Linear amplifiers
1) Outline of an amplifier to microwaves:
It is constituted from a transistor that with the technology they puts into effect can be is a FET that a BJT, it has in income an adaptation net towards the generator and in escape a net of adaptation towards the cargo, such nets in kind supply also to the feeding of the transistor.
2) Coefficient of reflection:
For the microwaves one prefers to abandon tensions and
currents and to refer instead to waves transmitted 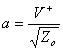 and reflected
and reflected 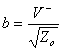 , particular interest
assume the coefficient of reflection
, particular interest
assume the coefficient of reflection ![]() then in term
of which often the adaptation is characterized, it in fact is worth 0
in the adaptation case as it is obvious since in this condition the
reflected wave is cancelled.
then in term
of which often the adaptation is characterized, it in fact is worth 0
in the adaptation case as it is obvious since in this condition the
reflected wave is cancelled.
3) Matrix of scattering:
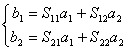 where the S parameters are said spread
parameters.
where the S parameters are said spread
parameters.
4) Expression of Gin for one net 2 doors loaded in escape:
![]()
where GL is the reflection coefficient on the cargo.
5) Expression of Gout for one net 2 doors loaded in income:
![]()
where GS is the reflection coefficient on the generator.
6) Transducer gain:
In the case that is the cargo that the inner stiffness of
the generator is worth Z0 = 50W comes defined the Transducer
Gain 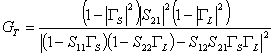 that depends is from the S parameters of the
transistor that gives the coefficient of reflection GS seen from its
income towards the generator and from the coefficient of riflessione GL seen from
its escape towards the cargo.
that depends is from the S parameters of the
transistor that gives the coefficient of reflection GS seen from its
income towards the generator and from the coefficient of riflessione GL seen from
its escape towards the cargo.
7) Consequences of the hypothesis of adaptation without losses:
Nets of adaptation without losses do not contain resistances and therefore they cannot dissipate active power, follows some that the gain in power of the amplifier coincides with the gain in power of the transistor.
8) Condition of maximum gain in the case of unidirectional active device:
If we have a unidirectional device, that that has as an
exampleS 21 = 0,G T is maximum in the case of
conjugated adaptation ![]() that is
that is ![]() e has had to the fact that both the doors are adapted
and therefore the power comes transferred all.
e has had to the fact that both the doors are adapted
and therefore the power comes transferred all.
9) Factor of K stability:
In the case of a bidirectional active device it is
demonstrated that so that GT is
maximum must at the same time be verified the conditions of conjugated
adaptation ![]() and
and ![]() . Resolving
the system 2 solutions for G Sare obtained and others 2 for GL that comes in
particular classified in function of the factor of
. Resolving
the system 2 solutions for G Sare obtained and others 2 for GL that comes in
particular classified in function of the factor of 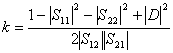 stability have that for k > 1 two valid solutions
in how much are alone the others 2 would demand of the active nets
while for k < 1 the maximum gain of the translation can infinitely
corresponding become to one oscillation condition.
stability have that for k > 1 two valid solutions
in how much are alone the others 2 would demand of the active nets
while for k < 1 the maximum gain of the translation can infinitely
corresponding become to one oscillation condition.
10) Condition of unconditioned stability and the maximum gain:
In case k > 1 it is had that a brace of solutions
introduces |GS| > 1 e |GL| > 1 that they cannot be verified inasmuch as the
adaptation nets are passive, the other brace of solutions is chosen
therefore, to second which solution is chosen has the following value
of the gain maximum 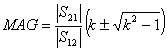 that is obtained in the case
of conjugated adaptation. If the second brace of solutions is
chosen it has also |Gin| < 1 and |Gout| < 1 that it implies that the conditions of
oscillation e
that is obtained in the case
of conjugated adaptation. If the second brace of solutions is
chosen it has also |Gin| < 1 and |Gout| < 1 that it implies that the conditions of
oscillation e ![]() cannot be
verified
cannot be
verified ![]() .
.
11) Planning in the case GT < MAG:
It is necessary to insert a maladjustment or to the door
of income or the door of escape or both, if as an example disadatta
the door of income GS ¹ Gin* while one lets adapted that one
in escape GL = Gout* it is had that GT comes to only depend on GS and comes
defined gain available 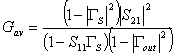 . Se GS ¹ Gin* we have that GT designs on the paper of Smith a paraboloide that has the
maximum point in the optimal value and decreases along of the circles
going away some, the circles in kind goes to steps of â?"1dB.
If instead disadatta in escape GL ¹ Gout* we have
the gain of
. Se GS ¹ Gin* we have that GT designs on the paper of Smith a paraboloide that has the
maximum point in the optimal value and decreases along of the circles
going away some, the circles in kind goes to steps of â?"1dB.
If instead disadatta in escape GL ¹ Gout* we have
the gain of 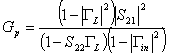 power and it is reasoned like in
the previous case.
power and it is reasoned like in
the previous case.
Alternatively a resistance of opportune value can be comprised in the transistor also to dissipate the demanded power, it can be placed or in series to the income of the amplifier or in feedback, the active device altogether obtained therefore introduces an inferior MAG regarding that one of the transistor therefore is not more necessary to maladjust in income or in escape or both, the only problem is that such resistore introduces noise and therefore badly it is lend to the realization of an amplifier to low noise.
