Accessories from laboratory
Directional couplers
1) directional Coupler:
Draft of a device 4 doors of which one door 1 is the
income door, door 2 is the door of characterized direct escape from
the coefficient of ![]() transmission, door 3 is the
door coupled characterized from the coefficient of
transmission, door 3 is the
door coupled characterized from the coefficient of ![]() connection, it is worth more 3dB for the applications
circuita them and than 6dB for the applications of measures, door 4
finally is the isolated door and is characterized from the
direttività
connection, it is worth more 3dB for the applications
circuita them and than 6dB for the applications of measures, door 4
finally is the isolated door and is characterized from the
direttività ![]() and the isolation
and the isolation ![]()
2) Classification of the bandwidths:
It is spoken about tight band if ![]() ,
wide band if
,
wide band if ![]() and the widest band if
and the widest band if ![]() .
.
3) riflettometrico Bridge:
Between generator and cargo they come inserted two
directional couplers, in the first one it marks them from the
generator enters on door 1 while on door 3 an electric power meter is
applied that measure a largeness proporziona them to the square of the
wave incident, door 2 instead is connected to door 2 of according to
coupler having instead on the door the 1 cargo and on 3 door also it
an electric power meter that measure a largeness proporziona them to
the square of the wave reflected from the cargo, doors 4 instead is
both sluices on an adapted cargo. In such a way a measure of the
coefficient of reflection is obtained 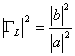 that but
risente of the fact that also the directional couplers insert of the
losses.
that but
risente of the fact that also the directional couplers insert of the
losses.
4) Couplers to 3dB:
The couplers to 3dB have the property to subdivide the power in equal parts between the direct door and the coupled door, however you they can be differences on is made of marks them, they are had therefore Hybrid to 90° and 180°.
5) Hybrid to 90°:
It is a coupler to 3dB in which it marks them on door 3 sfasato of 0° while it marks them on door 4 sfasato of 90°.
6) Hybrid to 180° e Rat Race:
It is a coupler to 3dB in which it marks them X in income to door 1 is sended in phase is to door 3 that to door 4 while it marks them Y in income to door 2 is sended in phase to sfasato door 3 and of 180° to door 4, that makes that to door 3 the S sum is had = X Y while to door 4 the D difference is had = X â?"Y.
A Hybrid example to 180° is the Rat Race whose doors are in order 2, 3, 1, 4 and are distanced between of they of l/4 while door 2 and the 4 are distanced from a long feature of line 3l/4, Admitting that to door 1 it enters marks them X and to door 2 it marks them Y we will have to 3 door the S sum = X Y while to 4 door differenza the D = X â?"Y.
7) Couplers in waveguide:
A typical coupler in waveguide is constituted from 2 having guides a long side in common, on it they are practices to you of the holes to opportune distances so that the power of income in a guide beyond exiting from the other side of the same guide enters in the holes and taking advantage of the combinations of phase, propaghi in the other guide only in a back, that can be obtained also closing on one metallic sheet at a distance opportune mail.
An other type of coupler is âT the Magicoâ? which had to the orthogonal intersection between a T and a L realized in waveguide, in it it marks them entering to door 3 only exits to doors 1 and 2 but not to door 4 where its way is under cut off for via of the dimensions of the guide.
Suppressors
8) Loss of insertion and attenuation of one net 2-doors:
The loss of insertion is the relationship between the power supplied from the generator to the cargo not adapted and the power supplied to the same cargo when a net characterized from the matrix of scattering is inserted also, is had:
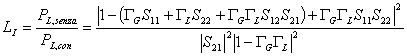
The attenuation is instead the loss of insertion when the
coefficient of reflection on the generator and the cargo, is both null ![]() where ToR it is the attenuation due to the reflection while ToD it is the attenuation due to the
dissipation.
where ToR it is the attenuation due to the reflection while ToD it is the attenuation due to the
dissipation.
9) Typology of suppressors:
to) fissi
they are constituted from cells to T or to p realizable as an example on coaxial cable by means of of the material dissipated you that she can be put in series to they centers in order to realize a resistance series RS or cross-sectional to resistance centers them in order to realize one R parallel// .
b) variable
pu² to come true itself with two coaxial cables in which one it slides in the other by means of of the micrometric lives, in the superimposition part it is absent centers them therefore is like having in series a coaxial one, a circular waveguide and an other coaxial one, the attenuation obtains making that to the frequency of job in the coaxial one a way under cut-off corresponds in the guide who therefore comes attenuated.
