically we have is to dx that to
sx ![]() . The optimal one for the figure of noise of
the system can be obtained in two distinguished modalities:
. The optimal one for the figure of noise of
the system can be obtained in two distinguished modalities:
to) with an preamplifier to gain much elevating it is had that the figure of noise of the system coincides with the figure of noise of the preamplifier, the problem of this solution is that the measure range is reduced and therefore is necessary to introduce a suppressor
b) if the figure of noise of the phantom analyzer is greater at least 10dB regarding the sum of the gain of the preamplifier and of its figure of noise then the figure of noise of the system is equal to the difference between the figure of noise of the phantom analyzer and the gain of the preamplifier.
15) dynamic Range and inner distortion:
The dynamic range is the difference between the maximum level of marks them and the minimal level of a second marks them that they can be visualizes to you at the same time concurring the measure of marks them more small with one fixed uncertainty. If it marks them RF it is in module too much elevated then the mixer will generate also its harmonicas that therefore are gone to add to an eventual one mark them in income to the same frequencies, the two contributed can but to be distinguished simply for the fact that varying the attenuation in income to the mixer they of income marks endures an attenuation To while the order products n endure an attenuation nA. To growing of the power in income the dynamic range is not limited from the noise but from the generation of the 2ª and 3ª harmonic.
16) Measurement Range:
The measure range differs from the dynamic range in how much marks them minimal and it marks them maximum can be visualizes to you not at the same time
17) Extension of the frequency range:
It is first of all necessary to remove the filter low-pass filter that it was had in income in order to eliminate the image, after which for the range until to 2.9GHz is continued to use the previous chain while for the extensive range the second harmonica generated from the mixer is taken advantage of and it is gone directly to passes centered band 321.4MHz that therefore it selects one
down-convertion. We can have an idea of the superimpositions in frequency between the others harmonicas tracing in plan fRF , f the curves fRF = f e fthe RF = f ± fthe IF in particular we call 1 f fIF and 1- the f - fIF analogous considering the harmonicas of the local oscillator we call n nf fIF and n- the nf - fIF , if we consider the range 1kHz-2.9GHz we have that the interval of fRF characterized from the 1- it is not overlapped to the intervals characterizes to you from the others f therefore low-pass filter will be sufficient to cut via the image.
In the case of extension of the frequency range the things are complicated in fact are superimpositions already between 1 and the 1- and to greater reason such superimpositions will be with the other ways in how much the bandwidth IF remarkablly have been reduced and then to growing of n it increases the slope of the straight ones and fortunately it gets worse the conversion gain.
18) Methods of identification of mark them:
There is is a solution software that a solution hardware, the solution software before consists in moving the local oscillator low of 2fIF and then up always of 2fIF in such case the just answer is that from the side in which the permanence is had of marks them. The solution hardware previews the sdoppiamento of first mixer, in particular if it has some on the branch that covers the band (1kHz, 2.9GHz) and an other on the branch that covers the banda (2.7GHz, 26.5GHz) in particular on the this last branch mixer is preceded from a preselector that is a filter to tight band (…approximately 20MHz) that it is piloted from the same one rampa that pilot mixer and therefore the ransom via the frequencies images. The preselector is realized with of the sferette of YIG.
Generator of marks them to microwaves
19) Typology of sources to microwaves:
to) sweppate Sources
They are based on I use of a VCO in which the frequency comes set up acting on a diode valve varactor or on of the YIG spheres, they have the problem that the power in varied escape of various dB to varying of the frequency therefore reruns to the ALC that is to the automatic gain control, in particular after the VCO a variable diode valve suppressor is placed PIN piloted from marks them that it is obtained rectifying and confronting with a reference marks them that obtains to the escape captured with a directional coupler previa amplification and filtering.
b) Sources to variable frequency in sintetizzatori said discreet steps
These sources are based on use of a fixed oscillator of reference, ve of are substantially three types
· Sintetizzatori digital them which generate lower frequencies regarding the reference
· Sintetizzatori directed with frequencies until to a maximum of 100MHz
· Sintetizzatori to phase coupling
20) Sintetizzatori digital them:
To every blow of clock a storage cell having in income variable a Damount q in function of the frequency that agrees to generate the sum to the its previous value, in such a way generates an address that a cell of memory containing in that date selects position the breast or the cosine of the address, also to the memory arrives the clock while the escape comes sended to a converter D/A and subsequently to a filter it low-pass filter whose task is to filter the shape of squared wave that it has been obtained. Naturally the storage cell once reached the its maximum ability comes annulled and it is begun from head.
