Reception in noise presence
Reception numerica in noise presence
1) Characteristics of the numerical reception in noise presence:
We suppose that a real numerical channel is affection from
AWGN, it can be represented on a base of ¥ payers whom the base to n payers contains on which the
useful process is represented. The noise nr(t) represented on the first N payers contains
remaining information on the process whilenthe (t) represented on the ¥ - N payers is independent is from the useful process that
from nr(t), it comes called
noise insignificant and neglected in the remaining trattazione.
The noise is represented therefore in the
space of marks them from the ![]() carrier where the nj they have density of probability
of 1° the
carrier where the nj they have density of probability
of 1° the  order, analogous it marks received them
rr(t) is described from the
observable carrier
order, analogous it marks received them
rr(t) is described from the
observable carrier ![]() with
with ![]() that
they are v.a. continuous in how much sum of a v.a. discreet and a v.a.
it continues.
that
they are v.a. continuous in how much sum of a v.a. discreet and a v.a.
it continues.
2) Demodulation and decision in noise presence:
It supposes itself that the numerical modulation has been
lacking in codifies and using a transformation series-parallel, has
associated to every element of the constellation one binary word with ![]() bit. The outline of the numerical
demodulatore is:
bit. The outline of the numerical
demodulatore is:
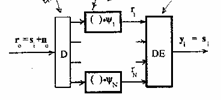 tothe escape of the bench of
correlatori the members r j of observable carrier r 0 have themselves that for via of the noise does not coincide
with no carrier of the constellation, have themselves in fact that the
probability to receive oncer j
that has been emitted sd is
tothe escape of the bench of
correlatori the members r j of observable carrier r 0 have themselves that for via of the noise does not coincide
with no carrier of the constellation, have themselves in fact that the
probability to receive oncer j
that has been emitted sd is ![]() and being the nj statistically independent is had
and being the nj statistically independent is had  .
.
A decisore is therefore necessary which applying a
decision criterion it associates r0 to one of the carriers of the constellation.
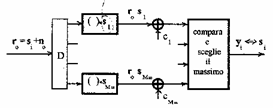
3) Criteria of decision:
CRITERION MAP (Maximum A posteriori probability)
 |
For every carrier sd that it can be emitted from the modulator it calculates the conditioned probability
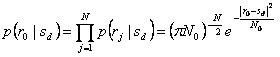 is
reached 3ª the formulation of second criterion MAP which chooses sj if
is
reached 3ª the formulation of second criterion MAP which chooses sj if CRITERION MILILITER (Maximum Likelihood = Maximum verosimiglianza)
It is a criterion subottimo according to which
every for ![]() the
¹ is chosen s j if j which banally the second formulation corresponds
alternative which chooses sj if
the
¹ is chosen s j if j which banally the second formulation corresponds
alternative which chooses sj if ![]() every for the ¹j that is chooses the
carrier sj of the
constellation that more close turns out to be to r0 . In this case being absent
the probabilities of emission of the single carriers, the decision
regions have all the same area.
every for the ¹j that is chooses the
carrier sj of the
constellation that more close turns out to be to r0 . In this case being absent
the probabilities of emission of the single carriers, the decision
regions have all the same area.
4) Probability of correct and wrong decision:
Remembering that the decision criteria do not make other
that to associate to every carrier of the constellation a decision
region, it follows some that the probability of corrected decision
conditioned to the issued carrier sd is the integral of ![]() on the
associatedD region d
to sd , has
on the
associatedD region d
to sd , has  that is while the probability of corrected decision is
that is while the probability of corrected decision is  and the probability of error Pand = 1-PC Finally the probability of P errorand is the probability that is a
wrong bit and is function of codifies of used modulation, as
an example in the case of antipodale modulation
and the probability of error Pand = 1-PC Finally the probability of P errorand is the probability that is a
wrong bit and is function of codifies of used modulation, as
an example in the case of antipodale modulation 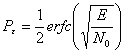 .
.
Linear esteem of marks them continuous
5) Characteristics of the continuous esteem:
The received process ![]() is the sum
of a stationary or ciclostazionario useful process with null medium
continuous realization s(t) to valor and spectral density famous P(f)
which a P(f) power corresponds, and of a noise Gaussian additive with
null statistical medium realization n(t) to valor and spectral density
N(f), beginning from r(t) the appraiser supplies a continuous esteem
linear
is the sum
of a stationary or ciclostazionario useful process with null medium
continuous realization s(t) to valor and spectral density famous P(f)
which a P(f) power corresponds, and of a noise Gaussian additive with
null statistical medium realization n(t) to valor and spectral density
N(f), beginning from r(t) the appraiser supplies a continuous esteem
linear ![]() of the single comprised useful part
s(t) in r(t), the esteem error store clerk is
of the single comprised useful part
s(t) in r(t), the esteem error store clerk is ![]() .
For a data moment tthe 0 performances of the appraiser are function of s(t) = s
and come characterized through the conditioned polarization
.
