Cellular systems
1) Attributes of a cellular system:
The main prerogative of a cellular system is that one to concur an increase of the number of circuits with virtually limitless disposition with the maturation of the system, such objective comes obtained by means of uses it combined of the technique of the riuso of frequency and the âCell splittingâ?.
2) Area of service, cluster and cell:
The service area is all the area that must be covered from the service, it comes subdivided in cells, groups of adjacent cells then constitutes a cluster if altogether they use without superimpositions all the band to disposition of the system.
3) Attenuation of distance between two points situates to you at a distance d:
The attenuation is proporziona them to d-g with g comprised between 1,5 in the case of
municipal and 5 in the worse city case, an intermediate reasonable
value is g= 4. In truth the
complete formula that characterizes the power received in function of
the transmitted power is ![]() , is said formula of
Friels.
, is said formula of
Friels.
4) modality and Factor riuso in order to increase it:
The distance attenuation renders the power received already to short distance from the emitter negligible, that can be taken advantage of in positive way ring-use the same band in zones where the emission from the previous emitter becomes negligible. The factor of riuso is the relationship between the band that would be necessary if all were covered the service area with various channels, and the B band really to disposition of the service
![]()
where ncell it is the number of cells in the service area, Bc is the assigned band to every cell and m are the number of cells of which the cluster is formed. Pu² to increase FR it is reducing m that but in kind is assigned, than increasing ncell that is diminishing the medium dimension of the cells however in this case increases the frequency of the handover and moreover g it diminishes however in short relationship S/N remains invariato.
5) Cell splitting:
A cellular system evolve towards a mature system subdividing the cells in cells of smaller dimensions in which the band of assigned frequency comes ulteriormente subdivided in smaller bands, ciascuna assigned to one of the sottocelle. The problem that of it derives is that it outside increases to the probability of Outage that is service, is worth to say the probability that a customer tests to use the service and this is not available.
6) Relationship S/N for a cellular system in phase begins them and mature:
For a cellular system in the phase it begins them has 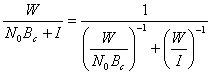 where W is the power emitted from the SRB while N0 is the noise power and it is the
power interfering produced from other SRB locate in adjacent cells and
using the same band of frequencies.
where W is the power emitted from the SRB while N0 is the noise power and it is the
power interfering produced from other SRB locate in adjacent cells and
using the same band of frequencies.
As the system grows, the cells becomes of more and more
small dimensions, derives some that the power emitted from the emitter
in order to reach edge cell is lower therefore can consider the single
interfering power 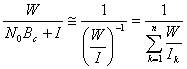 , in kind considers only the first
interfering crown that for a model of hexagonal cell it is constituted
from 6 interfering, calculating such relationship obtains
, in kind considers only the first
interfering crown that for a model of hexagonal cell it is constituted
from 6 interfering, calculating such relationship obtains ![]() .
.
7) Model of hexagonal cell:
The hexagonal model regarding that circular in how much is
preferred this last one introduces superimpositions between cells
while that hexagonal one does not have superimpositions and has the
minimal difference between beam the minimal and maximum beam, in
particular comes assumed as beam r of the cell the distance between the center of the hexagon
and one of you concern to us, of it derives that two centers cell are
at a distance mutual ![]() that
becomes 1 to pact to use the standardized beam
that
becomes 1 to pact to use the standardized beam ![]() .
.
The used coordinates are not orthogonal, in particular the axis u coincide with axis x while axis v introduces one counter-clockwise angle of 60° regarding the axis u.
8) Distance from the origin of the coordinated center of cell of (i,j):
![]()
9) Procedure in order to characterize cells isocanale in cluster various:
A brace of entire positi to you (i,j) that it characterizes the coordinates of the first interfering cell, ruotano is chosen therefore of 60° the aces is coordinated to you and therefore the same coordinates characterize the second interfering cell, are continued therefore sin when it is not returned to the first interfering cell, in such a way have characterized the first crown constituted from 6 interfering cells, in a generalized manner k_esima the crown are constituted from 6k interfering elements.
10) Dimension m of the cluster:
It is the number of cells that compose the cluster, is
found like squared of the distance from the origin of the center of
the coordinates for one whichever of the edge cells cluster, therefore ![]() .
.
11) Relationship W/I in function of the traffic in the system:
In a mature cellular system making the relationship
between the received useful power from distant cell r from
its SRB finishes them to edge and
the interfering power due to k_esima the interfering SRB locata at a
distance dkl è 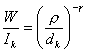 employee therefore exclusively from
employee therefore exclusively from ![]() fixed therefore being m a priori, is had that to growing
of the traffic of the system the relationship remains invariato.
fixed therefore being m a priori, is had that to growing
of the traffic of the system the relationship remains invariato.
12) Probability outside service:
![]()
where Pb is the probability to receive a wrong bit and Pb0 are a fixed value target for Pb that in 10 kind -3is worth therefore in short the error probability is the probability that the probability to receive a wrong bit is greater of 10-3.
13) Settorizzazione of the cell:
The system capacity carrying out the settorizzazione of the cells, it instead consists in equipping the SRB of antennas directives that can be increased omnidirezionali, in such a way the interfering power is only a third party of how much is had with the omnidirezionale antenna and relationship W/I increases of approximately 4,8dB in order reaching therefore nearly 22dB. Naturally the problem of this approach is that the number of resources comes ulteriorly subdivided and therefore increases to the probability service outside.
14) spectral Efficiency:
It is the relationship between the bit installments total
aggregate and the ![]() band available for the service:
band available for the service:
![]()
where ncel it is the number of cells of which the area is made up of service, K is the number of active customers who can be use to the inside of the same one and R is the bit installments associated to everyone of they, m to the usual is the B and dimension clusterC the assigned band to every cell. It is obvious that hS increases to growing of ncel that is diminishing of the medium dimension of the cells, is worth to say the how much the more system becomes mature like pure to growing of K, the system capacity which is function of the probability outside service that is of the probability that a customer wants to use the system and she does not find it available.
15) Rework of the expression of the spectral efficiency:
The band assignedB c
to every cell can then be expressed like product of the Bband ch associated to every channel
for the number of channelsn ch![]() , remembering that the factor of riuso is
, remembering that the factor of riuso is ![]() ha
ha ![]() where
where ![]() e
e ![]() is the spectral efficiency
for single customer.
is the spectral efficiency
for single customer.
In the orthogonal systems it is had k=nch and therefore to = 1 while in the not orthogonal systems it is k<nch therefore I must try to maximize the factor of riuso.
