Mixer
1) ideal Outline of mixer and simple real implementation :
It is constituted from a sinusoidale generator ![]() that is connected to a cargo by means of a switch
piloted from a wave having quadrant the frequency of the local
oscillator, such marks them can be developed in series of Fourier
that is connected to a cargo by means of a switch
piloted from a wave having quadrant the frequency of the local
oscillator, such marks them can be developed in series of Fourier ![]() . It marks them that she is obtained on the cargo is
the product of the two previous ones and if the amplitude of marks
them of the local oscillator is much greater one regarding the
amplitude of marks them RF has in escape all the sums and the
differences between the harmonicas of the local oscillator and mark
them RF. A simple real implementation previews a diode valve
with in parallel the local oscillator that polarizes it between the
conduction and the interdiction, on the anode reaches through a
resistance marks produced them from generator RF which it must be of
low level, such not to modify the state of polarization of the diode
valve.
. It marks them that she is obtained on the cargo is
the product of the two previous ones and if the amplitude of marks
them of the local oscillator is much greater one regarding the
amplitude of marks them RF has in escape all the sums and the
differences between the harmonicas of the local oscillator and mark
them RF. A simple real implementation previews a diode valve
with in parallel the local oscillator that polarizes it between the
conduction and the interdiction, on the anode reaches through a
resistance marks produced them from generator RF which it must be of
low level, such not to modify the state of polarization of the diode
valve.
2) Schematizzazione of the operation of the mixer:
We have in series marks them of the local oscillator and that RF, follows a stiffness ZL and the diode valve, applying Norton I transform the two generators of tension in generators of current with in parallel one admittance YL and one stiffness YD.
If the variation of the current in the diode valve
provoked from marks them RF it is so small from being able to confuse
in those drawn the characteristic of the diode valve with its tangent
is like if the RF the circuit saw a variable conductance in the time
therefore for the RF is behaved in way to delineate but variable in
the time, the value of this conductance pu² to be calculated
deriving the expression of the diode valve, has 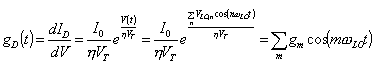 therefore we have expressed in series of Fourier also the conductance
which has the same regularity of the local oscillator.
therefore we have expressed in series of Fourier also the conductance
which has the same regularity of the local oscillator.
3) Matrix of conversion:
With reference to the previous one schematizzazione
inasmuch as the currents that pass to the heads of the diode valve are
the same ones that passes in the cargo it will have that the phantoms
of current and tension are the same ones that is ![]() , of
these we consider only positive the sidebands is had therefore
, of
these we consider only positive the sidebands is had therefore ![]() . We can therefore write = gV with the formalism of
the matrices
. We can therefore write = gV with the formalism of
the matrices  it evidences as the advanced band
of the harmonica of the local oscillator of N order acts on all the
other harmonicas of the current, only the diagonal alloy you finish to
the same frequency therefore as normal conductance happens for one.
it evidences as the advanced band
of the harmonica of the local oscillator of N order acts on all the
other harmonicas of the current, only the diagonal alloy you finish to
the same frequency therefore as normal conductance happens for one.
4) Configurations in order to realize different cargos to different frequencies:
The two following approaches can be followed:
to) realizing a leaking net that therefore it is behaved in different way to second of the frequency, this but is problematic in how much the courses demands is enough discontinuous
b) a symmetrical or antisymmetric configuration can be used that features in different way the various harmonicas, are possible various realizations and are the used method more.
5) Representation of mixer with one the net n-doors:
The conversion matrix suggests a representation of the mixer by means of a door net 2N, to every brace of doors is associated a brace of conjugated frequencies, evidently only the doors associated to the frequencies that interest to us will have to be sluices in conjugated way while those associates to the other doors must have a reactive cargo so as to to send back within power it leave of which she comes reconverted to the interest frequency, in such a way improve the gain of conversion of the mixer but it must be attention not to realize way right yed to you.
6) Rat and Coupler 180° Race:
It marks them in income to the S door comes transferred to the two escapes with a phase-difference of 0° while she marks them in income to the D door comes transferred to one of the two escapes with one phase-difference of 0° while to the other escape with one phase-difference of 180°. A possible realization of a coupler to 180° is by means of a Rat Race in which between the S income and the two escapes there are of lthe /4 while between the D income and the two escapes there are on one side l/4 and from the other 3/4l, this configuration concurs to make that it marks them to an income catches up the other income by means of two distances in phase opposition and therefore cancellations while marks them in income to the D door are reached door 3 with a delay of 180° regarding the same one mark them that it reaches door 2.
