Circuits type not electrical worker
Inducer
1) magnetic Circuit :
Draft of a circuit constituted from ferromagnetic materials, windings of excitation and eventually from traferri.
2) Law of Hopkinson :
![]() where " it is the reluctance
where " it is the reluctance ![]() e j is the flow through one coil of the circuit. It is
obtained applying to the theorem of the circuitazione of Ampere for H
to one inner line to the magnetic circuit.
e j is the flow through one coil of the circuit. It is
obtained applying to the theorem of the circuitazione of Ampere for H
to one inner line to the magnetic circuit.
3) magnetomotrice Force :
![]() measure in AmpereSpire
measure in AmpereSpire
4) Reluctance :
![]() is the opposition that the circuit offers to
the passage of the magnetic flow. Measure in AmpereSpire/Weber
is the opposition that the circuit offers to
the passage of the magnetic flow. Measure in AmpereSpire/Weber
5) magnetic Force on a current element :
![]() also is said
2ª the law of Laplace and derives from considerations experiences
them
also is said
2ª the law of Laplace and derives from considerations experiences
them
6) Force of Lorentz :
It means to describe the ![]() force which
it is subject loads punctiform q in motion in a field of magnetic
induction B. Draft of an always orthogonal force to the speed of
the particle and therefore cannot any be altered the module but the
single direction. It is gained from 2ª the law of Laplace
writing
force which
it is subject loads punctiform q in motion in a field of magnetic
induction B. Draft of an always orthogonal force to the speed of
the particle and therefore cannot any be altered the module but the
single direction. It is gained from 2ª the law of Laplace
writing ![]()
7) Law of Biot and Savart :
Also the law of Ampere is said 1ª, it means to describe
the field generated from an infinitesimal element of thread covered
from current I, has : ![]() , valid law in the case of circuits to infinitesimal
section, otherwise is necessary to replace with the flow of J.
, valid law in the case of circuits to infinitesimal
section, otherwise is necessary to replace with the flow of J.
8) Law of Faraday Neumann Lenz:
It means to describe phenomena in which a variation in the
time of the flow of B concatenato with the circuit it induces in it a
f.e.m. given from ![]() the flow variations can
derive from one of the following causes :
the flow variations can
derive from one of the following causes :
to) mechanical movement of the circuit
b) variation of the B field in the time
c) variation of geometry of the circuit
9) parasitic Currents or of Foucault :
If in a conductor a B field is had variable in the time,
executing the circuitazione of and along a whichever closed circuit
being ![]() finds a not null value therefore to the
inside of the conductor circulates currents induced parasitic or of
Foucault who embezzles energy to the magnetic field.
finds a not null value therefore to the
inside of the conductor circulates currents induced parasitic or of
Foucault who embezzles energy to the magnetic field.
10) Electromagnet :
Draft of a magnet that comes realized by means of a ferromagnetic material on which has bundled up a winding in which continuum flow slides, in such a way it is succeeded to polarize the material. The ferromagnetic material with the aim is chosen to only limit the dispersed flow.
11) permanent Magnets :
Draft of a material in the which permane magnetization also to continuation of the elimination of the excitation, draft customarily of ferromagnetic materials with high residual magnetization, therefore with hysteresis cycle much wide one.
12) equivalent Circuit electrical worker associated to an inducer:
The circuit electrical worker is constituted from a
generator Vg that R resistance
feeds one having windingg , is
then a generator of tension controlled from the flow that crosses the
winding. In the magnetic circuit it is had instead a controlled
generator, from the current that slide in the winding of excitation, a
reluctance and a K inductance that account of the losses due to the
currents of Foucault holds. The scope is to replace in the
circuit electrical worker the generator controlled with an equivalent
circuit, to such aim replaces the flow ![]() in the
expression of the generator, has
in the
expression of the generator, has 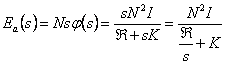 obtaining the
obtaining the 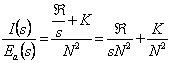 admittance therefore in the circuit electrical
worker equivalent of the inducer has generator Vg with in series the resistance of the winding Rg sluices on an inductance of
admittance therefore in the circuit electrical
worker equivalent of the inducer has generator Vg with in series the resistance of the winding Rg sluices on an inductance of
![]() value in parallel to a resistance of
value in parallel to a resistance of ![]() value which therefore is associated to the losses in the
iron due to the currents of Foucault, in the ideal inducer it is
infinite while the resistance of the windings is 0.
value which therefore is associated to the losses in the
iron due to the currents of Foucault, in the ideal inducer it is
infinite while the resistance of the windings is 0.
