Ondulatoria mechanics
1) Relation of De Broglie :
De Broglie supports that the light has a double nature, to
particellare and ondulatoria for which to an electron it is associated
is one mass that a wave. The relation that alloy the wavelength l of the cancellation to its
momentum 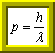 .
.
2) Observable and operating :
The observable ones are mechanical property that can be measured like position x, the momentum p and the energy and while the operating ones are use you in quantistica mechanics and ondulatoria mechanics and in short draft of particular mathematical instructions. Observable and operating they are re-united from one important relation that it asserts
that the single measurable possible values for an
observable one are those for which ![]() .
.
They are of particular importance the operating momentum ![]() and the operating energy total
and the operating energy total ![]() that also is called Hamiltoniana.
that also is called Hamiltoniana.
3) medium Value of one sequence of many measures of an observable one :
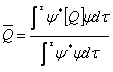
4) Equation of Schroedinger :
It describes the function of wave y(x, y, z, t) that is the wave associated to one endowed particle of massa.
![]() .
.
5) Meant physicist of the wave function :
The module picture of the wave function y that is ![]() represents
the density of presence of the particle in point x, y, z to the time
t. Such density goes multiplied for one constant of
normalization that renders unitarian the integral calculated on all
the space.
represents
the density of presence of the particle in point x, y, z to the time
t. Such density goes multiplied for one constant of
normalization that renders unitarian the integral calculated on all
the space.
6) Principle of indetermination of Heisenberg :
It asserts that there are conjugated braces of variable
for which when it increases the degree of acquaintance of one
automatically diminishes the degree of acquaintance of the other, the
brace of variable of interest in quantistica is the momentum and the
position of the electron well Heisenberg asserts that dates the
reduced dimensions of this particle, when we by means of a proton try
to characterize of the position we know to have taken it but the
photon yields to the electron energy and it sends it to blink goodness
knows where. The principle of indetermination of Heisenberg
asserts that the product of the uncertainties is worth ![]() .
.
7) Solution of the equation of Schroedinger in the free particle case :
The time is necessary to place V = 0 in the equation of
independent Schroedinger and to limit itself to the unidimensionale
case, is obtained :
![]()
In short it is had that the particle can be ovunque, we that is have one total indetermination on the position being moment for completely famous moment the momentum.
8) Condition of Bragg:
It is the condition for imposing to the wavelength of a cancellation incident with an angle q regarding axis x so that it can give place to constructive interference if sended against of the reticular plans separates from the distance d. the condizione to you
![]()
it is obtained characterizing immediately below the reticular plan, designing the beam that reflects on it and estimating the optical length in more regarding the reflection on the overhanging plan. So that the two beams are in phase are necessary that such difference of distance is a multiple n of the wavelength l. It is necessary to use a next wavelength to the distance between the plans therefore is necessary to use as probe of i beams x.
9) Calcolo di Laue for the amplitude of the diffuse wave and mutual reticulum:
Draft of a calculation that comes introduced in order to limit the error of base of the calculation of Bragg, that is considering the reticular plans like of the perfectly reflecting mirrors and therefore.
One of the points of the reticulum like origin is
considered Or, a point situated at a distance r from it comes invested from a flat wave ![]() that we will always consider to time t = 0. In r
that we will always consider to time t = 0. In r ![]() is
had but this point becomes source of secondary spherical waves for
which the amplitude of the cancellation on the detector place at a
distance r from r and R from
the origin it is
is
had but this point becomes source of secondary spherical waves for
which the amplitude of the cancellation on the detector place at a
distance r from r and R from
the origin it is ![]() where kr they are the
modules because in a spherical wave the two carriers are always
parallels.
where kr they are the
modules because in a spherical wave the two carriers are always
parallels.
The module picture of the amplitude of the found
cancellation is  the maximum of which it is
obtained cancelling the denominator that is for
the maximum of which it is
obtained cancelling the denominator that is for ![]() and therefore
and therefore ![]() where q it is an entire one.
where q it is an entire one.
The conditions of Laue for the maximum diffraction are obtained therefore:
![]()
![]()
![]()
where q, r, s is of the entire numbers they
are to the base of the definition of the mutual reticulum in how much
the carriers of translation of stesso the



they are such that one whichever they linear combination satisfies the equations of Laue for the maximum diffraction.
