Logical doors
TTL
1) Describe circuit TTL:
A transistor of income T 1 of the type to multiemettitore is had, on the n emettitori is applies you marks them of income while on the base the feeding through the R resistance is appliedb1 , the collector is connected to the base of the transistor T4 that acts as from sfasatore therefore on its emettitore has a resistance RE4 towards mass while on the collector one is had resistance RC4 towards the feeding. The two mark them in phase opposition go to feeding the BJT of pull-down 3T and the block of pull-up constituted from T2 (…fed through the resistance RC2 ) and from the D diode valve.
The door in issue carries out the Nand function in how much when all the incomes are to the state high T1 work in inverse active region and therefore it sends in saturation is T4 that 3T and therefore the escape is to the low state while if also one of the incomes only is to the low state it has that interdiceT 3 and T2 is in active region and therefore the escape is high.
2) Behavior of door TTL in the case of income to the low state:
JBE1 is polarized therefore T 1directly can be found or in active region or saturation, in order to verify its state it is assumed that it is in active region and currency thereforethe C1 = bthe B1 , finds that current of the order is one of but that it would have it are supplied from the base of T4 derives some that 4T interdice and therefore0 C1 @ therefore T1 is in saturation, in such interdice way 4T and consequently T3 while it is T2 that the D diode valve is in the active zone and therefore analyzing this mesh it obtains that the escape tension is worth 3,6V.
3) Behavior of door TTL in the case of income to the high state:
JBE1 is polarized inversely while JBC is polarized therefore T 1directly finds in inverse active region, while 3T and T4 can be in active zone or saturation, that it involves that on the base of T4 us it can be a tension comprised between 1,4V and 1,6V the B1 can therefore be estimated and multiplying it for b @ the 0,02 to obtain that the base current goes to end nearly completely in the collector of T1 . We assume that it is T4 that T3 is in saturation that it implies to have Va CE4 @ 0,2V and Va BE3 @ 0,8V with these values we calculatethe C4 and being already famous bthe D andthe B4 I can calculate s and to verify that effectively T4 is in saturation, clearly being also T3 in saturation is had that tension Vout = VCE3 = 0,2V.
4) Behavior of door TTL in the passage from low level in income to high level:
If Vin are to the low state it has that T1 is in saturation therefore VCE1@0,1V, of the rest has VB4 = Vin VCE1 therefore to growing of Vin grows also VB4 and when this catches up the value 0,65V (…which V in=correspond 0,55V) are had that T4 begins to lead but for via of the fall on JBE4 it is had that T3 will remain interdetto sin when Vin= 1,35V beyond which the escape tension diminishes very fastly until catching up the value of 0,2V.
5) Margins of noise of door TTL:
![]() in fact beyond 0,55V in income
the escape is had gradually passes from the high state to the low
state while for tensions of greater escape of 0,2V T3 it is not more in saturation.
in fact beyond 0,55V in income
the escape is had gradually passes from the high state to the low
state while for tensions of greater escape of 0,2V T3 it is not more in saturation.
Moreover ![]() is had.
is had.
6) Fan Out of door TTL for high level in escape:
If the escape is to high the logical level the T1 of the N connected doors they work in
inverse active region, and therefore their cargo transistors T3 and T4 are in saturation that it involves one tension VB4= 0,75V 0,75V=1,5V moreover being
directlypolarized J BC1
will be had that the tension VB1= 0,7V 1,5V=2,2V, can therefore be calculatedthe B1 and multiplying it for b obtaining the current
absorbed from every door that is indeed insignificant that is
approximately 14mTo,
multiplying it for the number of the doors the current is gainedthe E2 that slide in the
emettitore of the door driver and dividendola for (1 bD) obtains the
value ofthe B2 , analyzing the
escape mesh is had that whenthe B2 increases the tension Vout it diminishes therefore if we want to fix ![]() we must determine the minimal value that Vout pu² to assume and therefore the
maximum value ofthe B2 and
therefore we obtain the maximum number of doors that can be
connected, comes 2550 but in kind the constructor recommends a maximum
of 10 doors.
we must determine the minimal value that Vout pu² to assume and therefore the
maximum value ofthe B2 and
therefore we obtain the maximum number of doors that can be
connected, comes 2550 but in kind the constructor recommends a maximum
of 10 doors.
