Elements of quantistica mechanics
1) Equations of Hamilton - Jacobi:
![]()
![]()
they are equations in a position to completely describing the temporal evolution of a system of which the hamiltoniana is famous.
2) Comparison between the waves and the systems particle classics:
Position, speeds and energy of a classic particle can be
defined with infinite precision while for a ![]() wave
if x are famous the k are not famous and viceversa.
wave
if x are famous the k are not famous and viceversa.
3) Causes of the crisis of the classic mechanics:
The following effects do not find explanation with the classic mechanics:
Phantom of emission of the black body
The classic theory of Rayleigh and Jeans has determined that for l0® the energy emitted from the black body stretches to infinite, while in the truth experiments stretches they to 0, the hypothesis of Planck is that the exchange of energy between the walls of the black body and the cancellation happens in quantizzata shape multiple of a how much and0= hn .
Photoelectric effect
Draft of the electron emission from invested part of a solid one from a light bundle, experimentally is had that if the frequency of the photon incident is smaller of a minimum not it independently extracts no electron from the photon number incidents while if the frequency is greater enough also a single photon in order to extract an electron and the number is proporziona them to the number of photons incidents. The explanation came supplied from Einstein which it assumed that the electromagnetic wave yields to electrons energy in multiples of how much elementary and0= hn .
Atomic model of Bohr
The phantom of emission of an atom turns out characterized from lines very distinguished, the reason of that has been found in the model of Bohr which it previews that the electrons can ruotare around to the nucleus only on stationary orbits very defined from the quantization of the angular moment and that on such orbits the electrons do not emit cancellation.
4) Wavelength of De Broglie:
![]()
relation important in how much alloy is one one largeness to corpuscolare to one ondulatoria largeness.
5) Equation of Schroedinger:
![]()
6) Principle of correspondence:
![]()
![]()
7) Equation of continuity:
![]()
8) Product to climb of wave functions:
![]()
9) Expected value of an observable one:
![]()
in the case of operating hermitiani it is had that the expected value is one real largeness.
10) Solution of the equation of Schroedinger in the case of upgrades them independent from the time:
It is possible to decompose upgrades them in the product f(r,t) = T(t) u(r) that for the
part employee from the time it has ![]() solution while
the part employee from the time from place to the equation to the
autovalori
solution while
the part employee from the time from place to the equation to the
autovalori ![]() that general
solution has
that general
solution has ![]() .
.
11) Principle of indetermination:
![]()
it is a principle that derives from not the commutatività between the operating position and the operating momentum.
12) Function of wave of the free particle:
Draft of a flat wave ![]() and the electron
has momentum
and the electron
has momentum ![]() .
.
13) Function of wave of the particle in a hole of upgrades them to infinite walls:
Assuming it upgrades them null between â?"a and to and ¥ to the outside, it is had that
the levels of granted energy assume ![]() values and
the function of wave for n uneven is worth
values and
the function of wave for n uneven is worth ![]() while
for n equal is worth
while
for n equal is worth ![]() .
.
14) Function of wave of the particle in a hole of upgrades them to ended walls:
Assuming it upgrades them null between â?"a and to and U0 to the outside, one finds that
the energetic levels son those that satisfy the important equations![]() for equal solutions and
for equal solutions and ![]() for
uneven solutions being
for
uneven solutions being ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
15) Energies quantizzate in the case of a harmonic oscillator:
The energetic levels allowed are ![]() therefore have a not null minimal energy for n = 0 and the quantici
levels are distance to you between they of multiples of
therefore have a not null minimal energy for n = 0 and the quantici
levels are distance to you between they of multiples of ![]() .
.
16) Probability of Tunneling:
The probability of Tunneling diminishes esponenzialmente
to increasing of the larghezza d of the barrier that is ![]() .
.
17) Density of states in the cases three-dimensional, bidimensional, monodimensional:
In the case of the free particle 3D  is had, for the particle in a hole of upgrades them to
infinite walls that is free 2D has
is had, for the particle in a hole of upgrades them to
infinite walls that is free 2D has ![]() while for the
quantico thread that is the free particle 1D is had
while for the
quantico thread that is the free particle 1D is had 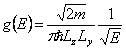
18) Function of distribution for classic particle, fermion, bosone:
The distribution function f(E) represents the probability
that the state to energy and has of being occupied, for a classic
particle has the distribution of Maxwell-Boltzmann ![]() ,
for fermions it characterizes to you from spin semintero instead has
the Fermi-Dirac distribution
,
for fermions it characterizes to you from spin semintero instead has
the Fermi-Dirac distribution 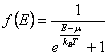 and finally for the
bosoni having spin entire the function of distribution of
Bose-Einstein is had
and finally for the
bosoni having spin entire the function of distribution of
Bose-Einstein is had 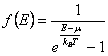 .
.