13) Characteristic of the inducer in not linear regimen:
From the law of Hopkinson ![]() it is
had that it would seem must it are to us a linear relation between the
flow and the force magneto-engine but one characteristic experiences
them extension that is saturation for which if we have one sinusoide
of flow that invades the not linear zone, they are come to create of
the intense currents much, these are due to the distortion that sees
the 3ª harmonic to add itself to the 1ª in controfase and
therefore the peaks are added.
it is
had that it would seem must it are to us a linear relation between the
flow and the force magneto-engine but one characteristic experiences
them extension that is saturation for which if we have one sinusoide
of flow that invades the not linear zone, they are come to create of
the intense currents much, these are due to the distortion that sees
the 3ª harmonic to add itself to the 1ª in controfase and
therefore the peaks are added.
Transformer
14) Permeability and conductivity in the materials:
Isolante s bassa m lowland
Conduttore s alta m lowland
Ferromagnetico s alta high m
ferriti s bassa high m
The better material for the nuclei is therefore the ferrite in how much gives to small place dispersed currents, but it is expensive therefore is preferred to use the ferromagnetic materials laminating them and inserting of the insulating layers between sheets.
15) Value of the back electromotive force that is generated when current in a winding slides:
For the law of Lenz ![]() for every coil
is had but it is necessary to consider that in kind the winding is
composed from N coils therefore
for every coil
is had but it is necessary to consider that in kind the winding is
composed from N coils therefore ![]() the sign less
pu² to disappear to pact to design the corresponding generator so
that it is opposed to the flow variation.
the sign less
pu² to disappear to pact to design the corresponding generator so
that it is opposed to the flow variation.
16) Circuit electrical worker associated to a transformer:
He is constituted from 2 separated meshes, in before that
idealizza the head physician has a generator Vthe 1 that feeds one having winding R resistancea 1 and controlled generator of ![]() value, being j1 flow dispersed in the head
physician. The mesh that describes the secondary one is
analogous therefore the equations is:
value, being j1 flow dispersed in the head
physician. The mesh that describes the secondary one is
analogous therefore the equations is:
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
17) associated magnetic Circuit to a transformer:
It is constituted from 3 meshes, one that the magnetomotrice force contains on the head physician and the relative reluctance to the flow dispersed in air from the head physician, one who contains the magnetomotrice force on secondary and the relative reluctance to the flow dispersed in air from the secondary one, and the mesh centers them that beyond to the relative reluctance to the nucleus it introduces relative a K inductance to the currents of Foucault, let alone the two magnetomotrici forces with towards the Concorde, the equations are:
![]()
![]()
![]()
18) Circuit electrical worker equivalent associated to a transformer:
One agrees to replace the two generators controls to you with of the stiffnesses, therefore the equations of the flows in the two equations of the generators are replaced control to you, are had:
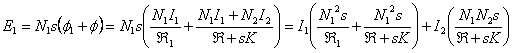
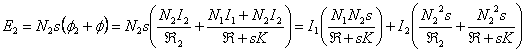
remembering that the matrix [ Z ] of 2 nets 2_porte connected in series is equal to the sum of the two matrices [ Z ] it is had:
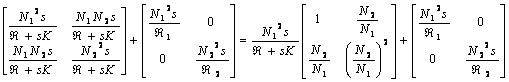
where the last matrix characterizes an inductance
mails in series on the head physician and one mails in series to the
secondary one, while the first matrix characterizes an ideal
transformer with relationship 1:n and finally the first fraction can
be decomposed in the parallel of one inductance of ![]() value and one resistance of value
value and one resistance of value ![]() .
.
