Introduction
1) Difference between analysis and synthesis:
The analysis consists in studying the property of a data arranges existing, it admits therefore an only solution, the synthesis instead part from the wished characteristics and reaches to a possible implementation of the system therefore the solution is not only and therefore comparazione for the location of the best solution is necessary one.
2) realizzativa Evolution of the filters:
Initially the filters were used only pass to you, the quality of the inductances are but pessima therefore with the advent of the operational amplifiers they came eliminated. Currently it is stretched to eliminate also the resistori being used of the filters to commutata ability.
3) Function of net:
![]()
it is the relationship between transformed of Laplace ![]() of the answer r(t) of the net and the transformed
one of Laplace
of the answer r(t) of the net and the transformed
one of Laplace ![]() of the excitation e(t).
of the excitation e(t).
In the case the income is sinusoidale and the stable
system has to regimen a sinusoidale answer with the same frequency and
that it only defers from the income for module and phase, for the net
function it has 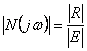 and
and ![]() .
.
4) Functions Driving Point:
Draft of functions defined on the same door, is had:
to) driving point impedance ![]()
b) driving point admittance ![]()
5) Relation between the elements passes present in the filter and the poles to you of its function of transfer:
For active nets the poles can be ovunque in the complex semiplan s, for nets RLC can be in all the left semiplan comprised the axis jw where but simple poles can be found single, in the case of nets RC the poles are found in the left semiplan while for nets LC they are found on the axis jw and are simple.
6) Functions of transfer of the various typology of filters:
to) Pass-low
![]() all the
zeroes are to infinite
all the
zeroes are to infinite
b) Pass-high ![]()
all the zeroes are in the origin
all the zeroes are in the origin
c) Pass-band 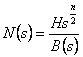
half of the zeroes is to the infinite and the other half in the
origin
half of the zeroes is to the infinite and the other half in the
origin
d) Notch
![]()
all the zeroes are on the axis jw
all the zeroes are on the axis jw
where in all the cases n it is the order of polynomial the B(s).
7) Denormalizzazione of frequency:
If p it is the variable standardized complex and s the
denormalizzata variable correspondent that ![]() has
implies that an inducer with
has
implies that an inducer with ![]() stiffness will have
denormalizzata stiffness
stiffness will have
denormalizzata stiffness ![]() therefore the
denormalizzato inducer has
therefore the
denormalizzato inducer has ![]() value analogous a
denormalizzato condenser has value
value analogous a
denormalizzato condenser has value ![]() .
.
8) Denormalizzazione of stiffness:
If zn(s) is the
standardized stiffness and zn(s)
the denormalizzata stiffness that ![]() has in the case
of a standardized inducer of L value implies that its denormalizzato
value is znL while for a
standardized condenser of value C the denormalizzato value is
has in the case
of a standardized inducer of L value implies that its denormalizzato
value is znL while for a
standardized condenser of value C the denormalizzato value is ![]() .
.
