Transistors effect field
1) Comparison between FET and BJT:
Advantages
to) income stiffness many elevated ( @ 1010W )
b) reduced dimensions
c) immunity to the noise
d) it is to unipolare
Disadvantages
the Banda*Guadagno product is inferior therefore in vhf is preferibile a BJT.
2) Principle of operation of the FET:
A bar of drugged semiconductor is had n, if on the gate ones constituted from a drugged semiconductor p a lot intensely, applies a negative tension, it is had that the splice pn is polarized inversely and therefore an emptying region will be had that, being the channel less drug addict, will extend mostly in it determining an impediment to the current flow, if we fix VGS and we apply one tension VDS we have that it varies linearly from the maximum value that it has on the source to the minimal value that it has on the drain. In a point whichever we will have that the tension is the sum of the two tensions, if this turning out is such to inversely polarize in intense way the splice pn, has the choking and therefore current does not slide somethe D but this verification never in how much ifD = 0 then not has fallen of does not upgrade them to the inside of the channel and therefore us cannot be the choking or ifthe D¹0 must be had that in the point in which the channel the current density has been interrupted it must go to infinite but that is not realistic.
3) Characteristic of escape for the configuration to source common:
The GS expresses the D in function ofV the DS having like parameterV, distinguishes the three following regions:
Ohmmica Region
It is the zone for which Vthe
DS is smaller of Vthe P that theoretically cancels the width of the channel, this
last one can be considered to constant amplitude 2b(VGS) employee therefore from Vthe applied GS, the FET behaves
therefore like one conductance controlled from Vthe
GS of  value.
value.
Region of constant current or saturation
When Vthe DS catches up VP , the
width of the channel becomes minim and of D value close to the source, to growing of Vthe
DS the amplitude of the channel stretches to being
constant along the same one as also the currentthe
D that slides in it, the characteristic is therefore
horizontal and to growing of inverse polarization VGS the pinch-off manifest already for Vinferior DS and therefore
one smaller is hadthe D .
The expression of the current in this region is  wherethe DSS are
the value of the ID for VGS = 0, from it it can be noticed that
the fet interdice when GS =V P is placedV .
wherethe DSS are
the value of the ID for VGS = 0, from it it can be noticed that
the fet interdice when GS =V P is placedV .
Region of breakdown
To growing of Vthe DS beyond the zone to constant current, verification the effect avalanche and has an abrupt increase ofthe D to almost constant tension, naturally to growing of inverse polarization VGS the breakdown catches up for Vinferior DS in how much the two causes is added.
4) Polarization of the FET:
FET to channel ânâ?
The circuit for the automatic polarization is constituted from the resistances RD (connected to VDD), RS (connected to mass) and RG mails between gate and mass sincethe G 0 "andthe S coincide withthe D has VGS = - IDRS that is a straight one of polarization that in the plan of the transcaratteristica passes for the origin, however because of the elevated dispersion of the parameters of the FET often it comes supplied one transcaratteristica relative to the tension of pinch off minimal and a relative one to the maximum tension of pinch off and to the aim reducing the variations ofthe D comes place a generator VGG in series to the resistance RG , however using a resistivo partitore R1 , R2 can be made less than this second generatore.
FET to enrichment
In this case it is necessary Va positive GS therefore becomes part a RG between drain and gate, in the which case GS =VDS howeverif operating conditions demand V GS ¹V DS can be connected a gate resistance R 1between and source, in both is had V the cases the FET thermally turns out stabilized however for Miller effect, lowers the resistance of income.
5) Model of the FET for small marks them:
The D turns out to be
function is of Vthe GS that of
Vthe DS therefore considering
one development in series of Taylor arrested to 1° the order has  from which the model of the FET for small can be
gained marks them in vlf constituted from one resistance rd mail between drain and source and in
parallel to a generator of current of value gmVGS.
The model in vhf is obtained from the previous one adding an
ability between every brace of clips of the FET, in particular Cgs and Cgd are relative to the splices and are comprised
between 1pF and 10pF while Cgd is the ability to the channel and is comprised between
100nF and 1pF.
from which the model of the FET for small can be
gained marks them in vlf constituted from one resistance rd mail between drain and source and in
parallel to a generator of current of value gmVGS.