19) Value of the parameters in magnetic the equivalent circuit in the case of the inducers mutually couples to you:
The losses in the windings (R are neglected…1®0, R2®0) and in the magnetic nucleus (…K®0), replacing in the equations
found for the real transformer, 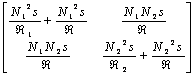 is had that
represents two indutori ones mutually couples to you, in fact the
terms on the greater diagonal is the inducers while the terms on the
smaller diagonal are equal and characterize the coefficient of mutual
induction.
is had that
represents two indutori ones mutually couples to you, in fact the
terms on the greater diagonal is the inducers while the terms on the
smaller diagonal are equal and characterize the coefficient of mutual
induction.
20) Value of the parameters in magnetic the equivalent circuit in the case of an ideal transformer:
If in the magnetic circuit they suppose null it is the
reluctance of the nucleus (…![]() ) that the relative
inductance to the currents of Foucault (…K®0) has
) that the relative
inductance to the currents of Foucault (…K®0) has ![]() and therefore
and therefore ![]() while supposing null the
flows dispersed in air ( …j1®0, j2®the
0) and resistances of the windings (…R1®0, 2R®0) has
for the circuit
while supposing null the
flows dispersed in air ( …j1®0, j2®the
0) and resistances of the windings (…R1®0, 2R®0) has
for the circuit ![]() electrical worker e
electrical worker e ![]() from cui
from cui ![]() ossia
ossia ![]() .
.
21) Coefficient of mutual induction M:
![]() where the equal one is reported to the case of
ideal transformer.
where the equal one is reported to the case of
ideal transformer.
22) Rendering of a transformer and method in order to calculate it:
It is much elevated a lot that is indicated in terms of the number of 9 present ones, as an example 0,99999. Since one is demanded elevated precision it is preferred to separately calculate the losses in copper and the iron:
to) Losses in the iron : It is necessary to leave the secondary one open, in such a way in it it does not slide current and therefore it does not slide any not even to the head physician (…and therefore sure we do not have losses in copper) therefore the transformer is equivalent to an equal generator to the nominal tension with in parallel one inductance and one resistance.
b) Losses in copper : Closing the secondary one in short circuit it is had that the primary flow al is much inferior respect al nominal flow and therefore the losses nel iron are minimal.
The sum of the two calculated losses cos¬ gives to the loss total of the transformer.
23) Relationships of transformation for the transformers trifase:
The following outlines are possible with respect transformation relationships to you:
to) star â " stella N' = N
b) triangle â " triangolo N' = N
c) star
â?"
triangolo
N' = ![]()
d) triangolo
â "
stella
N' =![]()
in the star the transformers have a single clip towards the escape while in the every triangle transformer has both the clips towards the escape.
24) practical Realization of a transformer trifase:
It must be taken advantage of all and the 3 columns putting a winding on ognuna of they.
Electric motors and generators
25) Principle of reversibility for blots some to them operating in continuous:
The power electrical worker distributed in a machine in continuous is equal to the generated mechanical power and viceversa.
It is demonstrated feeding with a continuous generator in
a circuit dipped in constant a B field; if an end of the circuit
is free to move on of the metallic contacts, has that on it for 2ª
the law of Laplace (…![]() ), acts a F=IdB force being d
the length of the branch and the current that crosses it.
), acts a F=IdB force being d
the length of the branch and the current that crosses it.
Of the rest for the law of Lenz (…![]() )
the varied branch muovendosi the flow cut from the circuit and
therefore produces to its heads one d.d.p.
)
the varied branch muovendosi the flow cut from the circuit and
therefore produces to its heads one d.d.p. ![]() therefore the power electrical worker
therefore the power electrical worker ![]() is
equal to the power meccanica
is
equal to the power meccanica ![]() .
.
26) Typology of realization of the rotor :
to) smooth Rotor, a traferro is come true constant by means of a cylindrical rotor having on the periphery of the hollow ones that wraps the windings.
b) salienti pole Rotor is come true with of the polar shoes opportunely sagomate, however there are of the zones in which the traferro it is much wide one and therefore the reluctance is elevated while in other zones the traferro it is smaller that it determines of the undesired modulations, but is constructively simpler regarding the smooth rotor.