7) Fan Out of door TTL for low level in escape:
If the escape is to the logical level low T1 of the N connected doors they work in saturation, and therefore their cargo transistors 3T and T4 are interdetti while T2 is found in active region. In order to calculate the current distributed from ciascuna cargo door the tension V B1 is estimated that is the sum of 0,2V had to VCE3 of the door driver with T3 in saturation and 0,8V had to VBE1 of the cargo door with T1 also it in saturation, pu² therefore to be estimatedthe B1 that being T4 interdetto it coincides withthe E1 that is with the current distributed from ciascuna cargo door, multiplying it for the number of the cargo doors the E3 obtains the current @ the C3 that slides in T3 of the door driver. To growing of the absorbed current T3 it ends in order to exit from the saturation that it happens when s > 0,85 imposing this value a fan-out is obtained maximum of 100 doors but the constructor recommends to connect some in emergency until to 10.
8) Appraisal of the time of climb for one door TTL:
LH
When the escape passes to the high state
has that the cargo condenser must be loaded, that the C2
happens with one current that is obtained multiplying for b the currentthe B2 that being T4 interdetto (…and therefore does not absorb
current) can be estimated simply. Replacing an equation is
obtained differentiates them from which evince that it loads he will
be naturally exponential with time constant ![]() .
.
HL is had that T3 must work in region attiva thereforethe C3 is constant and equal to 113mA if of it deduces that the ability discharge with one constant current sin when it does not reach 0,2V.
ECL
9) Describe door ECL:
It is constituted from an amplifier differentiates them in which on the base of npn a T2 a negative tension of reference V R is applied = -1.175V while on the base of the other npn T1 has the income tension, has one exited VOR on the collector of connectedT 1 to mass through RC1 and one exited VNOR on the collector of connectedT 2 to mass through RC2 , both the escapes then are equipped of transistor that acts as from buffer. The great advantage offered from the circuit is that T1 and T2 can be never found in interdiction or active region but in saturation, and therefore comes saved the time necessary riassorbire the charges from the base when it is wanted to be exited from the saturation.
In short the circuit is behaved like a current shunter that can slide all in a npn or all in the other or intermediate ways in order then to rejoin itself in the Rand . It is observed that the circuit comes fed between one negative tension and mass in order to concur the schermaggio and therefore to reduce the overlapped noise to the escape tensions.
10) Describe escape OR of door ECL:
We suppose that Vin are to the high state and are worth approximately 0V, is had that T1 is in active region while T2 is interdetto therefore the current of base of the separator T4 is simply equal to the current that crosses the RC2 , if for semplicità we consider it null is had that V0B4 = therefore the tension in escape is equal to the ddp to the heads of JBE4 that being T4 in active region is worth 0,75V, in truth holding account of the fall on the RC2 is had that for high income VOR= - 0,76V.
If Vin diminish until making to pass T2 in conduction and T1 in interdiction it has that the escape tension is equal to the sum of Vthe B4 and of Vthe BE4 = 0,75V in how much T4 it is in active region, of the rest VB4 the C2 is estimated multiplying the current=the E2 for the resistance RC2 in how much is negligible and with opposite sign the base currents of T4 and T2 . Moreoverand E2 can be calculated being famousV since T2 is in active region and therefore JBE2 = 0,75V, finds VOR = -1,54V.
11) Describe escape NOR of door ECL:
A Vin much interdice lowland T1 and therefore in it do not slide current therefore are had that VNOR is the sum of Vthe BE3= 0,75V in how much T3 is in active region and of the fall of tension on the resistance RC1 , NOR is obtainedV = -0,76V that is the same tension that is had on escape VOR when the income is to the high state.
To growing of Vin it is had that T1 passes in active region and therefore the fall has to its heads approximately 0,3V can therefore be calculated the tension of escape like sum ofV the BE3 more on the resistance RC1 which is obtained easy inasmuch as for a transistor in active region the collector current is approximately equal to the emettitore current, is obtained
VNOR = -1,72V that V in = are obtainedfor one -0,47V.
Increasing the V ulteriorlyin it is had that T1 enters in saturation and therefore Vthe NOR knows them until catching up the value of VNOR= - 1,45V for Vin= 0V.