The model in vhf is obtained from the previous one adding an
ability between every brace of clips of the FET, in particular Cgs and Cgd are relative to the splices and are comprised
between 1pF and 10pF while Cgd is the ability to the channel and is comprised between
100nF and 1pF.
Remembering the conventions in order to pass from a
generator of real current to a generator of real tension the
equivalent circuit can be obtained series for small marks them which
therefore it is constituted from a generator of tension having less
towards the drain and of value ![]() place in
series to one resistance of value rd .
place in
series to one resistance of value rd .
6) Transconduttanza:
 being
being

it is worth approximately 20mA for every volt of variation of Vthe GS .
7) Factor of amplification m :

it is obtained simply placing ![]()
8) Amplifier to generalized FET:
On the gate ones a generator v i is had , on drain a resistance Rd a generator vto and comes captured the escape vo1 finally on the source has a resistance RS a generator vs and comes captured escape vo2 . From this configuration disattivando the opportune generators, eliminating the opportune resistances and replacing the circuit equivalent of the FET for small mark them obtain the answers for the possible configurations. It is observed that being to us between gate and the channel a splice polarized inversely in the case of the FET or an oxide in the case of the MOSFET, a resistance is had in any case much high one and therefore it is useless to put them in series the inner resistance of generator v that is usually much lowland.
9) Configuration to source common:
The source is had to mass and it marks them of income on
the gate ones, marks them of escape comes captured on the drain, the
amplification in tension and the Rout series for small are obtained replacing to the FET the
equivalent circuit mark them, have ![]() e
e
![]() .
.
10) Configuration to gate common:
One has the gate ones to mass and it marks them of
income applied on the source while escape v01 comes captured on the drain, for the calculation
of Tov is necessary to
replace in the outline the equivalent circuit series of the FET and to
use the relation ![]() from which multiplying for m
from which multiplying for m ![]() is obtained therefore the tension generator can be replaced from a
generator of tension of value mVs with in
series one resistance of value mRs , unificando
the generators of tension and the resistance obtains
is obtained therefore the tension generator can be replaced from a
generator of tension of value mVs with in
series one resistance of value mRs , unificando
the generators of tension and the resistance obtains ![]() , finally dividend all the terms for
, finally dividend all the terms for ![]() obtains the value of the resistance of income
obtains the value of the resistance of income 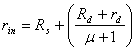 . It is observed that the gate ones do not absorb
current and therefore the current of income on the source is equal to
the escape current on drain qundi us does not interest the gain in
current.
. It is observed that the gate ones do not absorb
current and therefore the current of income on the source is equal to
the escape current on drain qundi us does not interest the gain in
current.
11) Configuration to drain common:
The drain is had connected directly to the feeding without
the resistance, marks them of income on the gate ones and it marks
them of captured escapeV 02
on the source, replacing the circuit equivalent for small it
marks them and reasoning therefore as for the configuration to gate
common ![]() and
and ![]() is
obtained. It is observed that being null the income current has
is
obtained. It is observed that being null the income current has ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
12) Split loaded amplifier:
It is had marks them of income on the gate ones and the escape comes taken is on the drain that on the source, if the two resistances are equal the two mark them that they are captured are equal in module but in opposition of phase, however the resistance of escape on the source are low while the resistance of escape on the drain is high therefore both the escapes must be continuations from a common collector that it acts as from buffer. The analysis is carried out gaining Tov and Rout is in the case the escape is taken on the drain that in the case it is taken on the source.
13) VVR:
Acronym of Voltage Variable Resistor, draft of a FET in the linear region, of which the resistance can be varied changing the tension applied on the gate ones.
14) Circuit AGC:
A transistor npn automatically polarized by means of R is
had1 and R2 , the income is applied on the base
through a block condenser while the escape is captured on the
collector, bufferizzata therefore rectified and filtered so as to to
obtain one tension that acting on the gate ones of a FET the
conductance varies some  .
.
Remembering that the amplification of tension ToV of a common emettitore with resistance
on the emettitore is ![]()
![]() is had that turns out function of the escape tension and therefore an
automatic control of the gain is had that comes used to the aim of
having a level of constant escape also in presence of a variable level
of marks them of income.
is had that turns out function of the escape tension and therefore an
automatic control of the gain is had that comes used to the aim of
having a level of constant escape also in presence of a variable level
of marks them of income.