27) Principle of operation of the dynamo:
A stator constituted from a ferromagnetic cylinder is
had on which they in ferromagnetic material around to which are
screwed of the polar expansions anch' are wrapped the windings of
excitation, in such a way the stator induce a magnetic field.
The streamlines of this field are firm in the time but they
come cut from or more coils which ruotano in how much connected to a
system that ago to turn the axis of the rotor, to the heads of these
coils second induce therefore of the variable currents in the time the
law of Lenz (…![]() ). In the case of the dynamo
a d.c. voltage is wanted to be generated therefore is necessary to
rectify these currents, to such aim comes true a collector to broken
ring so that on one of the two brushes there is always the same
polarity. In the operation to empty it is had that to growing
of the current of excitation of the stator it increases the tension to
empty present on the brushes in order then to remain almost constant
because of saturation effects. In the operation with the cargo
instead problems in phase of commutation and problems which had to the
induced reaction are introduced of.
). In the case of the dynamo
a d.c. voltage is wanted to be generated therefore is necessary to
rectify these currents, to such aim comes true a collector to broken
ring so that on one of the two brushes there is always the same
polarity. In the operation to empty it is had that to growing
of the current of excitation of the stator it increases the tension to
empty present on the brushes in order then to remain almost constant
because of saturation effects. In the operation with the cargo
instead problems in phase of commutation and problems which had to the
induced reaction are introduced of.
28) induced Reaction of in the dynamo:
The presence of currents that slide in the collector
second generates a magnetic field in the rotor the law of Biot and
Savart ![]() , such field reacts
with that due to the stator inducer, giving place to a demagnetizing
effect.
, such field reacts
with that due to the stator inducer, giving place to a demagnetizing
effect.
29) Problems with the dynamos in the phase of commutation:
The phase of commutation is that one during which the brush passes from a lamella the successive one, delicate one in how much is a phase much is produced of extracurrents that can damage the motor, such currents come limited by means of it use of some secondary poles places in middle position between the main poles or since this phenomenon moves the mezzeroes a axis, the brushes come moved in advance payment in the direction of the motion.
30) Ring of Pacinotti:
It is an elementary dynamo with a rotor constituted from
a ferromagnetic ring on which a winding closed on if same is placed,
the brushes are placed in diametrically opposite direction, well every
coil is behaved, for the law of Lenz ![]() , like a generator of tension of opportune value but so
that tensions on the left are all of the same sign and therefore also
for the tensions to right but of the opposite sign. In this way
it is succeeded to make that the tension on the brushes is constant.
, like a generator of tension of opportune value but so
that tensions on the left are all of the same sign and therefore also
for the tensions to right but of the opposite sign. In this way
it is succeeded to make that the tension on the brushes is constant.
31) tachimetrica Dynamo:
It is a device that obtains realizing the stator with a permanent magnet therefore the flow is constant and it is had that the tension on the collector is due only to the speed of spin of the rotor. Not there is much difference with the traditional, single dynamo that is made with precision trying to eliminate all the causes that in a normal dynamo can render the flow not exactly constant.
32) Principle of operation of the motor to continuum flow:
It uses the same system of the dynamo, that is a stator is
had that generates a constant magnetic field through of the polar
shoes with of the windings in which slides a continuous one, the rotor
instead is constituted from a coil which comes fed in continuous from
an external generator, on the coil covered from current will act
therefore a force given from 2ª the law of Laplace ![]() that will stretch to make to ruotare in a back the coil,
but such force ruotando becomes of opposite sign therefore the coil
ruoterebbe to the contrary, in order to avoid it sign to the feeding
by means of a collector to broken ring is changed.
that will stretch to make to ruotare in a back the coil,
but such force ruotando becomes of opposite sign therefore the coil
ruoterebbe to the contrary, in order to avoid it sign to the feeding
by means of a collector to broken ring is changed.
33) Circuit equivalent of the motor to continuum flow:
It is constituted from 2 separated meshes, the first
relative one to the stator has a continuous excitation in with inner
resistance Rs and relative a Kinductance s to the
windings of stator. The equations are ![]() e
e ![]() where in last the inductance it comes
neglected in how much in continuous is short circuito.
where in last the inductance it comes
neglected in how much in continuous is short circuito.