12) Condition of instability upgrades them:
We have that k < 1, that can make that for some |GS| < 1 is had |Gout| > 1 and also that for some |GL| < 1 is had |Gin| > 1 both are of the necessary conditions for the oscillation of the circuit that however will only oscillate in the case improperly is loaded. The values that lead to the instability are design to you directly on the paper of Smith di GL and GS and go to constitute the regions of instability for which the gain stretches to infinite when it is attempted to adapt in conjugated way is in income that in escape.
13) MSG:
If an amplifier must also be realized having k>1 it is
necessary to maladjust or in income or escape so that the gain is not
infinite and therefore the circuit does not oscillate, as an example
supposes to maladjust in income and is Gexternal S to the instability
region, the gain is given from the circle on which G Sis found . In
this way a whichever gain between 0 can be obtained and ¥ however is necessary a safety margin
in how much the precision of the parameters of the transistor is
limited, to such aim defines maximum stable gain MSG like the gain
that we have when moving GS towards the instability region is had that GL reaches the
limit of the instability region, is had 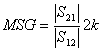 . An
analogous result obtains disadattando the escape door.
. An
analogous result obtains disadattando the escape door.
14) MSG in the case of nets of adaptation with losses:
If we make that the transistor comprises also a resistore
it can make that the gain is not infinite even if the escape and
income doors are both adapted in conjugated way, in this case the
total active device will have been characterized from a maximum stable
gain 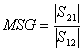 .
.
15) Amplifiers to wide band:
The adaptation methods up to now adopt to you are valid for a single frequency, many amplifiers instead must have a constant gain to the inside of a frequency band that becomes more and more wide, inoltre are had that gain MAG or MSG of an amplifier in kind diminishes to growing of the frequency therefore is necessary to make in way to have the MAG or the MSG for the frequency higher present in the band and instead to have a gain more low as is approached to us the inferior end of the band. In order to realize such amplifiers in kind they are used of the nets of adaptation with losses in which are had of series LR, in such a way makes so that the resistance you weigh less and less to growing of the frequency. Alternatively series LR can be placed in the feedback of the active device, such feedback moreover contributes very to render the flat gain in band.
16) unidirectional Coupler:
It is a device to 4 doors, it is had that it marks them that enters to a door is sended to two doors of escape while is not sended to third, in particular in the case of a directional coupler 3dB has that the power to door 1 comes sended to half to the door 2 and halves to door 3, but the two marks them is between they sfasa you of 90°.
In truth to door 4 much not null small is had a power but and can be taken advantage of in order to make of the measures of power on a power amplifier.
17) balanced Amplifier:
It is an outline that concurs to realize better powers
higher and adaptations, is based on I use of two directional couplers,
the first one shunts the power of income to two amplifiers and the
second of it sum the escapes, taking advantage of the relations
between makes and the reciprocity of the directional coupler is
succeeded to demonstrate that the powers reflected from the amplifiers
elidono are on the source that on the cargo while laddove they are
added is sufficient to place one 50 resistance toW in order to adapt. The only
defect of the outline is that the directional couplers are dispositi
to you that they dissipate part of the power and are also enough
cumbersome.
Amplifiers to low noise
18) Cifra of noise:
It is given from the relationship between the
segnale/rumore in income to the amplifier and that one in escape from
the same ![]() it is always greater of 1 in how much
cannot be had a device that improves the segnale/rumore relationship
that it has in income. Moreover in the case of one falled of
amplifiers it is had that the total figure of noise is influenced
massimamente from the figure of noise of the first a stages which
comes therefore demanded to amplify very and to introduce noise
little.
it is always greater of 1 in how much
cannot be had a device that improves the segnale/rumore relationship
that it has in income. Moreover in the case of one falled of
amplifiers it is had that the total figure of noise is influenced
massimamente from the figure of noise of the first a stages which
comes therefore demanded to amplify very and to introduce noise
little.
19) Cifra of noise of a transistor:
For a transistor the noise figure depends from as it is
loaded in income, while he is independent from the cargo in escape in
particular from a microscopical analysis obtains the following ![]() expression therefore has the minimal value in the
case has in income the optimal admittance of noise YN which an optimal G corresponds s,n.
Going away from optimalG s,n a worsening of the figure of long noise
of the circles is had that are various regarding those of the maximum
gain therefore are necessary to find a compromise between the two
various requirements.
expression therefore has the minimal value in the
case has in income the optimal admittance of noise YN which an optimal G corresponds s,n.
Going away from optimalG s,n a worsening of the figure of long noise
of the circles is had that are various regarding those of the maximum
gain therefore are necessary to find a compromise between the two
various requirements.
20) Criteria of plan of an amplifier to low noise:
Considering a stable transistor unconditioned therefore with k > 1 we have that they cannot be verified at the same time is the condition for the maximum gain that that one for the minimal figure of noise however the points of ceiling of relati you the circles in which the worsening of the largenesses he is constant are the points on which must be chosen the compromise point, in particular if we are planning an amplifier to vhf it earns little therefore we approach ourselves the maximum gain losing something in terms of noise figure while if we are to vlf where the gain it is already high, we will approach ourselves the point of optimal for the noise figure.
In the case of potentially unstable transistor that is with k < 1 it is from avoiding I use it of resistances in series to the transistor while with the aim to reduce the MSG while it is a lot used the method that consists in placing a resistance in feedback, it in fact concurs to approach the optimal one of GS for the figure of noise the optimal one of GS for the gain.
21) Role of the polarization in the plan of amplifiers to low noise:
In kind the minimum of the noise figure has for one inferior polarization regarding that necessary one in order to have the maximum of the gain.
