Transistor MOS
1) Describe the structure of a NMOS to enrichment:
A condenser MOS is had constituted from a metal, an oxide and a p_doped, ai heads della oxide we have two drugged regions n connected ai clips of Drain and of Source, applying a positive tension al gate is had that in a first time the below region is emptied of gaps after which al to grow of VG is arrived to having a channel of minority bearers that concurs the electron flow dal Source al Drain.
2) approximate Analysis ofthe DS with the control of loads:
The currentthe D that
slides in the channel is given simply from the relationship between
loads Qn and the T timetr that it employs to cross the channel,
in particular has 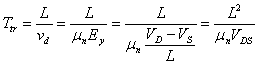 while
while ![]() replacing ha
replacing ha 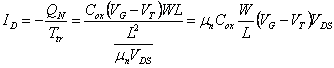
3) complete Analysis ofthe DS with the control of loads:
In this case the fall is not neglected of upgrades them
that it is had along the channel, however in order to simplify the
trattazione uses the approximation of gradual-channel second which the
fields in the direction y (…from the Drain to the Source)
are infinitesimal regarding that they are had in direction x
(…from the gate ones to the bulk) moreover is assumed that
the length of the L channel is greater of the length of the region of
emptying to the Drain. The fall of upgrades them to the inside
of a feature of the having channel R resistance is ![]() where
where ![]() replacing is
obtained
replacing is
obtained ![]() , integrating for separation of the variable
ones and replacing the value of mn
, integrating for separation of the variable
ones and replacing the value of mn 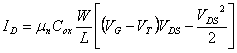 is obtained
draft of parabolas that expressthe D to varying of VG however they only have value for VDS < VG â "
VT beyond in fact
implies an improbable conductance differentiates them negative and it
loads not negative in the channel. However for VDS > VG â " VT is had that the channel is interrupted close to the drain
and therefore a fort is created electric field who ago that the speed
of the bearers is maximum and constant thereforethe DS are constant and insensitive
to Vthe DS its value in this
region of operation is in fact
is obtained
draft of parabolas that expressthe D to varying of VG however they only have value for VDS < VG â "
VT beyond in fact
implies an improbable conductance differentiates them negative and it
loads not negative in the channel. However for VDS > VG â " VT is had that the channel is interrupted close to the drain
and therefore a fort is created electric field who ago that the speed
of the bearers is maximum and constant thereforethe DS are constant and insensitive
to Vthe DS its value in this
region of operation is in fact ![]() .
.
4) Determination of VT :
The NMOS in saturation is put cortocircuitando the Gate
with the Drain, therefore from ![]() the draft of a
straight one can
the draft of a
straight one can ![]() be designed to the characteristic
of to varying of V D that
intersects the abscissa in VT and
whose slope can be used in order to determine mobility.
be designed to the characteristic
of to varying of V D that
intersects the abscissa in VT and
whose slope can be used in order to determine mobility.
5) Body Effect:
As for the determination of VT also in this case the NMOS in saturation is placed
cortocircuitando the Gate with the Drain moreover applies one tension
VB to the bulk, to its to grow is
had that the straight one that represents ![]() to
varying of VD trasla in parallel
with if same and therefore to growing of VB it increases also VT .
to
varying of VD trasla in parallel
with if same and therefore to growing of VB it increases also VT .
5) Transconduttanza:
It can be calculated deriving the ID regarding VG obtains ![]() per VD < VS sat .
per VD < VS sat .
6) Time of transit:
The time of transit in the channel of a MOS in having
saturation the Source to mass is estimated with the integral ![]() where
where ![]() and VC pu² to be gained resolving for
separation of variable the equation differentiate them
and VC pu² to be gained resolving for
separation of variable the equation differentiate them ![]() ,
, 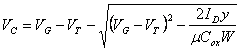 is obtained that replaced and
integrated it supplies
is obtained that replaced and
integrated it supplies ![]() .
.
7) CMOS:
It is a circuit constituted from a PMOS and a having NMOS the Drain in common while the Source of the PMOS is to VSS while the Source of the NMOS is to mass, the Gate instead is cortocircuita to you and to they it comes applied marks them of income while the escape is taken on the Drain. The main characteristic of this configuration is that one of the two MOS only absorbs current during the commutations in how much alternatively is interdetto and the other is in active region.