The second mesh is relative to the armor of the rotor, has
a continuous excitation in Vto with inner resistance Rto while andto it is
the tension to the heads of the rotor due to the motion in a magnetic
field. The equations are ![]()
![]() e
e ![]() .
.
34) mechanical Characteristic:
It expresses the value of the brace in function of the
angular velocity 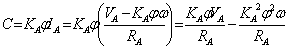 , draft of a straight one to
negative slope that intersects the vertical axis in correspondence of
the cue brace
, draft of a straight one to
negative slope that intersects the vertical axis in correspondence of
the cue brace ![]() while it intersects the axis of the
speeds in correspondence of the pulsation limit
while it intersects the axis of the
speeds in correspondence of the pulsation limit ![]() .
Varying the tension on the rotor the straight one trasla in
parallel with if same (…in fact is to the numerator is
in wL that in C(0)) while varying the tension on the stator the
straight one changes slope (…in fact from the stator
tension and therefore on the stator currentthe S depends the
.
Varying the tension on the rotor the straight one trasla in
parallel with if same (…in fact is to the numerator is
in wL that in C(0)) while varying the tension on the stator the
straight one changes slope (…in fact from the stator
tension and therefore on the stator currentthe S depends the ![]() flow which it
is to the numerator in C(0) and to the denominator in wL ).
flow which it
is to the numerator in C(0) and to the denominator in wL ).
35) Motor with excitation in derivation:
It is had that the tension that feeds the armor, goes to feeding also the stator, obtains one characteristic nearly vertical mechanics that illustrates as this logon is ideal for applications in which constant speed to varying of the cargo is demanded one, like as an example in the tools.
36) Motor with excitation in series:
It is a motor that has an only generator, is for the rotor that for the stator, is characterized from a characteristic curve type equilateral hyperbola and therefore mechanical power P=Cw maintains constant. A lot is a type of used feeding laddove is demanded of the elevated braces of cue, like in the case of the electric traction, but attention must be made because in cargo absence the escape speed is had which stretches to infinite.
37) Reversal of the march sense:
It is obtained changing the sign to the feeding of the rotor, in how much if we changed it to the feeding of the stator would be also to compensate a residual flow.
38) Reversal of the sense of march for a motor fed in series:
It is useless to alter the sign of the generators, is necessary to insert a dynamic commutator.
39) Reversal of the sense of the energy:
With reference to the tilted given mechanical
characteristic from the straight one, reversal of the sense of the
energy is had that is passage from generator motor and viceversa, when
the power ![]() passes from positive to negative, this
naturally pu² to happen is because the brace becomes negative, is
because the spin speed becomes negative.
passes from positive to negative, this
naturally pu² to happen is because the brace becomes negative, is
because the spin speed becomes negative.
40) Machine sincrona:
A machine is motor it or generating, it is said sincrona if the speed of mechanical spin is proporziona them to the spin speed electrical worker.
41) rotary Field:
They have on the stator a system trifase applied to of the windings situates to you to 120° between they, have the fields:
![]()
![]()
![]()
for which total is had ![]() an induction field that remains constant that is
an induction field that remains constant that is ![]() if if
if if ![]() .
.
42) Principle of operation of the alternator:
It is a machine that converts mechanical energy in electric power trifase, the rotor is constituted from many magnetic poles (…comes obtained through an electromagnet that is of the windings in which slides one continuum flow) which are in mechanical spin and determine therefore rotary a B field with the speed of the rotor that it induces in the windings of stator disposed to 120° between they a symmetrical system of tensions trifase.
43) Reaction of armor:
In the operation of the machine sincrona from generator (…alternator) the currents induced in the windings of stator gives place to a rotary field that is opposed to the motion of the rotor.