10) Divisor of tension Kelvin - Varley:
E' a precision suppressor that acts as from standard to
inferior frequencies to the 10kHz, it supplies ![]() where to , b , g , d they are
everyone comprised between 0 and 9 on the base of the position of a
crawling contact that it covers two resistances on the series of
resistances, in particular the divisor is constituted from 4 series of
resistances, before is constituted from 10 resistances of value 125R
while the others 3 are constituted from 11 equal resistances whose
values are progressively uniforms for 5. If we want instead to
realize a divisor on N base are necessary N resistori in the last
stage and N 1 in the previous ones and the relationship must be
decreasing of N/2 factor.
where to , b , g , d they are
everyone comprised between 0 and 9 on the base of the position of a
crawling contact that it covers two resistances on the series of
resistances, in particular the divisor is constituted from 4 series of
resistances, before is constituted from 10 resistances of value 125R
while the others 3 are constituted from 11 equal resistances whose
values are progressively uniforms for 5. If we want instead to
realize a divisor on N base are necessary N resistori in the last
stage and N 1 in the previous ones and the relationship must be
decreasing of N/2 factor.
Insulators and circolatori
11) Circolatore:
She is a not mutual member to 3 doors who is based on the property of some ferromagnetic materials, in particular its function is to concur the transfer of only marks them in a back.
12) Insulator:
It is a circolatore in which a door has been sluice on adapted cargo, it is a lot used in the case that is wanted to be transferred all independently the possible power from the generator to the cargo from the value of this last one.
Amplifiers
13) Chain of amplification:
In kind in proximity of the antenna or the generator an amplifier to low noise is had whose scope is that one to raise the level of marks introducing them the possible minimum noise, subsequently has of the gain amplifiers actions to elevate the level of marks them and finally the chain is closed with a power amplifier.
14) Characteristics of the gain amplifiers:
to) band passing to 3dB and ripple
b) gain in power ![]()
c) 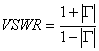 is in income that in
escape
is in income that in
escape
15) Characteristics of the amplifiers to low noise:
Beyond to the characteristics of the gain amplifier there are also following:
to) the figure of noise 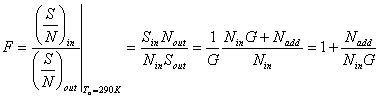 that in the case of a chain of amplifiers
assumes the shape
that in the case of a chain of amplifiers
assumes the shape ![]() from which it
evidences that the first amplifier beyond to a low noise must be
characterized also from a high gain.
from which it
evidences that the first amplifier beyond to a low noise must be
characterized also from a high gain.
b) the smallest MDS that is marks them
that it can be amplified distinguishing it from the bottom noise, it
is worth ![]() where i â?"111dBm they are
3dBm over the deliberate MDS for one ambient band of 1MHz to
temperature.
where i â?"111dBm they are
3dBm over the deliberate MDS for one ambient band of 1MHz to
temperature.
16) Characteristics of the power amplifiers:
Occorre as an example to hold account also of the
linearity of the amplifier considering a development until to 3° the
order does not have ![]() and applying a
and applying a ![]() tone it is evidenced in escape beyond to the tone of
amplified income also its harmonicas, a continuous one and a term of
jam produced from the cubical term but that it goes to sottrarsi to
fundamental therefore the power of escape stretches to saturate to
growing of the income power, therefore the power amplifiers are
characterize to you also from characteristic following:
tone it is evidenced in escape beyond to the tone of
amplified income also its harmonicas, a continuous one and a term of
jam produced from the cubical term but that it goes to sottrarsi to
fundamental therefore the power of escape stretches to saturate to
growing of the income power, therefore the power amplifiers are
characterize to you also from characteristic following:
to) if both the largenesses come expressed in dB and represented on a diagram we can characterize the point of jam to 1dB as that value of the power of income for which the escape power is reduced of 1dB regarding the value that it would have in the linear case.
b) the dynamic range comes defined like the difference between the power of income correspondent to the Minimum Detectable Signal and the point of jam to 1 dB.
c) the efficiency of the amplifier ![]()
d) Power Added Efficiency 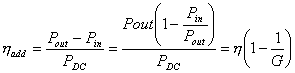
Applying in income to the amplifier it marks them to two tones evidences the presence of terms of jam, abolition, intermodulazione that can be estimated by means of the following largenesses:
to) IP3 it is the point of intercepts of 3° the order that is on the diagram that expresses Pout[ dBm ] according to Pin[ dBm ] is the power of income correspondent to an intersection between the extension of the straight one that it represents the linear term and the extension of the straight one that it represents the cubical term, in kind the quality of an amplifier is high how much the more is high IP3 , it tos be distant from the point of jam to â?"1dB approximately 10dB theoretically for the amplifiers to solid state, in the practical one tos be distant approximately 8dB.
b) Spurious Free Dynamic Range is worth ![]() and represents the range of powers in income for
which in escape from the amplifier I do not have spurie frequencies,
value 2/3 is deduced from geometric considerations on the plan that
expresses Pout[ dBm ] P
in[according to dBm ].
and represents the range of powers in income for
which in escape from the amplifier I do not have spurie frequencies,
value 2/3 is deduced from geometric considerations on the plan that
expresses Pout[ dBm ] P
in[according to dBm ].
c) Adjacent Channel Power Ratio
considers a subdivision of the phantom in channels, assumes marks them
of income entire contained in a channel, it will be had that it marks
them of escape is present also in the adjacent channels, considering
one only of the two and integrating the contributions in power it is
had ![]() .