7) Mixer singularly bilanciato:
It marks them RF enters to the S door of a coupler to 180° while it marks
them enters to the D door ,
to the escape that does not endure some phase-difference has the
cathode of a diode valve connected to the anode of a diode valve whose
cathode instead is connected to the other escape of the coupler, the
escape comes captured through a resistance in the point of encounter
of the two diode valves for that one up assumes one characteristic not
linear simplified of the ![]() type with the positive
current in the back from the anode to the cathode while for the other
diode valve the current slides from the cathode to the anode and
therefore
type with the positive
current in the back from the anode to the cathode while for the other
diode valve the current slides from the cathode to the anode and
therefore ![]() is had. For the property of the
coupler on the diode valve up we will have that VRF and VIT are in
phase therefore the V to replace in the equation are
is had. For the property of the
coupler on the diode valve up we will have that VRF and VIT are in
phase therefore the V to replace in the equation are ![]() while on diode valve low V sfasata IT of 180° and therefore the V to
replace are
while on diode valve low V sfasata IT of 180° and therefore the V to
replace are ![]() . Carrying out the substitutions
and adding it is obtained in the branch of escape
. Carrying out the substitutions
and adding it is obtained in the branch of escape ![]() therefore marks them to comes IT cancelled from the symmetry that
it is much profit in how much avoids I use it of filters that must
cancel mark them much fort. Inverting between of they the
incomes it can be made in way to cancel marks them VRF .
therefore marks them to comes IT cancelled from the symmetry that
it is much profit in how much avoids I use it of filters that must
cancel mark them much fort. Inverting between of they the
incomes it can be made in way to cancel marks them VRF .
8) doubly balanced Mixer:
A bridge of diode valves is had everyone with the cathode connected to the anode of the successive diode valve, to two opposite extremities it is applied by means of a transformer marks them V while to the others two extremity by means of a taken transformer to centers them is applied marks them VRF and from the taken one they centers captures themselves marks them VOUT . For the analysis the sign of V the RF is considered and the filler inner to the diode valves, analogous of the V the filler externally to the diode valves, then write the terms of the V the and VRF to i sides of the bridge that go to the taken transformer to centers them and then they are added, obtains in escape single member VVthe RF therefore this configuration eliminates is V the that VRF .
9) Mixer active:
There are 3 regions of operation of a mixer active, are regions in which strong variations of the characteristic are had, excludes the region of break-down for its destructive characteristics. Region 1 is to the limit of the saturation and it does not come used in how much is much noise and dissipation and then does not have sense in how much the transistor comes substantially used like diode valve, is then zone 2 that is to the limit of the interdiction for which the transistor fast one from the conduction passes in way much to the interdiction, can be thought next to this region of operation like to a diode valve with in series an ideal switch who comes piloted from the local oscillator. The third zone is near the origin of the characteristics for it applies V to the gate ones and VRF to the drain, in short is like having a simple switch.
10) subarmonico Mixer:
Two diode valves are had, between the cathode of one and
the anode of the other applies V and VRF and takes also the escape
through a resistance, on the diode valve that it has more of the
tensions on the anode is worth ![]() the while for the
other it is worth
the while for the
other it is worth
![]() , therefore replacing in both
, therefore replacing in both ![]() and adding we have in
and adding we have in ![]() escape in
particular this configuration eliminates the second harmonica of the
local oscillator concurring therefore in simple way I use it of
escape in
particular this configuration eliminates the second harmonica of the
local oscillator concurring therefore in simple way I use it of ![]() the .
the .
In the practical one then in escape one becomes part l/4 that is a short one to w but an open to 2w in income instead places l/4 that is a short one to the frequency that is had in escape so as to to avoid that it comes brought back in income.
11) Multiplier of frequency:
In order to generate advanced harmonicas a not linear device is sufficient which a diode valve, it in particular can be used like one not resistiva linearity (…to wide band but with low gain of conversion) or like one not capacitiva linearity (…selective in band but with higher gain of conversion). From the progettuale point of view it is far away attempted to be from the circles of instability at least for the doors to vlf like that one of the local oscillator even if more one is close to such circles more increases the gain than conversion, in kind then one opportune choice of the polarization point concurs to exalt the just harmonica.