12) Determination of the amplitude of the transition region:
Both the npn in active region are considered, the
emettitore currents have expression ![]() and
and ![]() replacingand =E1 the E2 pu² to gain
replacingand =E1 the E2 pu² to gain 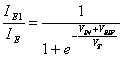 that just is such that when Vin= Vrif are had thatthe E1=the E2 .
Imposing that the relationship between the currents is worth
0,05 and also 0,95 they obtain two values of DV that they indicate as the transition region is
symmetrical regarding the tension - VRif and is worth 150mV.
that just is such that when Vin= Vrif are had thatthe E1=the E2 .
Imposing that the relationship between the currents is worth
0,05 and also 0,95 they obtain two values of DV that they indicate as the transition region is
symmetrical regarding the tension - VRif and is worth 150mV.
13) Process of commutation in one door ECL:
We consider that escape OR of a door ECL sluice on one condenser CL passes from the high state to the state low which corresponds a tension in escape of -1,54V is had that the condenser is loaded esponenzialmente stretching to â?"5,2V but reached â?"1,54V remains constant then.
14) Dissipation of power in one door ECL:
We consider escape OR of a door ECL is when the income is low that when is high, the power distributed from the generator is estimated like product of the tension to the heads of the generator for the sum of the current that slides in the resistance of emettitore and of the current that slides in the emettitore of T4 .
15) Fan Out of door ECL:
The Fan Out on level 0 does not come calculated in how much a level 0 in escape determines that the transistor T1 of the cargo doors is interdetto and therefore it does not absorb current while as far as the Fan Out on level 1 the minimal level for the error margin is prevailed on level 1, as an example D1 = 0,2V and the minimal tension in escape is deduced correspondent to the high state, through it and knowing that T1 of the cargo doors is in active zone it calculates the current absorbed from ciascuna of they. For same Vthe OH the current distributed from the door is estimated driver and therefore it can be calculated the maximum number of doors that can be connected to door ECL, such number is approximately 500 however the constructor recommends in emergency the maximum number of 20 doors.
MOS
16) Expressions of the currents in a NMOS and a PMOS:
Region of triodo
if ![]() then ha
then ha ![]()
Region of saturazione if ![]() then ha
then ha ![]()
Where ![]() being t the thickness
of oxide under the gate ones, W the width of the channel and L its
length.
being t the thickness
of oxide under the gate ones, W the width of the channel and L its
length.
It is observed that for a PMOS the equations are the same ones to pact to invert the pedici.
17) Effect of the temperature on the Mosfet:
To growing of the temperature the two effects are taken place following:
to) Vthe T it diminishes of 2,5mV/ °C
b) mobility diminishes in how much the reticulum is subject to greater vibrations and therefore there are many hits of the bearers
however an increase of the temperature predominates according to effect therefore produces one lessening of the current.
18) Invester to MOS:
He marks them of income is applied on gate of a MOS of the
type to enrichment having like cargo a resistance or in the integrated
circuits an other MOS that can be saturated, or also of type to
emptying so that the channel is formed already in absence of tension
on the gate ones. If Vin < VT are had that
the channel is not formed from the side of the source and therefore to
greater reason they do not give the side of the drain and therefore
the MOS is interdetto, when Vin > VT are had that
VDS > VGS â?"VT @ the 0 therefore NMOS enters in saturation, the
current that slides in it is ![]() that must be
replaced in
that must be
replaced in ![]() the obtaining the tension of
escape from the invester when it finds itself in the region of
saturation from which it exits for
the obtaining the tension of
escape from the invester when it finds itself in the region of
saturation from which it exits for ![]() , replacing
the value of Vout previously
calculated it is had that this happens for Vin = 3,4V. In the saturation region the
expression ofthe DS is
, replacing
the value of Vout previously
calculated it is had that this happens for Vin = 3,4V. In the saturation region the
expression ofthe DS is ![]() , replacing it in
, replacing it in ![]() the gains the
tension of escape from the invester when the NMOS is found in the
region of triodo. A parameter a lot important is
the gains the
tension of escape from the invester when the NMOS is found in the
region of triodo. A parameter a lot important is 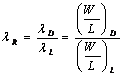 in as far as growing of lR the transition of the escape between
the levels ups and downs becomes steeper and therefore faster.
in as far as growing of lR the transition of the escape between
the levels ups and downs becomes steeper and therefore faster.