.
Mixer
17) Mixer:
It is a dispositive action to traslare in frequency marks them RF produces in fact to all the linear combinations of the two frequencies that it has in income, containing a information and the other due to the local oscillator, to such aim must necessarily be not linear. A realization example is by means of a having generator pulsation w1 that is connected to the cargo through a switch piloted from a wave quadrant to frequency w2 .
18) characteristic Parameters of a mixer:
to) Gain of conversione ![]() , it reduces to growing of power RF regarding potenza
the reaching the saturation in analogous way how much has itself
for the amplifiers, also in this case it comes in fact defined the
point of jam to -1dB like the Pin, RF for which Pout, IF is reduced of 1dB regarding the value that it would have in
the case sends in income a single tone.
, it reduces to growing of power RF regarding potenza
the reaching the saturation in analogous way how much has itself
for the amplifiers, also in this case it comes in fact defined the
point of jam to -1dB like the Pin, RF for which Pout, IF is reduced of 1dB regarding the value that it would have in
the case sends in income a single tone.
b) ![]() Isolation
therefore we consider powers to various doors but to the same
frequency, in this case the member to frequency RF goes to door IF for
means of superficial currents. Much attention is placed towards
the
Isolation
therefore we consider powers to various doors but to the same
frequency, in this case the member to frequency RF goes to door IF for
means of superficial currents. Much attention is placed towards
the ![]() isolation in how much for the detailed lists
of the mixer marks them must have power much greater one regarding
marks them RF which then usually it is connected directly to an
antenna therefore if the isolation is insufficient it irradiates marks
them.
isolation in how much for the detailed lists
of the mixer marks them must have power much greater one regarding
marks them RF which then usually it is connected directly to an
antenna therefore if the isolation is insufficient it irradiates marks
them.
c) the paper of the spurie has on the
abscissas possible frequencies IF while on the formers there are
possible frequencies RF, the correct zone of job of the mixer
characterizes a rettangolino while to the spurie frequencies of ![]() income, than they are had in case RF and IT they
are bands and not single tones, are associated of the straight ones
which do not have to cross the rettangolino, otherwise a change of the
plan of the frequencies becomes necessary.
income, than they are had in case RF and IT they
are bands and not single tones, are associated of the straight ones
which do not have to cross the rettangolino, otherwise a change of the
plan of the frequencies becomes necessary.
19) singularly balanced Mixer:
to) it is sent marks them hybrid RF to the S income of one to 180° and
it marks them to the D income of the same one, escape RF LO is connected to the anode of
a diode valve that acts as from 1° mixer while escape RF-LO is
connected to the cathode of a diode valve that acts as from 2° mixer,
the two mark them then are added and come leak to you. The
advantage of this configuration is that the ![]() isolation is that one of the hybrid, the disadvantage is
that the adaptation is function is of the adaptation of the hybrid
that of the mixer.
isolation is that one of the hybrid, the disadvantage is
that the adaptation is function is of the adaptation of the hybrid
that of the mixer.
b) the outline is identical to the previous one with the exception to use one hybrid to 90° instead that that one to 180°, the two configurations are specular in the sense that with this last outline is the adaptation to only depend on the hybrid while the isolation depends is from the hybrid that give the diode valves.
c) the third possible outline is used in how much if I have of the FET is difficult to turn them as it is made for the diode valves, therefore uses two hybrid to 180° between which the two are placed dispositi to you that they act as from mixer.
20) doubly balanced Mixer:
They are possible the configuration Ring and Star, demand at least 4 not linear members and introduce a low gain of conversion, approximately 8dB against the 10dB of the mixer singularly balanced, however they have optimal property of rejezione of the spurie and operate with greater bands.
21) Mixer to rejezione of image:
Through one hybrid to 90° it marks them of income comes sent in phase to a mixer and sfasato of 90° to an other mixer, to both then it reaches through splitter a same one marks them from, marks them produced IF come then sendes everyone to you to a door of income of other hybrid to 90° to one of its escapes I will have the USB regarding while to the other escape avr² the LSB.
