Diode valves to emission of light
1) Characteristics of the LED:
Low optical powers of escape, wide phantom and incoherent emission, all ci² low speed determines one that ago to prefer the LASER in the optical systems of telecommunicationses.
2) Phantom of theoretical and real emission:
The theoretical phantom is ![]() being
being 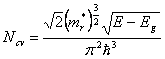 , the real phantom is the much most symmetrical one for
via of following:
, the real phantom is the much most symmetrical one for
via of following:
to) âband tailingâ? that is for high concentrations of drugging the donor level it is much next one to the conduction band for which it is like if this it is lowered and therefore it renders the gap inferior
b) they can happen also hits photon fonone electron which also being little probable interests photons to inferior energy regarding the gap
c) the transition that produces the fonone can happen also between a trap situated to the inside of the Gap and the band of valence, therefore issued photons also to inferior energies to that one of the gap will be had
3) relative spectral Width:
![]()
4) typical Structure of the LED:
We consider a structure in GaAs, a drugged substrate n is had to which the metallic contact is applied on one side while on the other side it is deposited a epitassiale layer also n which it introduces a greater reticular regolarità and on it a layer with spread of type p. Tale is had last layer is covered alone in the part centers them from a metallic contact in how much an important area must be left free for the photon spillage.
5) LED âBurrus Typeâ?:
Draft of a LED that maximizes the connection with the fiber optic, the layer advanced is a type substrate n which it comes eroded in order to approach the splice the advanced surface, a region p_doped separated from the positive contact through a present oxide is had then ovunque unless in the part they centers, in such a way the current passes only through this small section that then coincides with the section of the nucleus of the fiber.
6) Effects of the temperature on the LED:
An increase of the temperature can vary the spectral distribution, reduce the emission efficiency and make to diminish the average life of the LED.
7) inner quantica Efficiency:
In a LED they are possible is radiative recombinations that not radiative, the entities of these two processes are influenced from the type of gap and from the quality of the material, making reference to minority electrons in type regions p is had
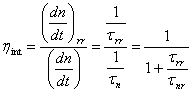 being trr the medium time of life of electrons had to
radiative recombinations. In order to render hint @ 1 it is
necessary that the radiative recombinations are much faster than those
not radiative that is trr < < tnr .
being trr the medium time of life of electrons had to
radiative recombinations. In order to render hint @ 1 it is
necessary that the radiative recombinations are much faster than those
not radiative that is trr < < tnr .
In the case of a semiconductor to gap indirect in kind h = 10-5 while for one to gap directed h = 0.5.
8) generated optical Power from a semiconductor:
![]()
where Nphot is the n° of photons generates in the semiconductor and the current to you of injection of the splice.
9) external quantica Efficiency:
All the photons do not generate to you effectively succeed to exit from the splice, the external quantica efficiency is exactly the relationship between the photon number emitted from the semiconductor and the number of bearers who cross the splice, the factors that limits it are following:
to) the splice the half of the produced cancellation emits in all the directions therefore only catches up the surface.
b) For greater angles of incidence of the angle limit the splice will determine one reflection total preventing to such cancellation of fuoriuscire from the device
c) Reflections of Fresnel that happen also for angles of incidence to inferior the angle limit, the transmission coefficient can be increased inserting between the semiconductor and the having air layer an intermediate refractive index between the two values
d) the issued cancellation has advanced energy to that one of the gap therefore can riassorbita to the inside of the material creating of the braces electron - gap, such effect can be reduced placing the splice more close possible to the surface, catching up but a compromise with the inner efficiency which diminishes in this direction in how much approaching itself the surface increases the n° of traps and therefore the not radiative recombinations.
10) Efficiency total:
![]()
where NA is the numerical opening of the fiber and f' the
fraction of irraggiata power that succeeds to exit avoiding a
reflection total while ![]() is the transmission
coefficient.
is the transmission
coefficient.
11) LED to double eterostruttura and its advantages on the traditional LED:
It is constituted from a eroded substrate so as to to lodge the fiber optic, under of it 2 times are alternated a semiconductor to gap wide AlGaAs and one to gap tightened GaAs, in such a way obtains that:
to) the minority bearers they are confines to you in the layer to gap tightened situated between 2 layer to gap wide
b) the layer to gap wide he is transparent to the issued cancellation for tightened recombination in the layer to gap and therefore it comes eliminated the problem of the resorption
c) the layer to gap wide has in kind smaller refractive index that it implies that the cancellation is confined in the layer to gap tightened.
12) Edge emitting DH LED:
A lot reduced is used for connection with diameter fibers, in short takes advantage of the fact that the semiconductor to gap wide has a greater refractive index of that one to gap tightened that therefore it is behaved like a waveguide.
13) Answer in frequency of the LED:
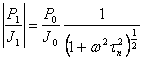
where P1 is the part
of the optical power employee from the time while Por is the independent part, it has
itself that for advanced frequencies ![]() to the
source loses efficiency, can be increased reducing trr increasing the
concentration of drugging finding but a compromise in how much in such
a way is reduced hint .
to the
source loses efficiency, can be increased reducing trr increasing the
concentration of drugging finding but a compromise in how much in such
a way is reduced hint .