19) Realization of doors MOS:
AND obtains placing in cascade two NMOS while the cargo is saturated that is constituted from a having MOS the gate ones cortocircuitato with the drain, is had that a tension of income Vin < VT is considered like 0 a logical one and does not create the channel, achieves some that pu² not to slide current and therefore the escape tension is always to level 1 when to one of the two MOS of income it is applied one 0.
NOR have two MOS in parallel that is with the source and the drain in common, on this last one the MOS of cargo of saturated type is had and comes captured the escape tension that will be to the high state only when to both the MOS of income come applied 0 and therefore is interdetti and the escape is to the high state.
20) Time of climb and time of reduction of one door MOS:
The time of climb is ![]() while the
time of reduction is
while the
time of reduction is 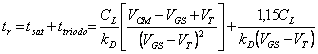
it is observed that the time of climb is the much greater of the time of reduction in how much channel of the cargo transistor must be along and tightened to the aim of having a fast transition between the two logical levels but in such a way small current can slide in it only one that must load the ability with the successive doors. The discharge of the condenser happens passing from the region of interdiction to the saturation region and therefore to the region of triodo, in last the two regions the times of discharge are differently estimated being variousthe DS that slide in the MOS.
CMOS
21) Door CMOS:
It marks them of income is applied is on gate of a connected having PMOS the source to VSS that on gate of a connected having NMOS the source to mass, the escape instead is taken on the drain of both. In short in such a way the times of commutation regarding door MOS in how much are reduced exist always a distance to low resistance for load and the discharge with the present capacitivo cargo to the escape of the door. In order to realize the symmetry it is necessary that the k of the PMOS it is approximately equal to the k of the PMOS but being mobility of electrons approximately the double quantity of that one of gaps, is necessary that the l of the PMOS it is the double quantity of the l of the NMOS.
22) Invester CMOS:
For Vin < VTN he has himself that T1 is interdetto while T2 is in active region and therefore the escape is to the high level and is worth VSS analogous for Vin > VSS â?"VTP is had that T2 is interdetto, while T1 is in active region therefore Vout = 0V.
In intermediate situations he has himself that or both the MOS are in saturation or active region but having to be equalto the DS , uguagliando their expressions in the NMOS and the PMOS in function of the operation region, obtains the value of the Vout for whichever tension of income. From a study of the expression of the current one finds that it comes nearly dissipated exclusively during the commutation that therefore will have to be rendered steep most possible.
23) Door Nand CMOS:
Part from an invester CMOS to which it comes applied one of the two marks them of income, between the NMOS and the mass places the NMOS of according to invester CMOS on whose gate the income is applied 2° which it reaches also the PMOS that is found in parallel to the PMOS of 1° the CMOS.
24) Door Nor CMOS:
Part from an invester CMOS to which it comes applied one of the two marks them of income, between the PMOS and VSS places the PMOS of according to invester CMOS on whose gate the income is applied 2° which it reaches also the NMOS that is found in parallel to the NMOS of 1° the CMOS.
25) Dissipation of door CMOS:
The dissipated power is the sum of three contributions, a
static power ![]() due to the fact that in the
realization integrated is various undesired diode valves, a power
short circuit
due to the fact that in the
realization integrated is various undesired diode valves, a power
short circuit ![]() that is that one that is had
when it is the PMOS that the NMOS is in saturation and a dynamics
power
that is that one that is had
when it is the PMOS that the NMOS is in saturation and a dynamics
power ![]() that are the dominant term and can be
reduced diminishing the ability or the tension of feeding making but
attention because the last provision determines an increase of the
delay of the door.
that are the dominant term and can be
reduced diminishing the ability or the tension of feeding making but
attention because the last provision determines an increase of the
delay of the door.
26) Latch - Up:
In the integrated realization of door CMOS various undesired diode valves are present, they damage place to a npn and to a pnp, these two transistor are joined between they to form a circuit with with the resistances of the substrate of type n and type p. It is had that if a disturbance or a photonic irradiation increases the current on the emettitore of the npn it ingenders a positive reaction that for one small applied tension gives place to one elevated current that right ys the CMOS. In particular the curve that describes the Latch-up is characterized from a Trigger Point and one tension of Hold.
In order to reduce the malfunctioning it can or be reduced the resistances of the substrate or the gain of the BJT.