44) Principle of operation of the motor sincrono:
It is a machine that converts electric power trifase in
mechanical energy, in particular the system trifase applied to the
windings of stator creates a rotary field B that drags with if the
rotor which it is like a permanent magnet (…realizes
per² with an electromagnet fed in continuous). The speed of
rotor wm is tied to the pulsation of trifase wand from the
customary relation of the rotary field ![]() being n
the number of the poles. The mechanical characteristic is
straight vertical therefore a motor sincrono only works for
being n
the number of the poles. The mechanical characteristic is
straight vertical therefore a motor sincrono only works for ![]() and in order to catch up it needs it of a launch
motor.
and in order to catch up it needs it of a launch
motor.
45) Typology of rotores for the induction motor:
In the induction motor the rotor is not fed but corto-circuitato and always to smooth poles, the typology are had:
to) rotor avvolto it is constituted from 3 windings like those of stator but places in parallel between they
b) cage rotor of scoiattolo is constituted from conduttrici bars parallels connected electrically to the ends
46) Principle of operation of the induction motor:
The system trifase applied to the stator gives place to ruotante a B field which indurrà in the windings of rotor fem but a rotor is closed, therefore in it three symmetrical currents in the time in three symmetrical windings in the space will slide (…considering the wrapped motor), this for the law of Lenz give place to a field BR that is overlapped to that product from the stator. It but will not never catch up the speed of the field in how much is just this light phase-difference to concur the motion.
47) mechanical Characteristic of the induction motor:
Much small is characterized from a cue brace that they until to the maximum brace knows, in order then to ridiscendere and to have null brace in correspondence of the maximum speed, the ascending feature of the characteristic is unstable, in how much if an obstacle is met reduces the speed and also the brace. The feature descendant of the characteristic is instead that operating one, in how much the presence of an obstacle that reduces the speed, gives place to an increase of the brace.
48) Modality of starter of the induction motor trifase:
In theory this type of motor does not have need of a motor of launch in how much introduces a not null brace of cue, but for some applications it could be not sufficient, then uses following the three techniques:
to) one looks at that increasing to the resistance of the stator the cue brace it increases, therefore the windings of stator come connects to you to of the reostati ones which completely are inserted to the starter in order then completely to be disinseriti to regimen in how much otherwise would have strong losses for Joule effect.
b) the brace increases to the square of the applied tension proportionally trifase therefore if to the cue the windings of stator come connect to you to triangle, has a higher tension of cue regarding the regimen situation in which the clips they are connects to you to star.
c) the cage motor double of scoiattolo more introduces an elevated brace of cue, it is for that comes used in all those cases in which the motor it is subject to frequent ignitions.
49) Sliding of the induction motor:
Speed wc with which the field wheel in the stator is
greater of speed wm with which wheel the rotor. The sliding of it
characterizes the difference percentage ![]() in particular is worth 0 in the motor sincrono while it is worth 1 in
the case that the motor is firm.
in particular is worth 0 in the motor sincrono while it is worth 1 in
the case that the motor is firm.
50) Calcolo of the rendering of the induction motor:
Since the rotor is not excited, it can be seen like a simple resistivo cargo, and therefore the induction motor can is considered like a circuit with 2 inductances coupled in which the head physician who characterizes the stator is sluice on an alternated generator while the secondary one that identifies the rotor, is closed on one resistance.
Active power in the stator ![]() in how much the first term within parenthesis is imaginary pure while
of according to term we consider
in how much the first term within parenthesis is imaginary pure while
of according to term we consider ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Active power in rotore ![]() the .
Moreover from the budget of the currents it is had that the
mechanical power is equal to the power distributed from the stator
less the power dissipated from the rotor
the .
Moreover from the budget of the currents it is had that the
mechanical power is equal to the power distributed from the stator
less the power dissipated from the rotor ![]() and therefore the rendering is
and therefore the rendering is ![]() smaller
therefore is the greater sliding is the mechanical power.
smaller
therefore is the greater sliding is the mechanical power.
51) Induction motor monophase:
Online of principle it is an induction motor trifase in which one of is made of the stator is detached, this determines that the produced field is not rotary but alternative and lies in the direction of the bisettrice to the plan of two hypothetical coils of stator, however this field can be interpreted like the ruotanti sum of two lives B in opposite back, well if the motor is initially firm they elidono mutual, but if the motor is initially in motion then the two braces are various in how much are various the sliding regarding the rotor.