MOSFET
15) Principle of operation of the MOSFET:
The typology of MOSFET are following:
MOSFET to enrichment
A type substrate is had n- in which they are drowns drugged traps to you pconnected to the clips
of the drain and the source, between the clip of gate and the
substrate it is present an oxide layer that in short an ability
determines, applying a negative tension on the gate ones, it is had
that on the other slab of the condenser, that one that coincides with
the substrate, will come recalls you from the same substrate of the
positive bearers you, whose number increases growing of the negative
tension applied to the gate ones, after all therefore creates a
channel that combines the drain and the source in which the bearers
are the gaps this channel comes called "reversal zone".
It is had that if ![]() is in ohmmica zone
for whichthe D it increases
growing of Vthe DS while if
is in ohmmica zone
for whichthe D it increases
growing of Vthe DS while if ![]() the channel shape and in the device does not
slide one current
the channel shape and in the device does not
slide one current ![]() . The MOSFET to enrichment
to channel "p" is slower and introduces a greater resistance regarding
the channel "n" in how much in the oxide layer is present of Ionian
positive furnitures you, than in the type to channel "n" they are
rejected towards the substrate altering some the answer allorchè
polarizes the gate ones with a positive tension in order to create the
channel while in the type to channel "p" in order to create the
channel it is demanded on gate a negative tension that attracts Ionian
positive furnitures you to the metal where they do not introduce
deleterious effects.
. The MOSFET to enrichment
to channel "p" is slower and introduces a greater resistance regarding
the channel "n" in how much in the oxide layer is present of Ionian
positive furnitures you, than in the type to channel "n" they are
rejected towards the substrate altering some the answer allorchè
polarizes the gate ones with a positive tension in order to create the
channel while in the type to channel "p" in order to create the
channel it is demanded on gate a negative tension that attracts Ionian
positive furnitures you to the metal where they do not introduce
deleterious effects.
MOSFET to emptying
A substrate of type is had p in which they are drowns drugged traps to you nconnected to the clips of the drain and the source, these are connect to you through a type channel n, between the clip of gate and the substrate is present an oxide layer that in short determines an ability, applying a null tension on the gate ones, is had that in the channel current in function of V the applied DS canslide regularly, applying instead on gate a negative tension, is had that on the other slab of the condenser, that one that coincides with the channel, will come recalls you of the positive bearers you minority which they reduce the conductance of the channel, naturally also applying a positive tension other electrons in the channel are recalled and therefore the MOSFET works to enrichment.
The value of the tension V T can be reduced optimizing the following interfacciamento, dissipation, feeding and speeds in ways:
to) instead using a crystal of Silicon with guideline < 100> that < 111 >
b) to add to SiO2 of SiN4 so as to to double the dielectric constant
c) instead of the electrode of gate metallic to use drugged silicon with boron.
16) Invester a MOSFET:
In the simpler version a MOSFET is had piloted on the gate ones fed through a resistance on the drain and with the source to mass, in the digital circuits them but the resistance it must be replaced from a MOSFET, have following the possible outlines:
Invester to MOSFET with saturated cargo
Cortocircuitando gate and drain of the FET of cargo cargo the its straight one is the parabola that joins i points VGS = VDS , if the ribaltiamo, trasliamo and we bring back on the characteristic of escape of the pilot, it of it becomes the straight one of cargo, from this representation can itself be extracted the transfer characteristic that it evidences as the escape tension is inferior regarding the tension of feeding of an equal amount to Vthe THRESHOLD of fet of cargo moreover the tension of escape is not null in presence of the maximum tension of income but it is worth VON, such tension he can himself be reduced using a cargo transistor the much smallest one regarding the pilot, in any case per² the swing of the escape tension is reduced regarding the swing of the income tension, in order to resolve the problem use the following solutions circuita them:
Invester to MOSFET with cargo not saturated
Through a battery the MOSFET of cargo is polarized so as to to make it to work in the ohmmica region, the straight one of cargo is therefore to delineate and concurs of having for the escape tension a swing maximum, the defect of this configuration is to demand a second battery.
Invester MOSFET enhancement with cargo of Depletion type
Using as loaded a MOSFET depletion can be avoided I use it of 2ª the battery in how much the channel is formed and therefore conduction also for V GS=0 is had if the pilot is of type enhancement and is the much largest one of the mosfet of cargo obtains one swing maximum of the escape tension. The defect of this configuration is that it is complicated to realize very near a MOSFET depletion and a enhancement.