For a data moment tthe 0 performances of the appraiser are function of s(t) = s
and come characterized through the conditioned polarization ![]() , the conditioned variance of the
, the conditioned variance of the ![]() error and the medium quadratic error conditioned
error and the medium quadratic error conditioned  whose expected values are
respective the
whose expected values are
respective the ![]() polarization, the variance of
the
polarization, the variance of
the ![]() error and the quadratic error medium
error and the quadratic error medium ![]() . An adimensional relative pointer
called quality of the continuous esteem has itself moreover
. An adimensional relative pointer
called quality of the continuous esteem has itself moreover  that in short is a relationship beacon-noise.
that in short is a relationship beacon-noise.
6) Characteristics of appraisers LTI:
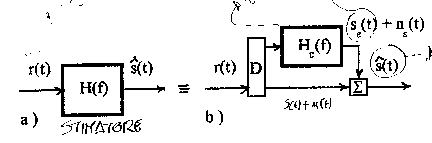 The appraiser must necessarily introduce distortion in how
much must favor the transit of the spectral members of r(t) for which
he marks them useful prevails on the noise and hindering instead the
transit of the members for which the noise prevails on marks them.
Admitting the single linear distortion of amplitude the
following outline is had equivalent for the appraiser whom it
evidences as the continuous esteem is is composed from 4 addends
The appraiser must necessarily introduce distortion in how
much must favor the transit of the spectral members of r(t) for which
he marks them useful prevails on the noise and hindering instead the
transit of the members for which the noise prevails on marks them.
Admitting the single linear distortion of amplitude the
following outline is had equivalent for the appraiser whom it
evidences as the continuous esteem is is composed from 4 addends
![]() where n(t) and nand(t) they are disturb while sand(t) is a disturbance
if
where n(t) and nand(t) they are disturb while sand(t) is a disturbance
if  .
.
One finds that the characteristics of the appraiser
sono ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,  ,
,  being Pand the power of the
disturbance due to the linear distortion of amplitude,
being Pand the power of the
disturbance due to the linear distortion of amplitude, ![]() the power of the single noise in escape and
the power of the single noise in escape and ![]() the power of the process of esteem LTI. It is
observed that the optimization of the quality of the esteem is
invariant regarding the presence of a constant factor in the employed
function of transfer, this result comes employed for ricondursi always
to the case particular of noise Gaussian additive white man by means
of one sbiancatore
the power of the process of esteem LTI. It is
observed that the optimization of the quality of the esteem is
invariant regarding the presence of a constant factor in the employed
function of transfer, this result comes employed for ricondursi always
to the case particular of noise Gaussian additive white man by means
of one sbiancatore  to put in front to the
appraiser and one sbiancatore complementary to postplace.
to put in front to the
appraiser and one sbiancatore complementary to postplace.
15) Typology of appraisers LTI:
Optimal linear appraiser of Wiener-Hopf
Diminishing ![]() the quality of
the esteem is maximized, such optimization is carried out from the
filter of Wiener-Hopf
the quality of
the esteem is maximized, such optimization is carried out from the
filter of Wiener-Hopf  with
with ![]() , antitransforming finds a real impulsive answer and
equal therefore antimotive therefore the quadripolo is not physically
realizable, then uses a filter whose impulsive answer approximates
that one of Wiener-Hopf per t > 0 but it is null for t < 0.
, antitransforming finds a real impulsive answer and
equal therefore antimotive therefore the quadripolo is not physically
realizable, then uses a filter whose impulsive answer approximates
that one of Wiener-Hopf per t > 0 but it is null for t < 0.
Linear appraiser with optimal cut of band
We consider for semplicità a noise white man
with spectral density N0 , the
linear appraiser with optimal cut of band has function of rectangular
transfer that is worth gt0 for
the frequencies comprised between f1 and f2 for which the
useful process prevails on the noise and is worth elsewhere instead 0.
The quality that turns out some is 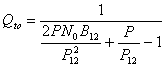 and is
maximized for
and is
maximized for ![]() the physically realizable
filter introduces an attenuation of 6dB to the cut frequencies and
determines a relationship greater beacon-noise regarding that it would
be had with the rectangular filter.
the physically realizable
filter introduces an attenuation of 6dB to the cut frequencies and
determines a relationship greater beacon-noise regarding that it would
be had with the rectangular filter.
Not polarized linear appraiser
If we have a process received with useful part closely limited in the B band = fM â " fm, we can reduce the noise generating but distortion using a filter with band B12 < B.
If the scope is instead to reduce the distortion, the
appraiser must be polarized that is does not have to be a filter with
frequencies of cut that coincide with the ends of the useful band, in
such case in fact the quality of the ![]() esteem
comes to coincide with the relationship beacon-noise to the Q escape.
esteem
comes to coincide with the relationship beacon-noise to the Q escape.
Such appraiser is famous also in absence of acquaintance of the spectral density of useful power and its quality is gained immediately, is therefore preferred to the other appraisers also because to growing of the quality of the esteem, it turns out to you differ little.
