Oscillating stabilities and
1) Effect of the feedback on the bandwidth:
The negative feedback is in a position to widening the
bandwidth, for the simple reason that reduces the gain of the
amplifier, must but to make attention the fact that only comes widened
the band regarding the parameter for which is planned the amplifier
that is the tension, the current, the transresistenza or the
transconduttanza, while the relative band to the other parameters
remains unchanged. The new frequencies of cut wfl and wfH can be deducted replacing respective 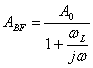 and
and 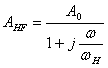 in
in ![]() the obtains
the obtains ![]() e
e ![]() . It is observed that in analogous way the positive
feedback increases the gain and tightens the band.
. It is observed that in analogous way the positive
feedback increases the gain and tightens the band.
2) unstable System :
Draft of a system that, excited from marks them to step, gives an answer that grows indefinitely.
3) Criterion of Nyquist:
In the hypothesis that the gain to chain opened Tob does not have poles in the skillful semiplan, the correspondent arranges to chain sluice is stable if the diagram of Tob does not enclose the point critico -1 j0.
4) Margin of gain:
It is the value in dB of |Tob| calculated to the frequency to cui Tob = 180°.
5) Margin of phase:
It is the calculated complement to 180° diTo b to the frequency to which the module it is worth 0dB.
6) Classification of the amplifiers:
to) Sinusoidali
b) To rilassamento (…in how much they use of the time constants)
7) Criterion of Barkhausen:
The two braces must be satisfied following equivalents of relations:
to) Im[Ab(w0)]=0 Re[Ab(w0)]=1
b) [ Tob(w0) ] = 0 |Tob(w0)| = 1
in short in order to maintain an oscillation it is necessary that the total phase-difference along the ring is zero and that the ring gain is equal to 1 while in order to establish the oscillation it is initially necessary to have Tob >> 1, will be the linearity or a automatic gain control not to guarantee that to regimen the conditions of Barkhausen are respected.
8) Number of members reatti to you necessary in order to have an oscillator:
A single reactive element introduces a phase-difference between 0 and 90° therefore, since for the criterion of Barkhausen the total phase-difference along the ring must be zero turns out necessary at least two various or equal elements reatti to you to pact to connect them in series and an other in parallel so that the phase-difference introduced from an element is equal and opposite to the phase-difference introduced from the other element.
9) bridge Oscillator average of Wien:
It uses an amplifier not inverting with one series RC between income and escape and a parallel RC between income and mass,
the expression of the tension to the inverting
clip is not 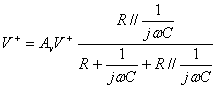 from which numerating dividend and
denominator for
from which numerating dividend and
denominator for ![]() and equaling i coefficients of
vi obtains
and equaling i coefficients of
vi obtains 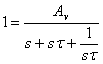 from which in order satisfying
from which in order satisfying ![]() it is necessary that
it is necessary that ![]() and to such pulsation has
Re[Av]=3 therefore for
possession |Tob|= 1 must be b= 1/3.
and to such pulsation has
Re[Av]=3 therefore for
possession |Tob|= 1 must be b= 1/3.
10) bridge Oscillator of Wien:
The circuit is the same one of the bridge oscillator
average of Wien unless comes used an amplifier differentiates them
with one negative feedback through a partitore R1 , R2 . The expression of the tension to the inverting clip
is not 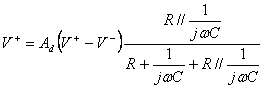 embezzling to it the tension to the
inverting clip
embezzling to it the tension to the
inverting clip ![]() gains an expression from which
cancelling the imaginary part it has
gains an expression from which
cancelling the imaginary part it has ![]() and
and ![]() therefore in order to respect the condition of
Barkhausen is sufficient that it is R1= 2R2 . More
in a generalized manner Tod it can assume whichever value comprised between 1/3 and ¥ in fact varying the
relationship of the resistances that determines the negative feedback
always succeeds to verify the conditions of Barkhausen.
therefore in order to respect the condition of
Barkhausen is sufficient that it is R1= 2R2 . More
in a generalized manner Tod it can assume whichever value comprised between 1/3 and ¥ in fact varying the
relationship of the resistances that determines the negative feedback
always succeeds to verify the conditions of Barkhausen.
11) Oscillator to phase-difference:
It is constituted from an inverting amplifier which sfasa
of 180° therefore in order respecting the condition of second
Barkhausen which the phase-difference along the ring of an oscillator
must be 0° is necessary to insert of the nets that sfasino of 180°.
It is opted for of nets RC in at least expensive and with
elevated Q more regarding the RL, ciascuna of they sfasa between 0 and
90° however the advanced end 90° can not be caught up for the presence
of parasitic resistances and then it is necessary to insert 3 nets RC
instead that two. The expression of the v is writteni , using Thevenin 3 times therefore
uguagliando to 1° and 2° member the coefficients of the same one 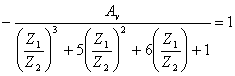 is obtained from which being
is obtained from which being ![]() and
and ![]() or viceversa, it is observed that the
condition of Barkhausen on makes is rispettata if the sum of the
powers to dispare is zero that is if
or viceversa, it is observed that the
condition of Barkhausen on makes is rispettata if the sum of the
powers to dispare is zero that is if 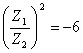 from
which
from
which ![]() is obtained if the condenser is in
series to the escape therefore the feedback is alone in alternated
while a pulsation higher
is obtained if the condenser is in
series to the escape therefore the feedback is alone in alternated
while a pulsation higher ![]() in the case is
obtained the condenser is in derivation and therefore the feedback
goes planned also in alternated. In both the cases for w=w0 obtain Tov= 29 that it renders the oscillator much critic
and difficult to realize above all in the case in which the
resistances they are in series and therefore they influence on the
polarization of the amplifier.
in the case is
obtained the condenser is in derivation and therefore the feedback
goes planned also in alternated. In both the cases for w=w0 obtain Tov= 29 that it renders the oscillator much critic
and difficult to realize above all in the case in which the
resistances they are in series and therefore they influence on the
polarization of the amplifier.
12) Oscillator to 3 points:
Stiffness Z 1 from the income towards the
common one, onestiffness Z
2 from the escape towards common and oneis constituted from an amplifier of
transconduttanza inverting with one stiffness Z3 between the income and the escape. The
expression of tension V to the income of the amplifier is ![]() from which uguagliando i coefficients of v
from which uguagliando i coefficients of v ![]() is obtained that it is not verified if all and the 3
stiffnesses are pure imaginary in how much would have the equality
between an imaginary number and a real number, in particular or Z1 or Z2 must possess a real part. In the case that Z1= R1//jX1 replacing in the previous one finds for makes the condition
is obtained that it is not verified if all and the 3
stiffnesses are pure imaginary in how much would have the equality
between an imaginary number and a real number, in particular or Z1 or Z2 must possess a real part. In the case that Z1= R1//jX1 replacing in the previous one finds for makes the condition ![]() and
and ![]() , analogous in the
case that 2Z = R2//jX2 with the same considerations is reached the conditions
, analogous in the
case that 2Z = R2//jX2 with the same considerations is reached the conditions ![]() e
e ![]() is observed
that in duale way an oscillator to 3 points also by means of a
transresistenza amplifier can be realized with 3 admittances that go
towards the common one. Having to be null the sum of the
reattanze one is had that two elements must be condensers and
inductance or viceversa.
is observed
that in duale way an oscillator to 3 points also by means of a
transresistenza amplifier can be realized with 3 admittances that go
towards the common one. Having to be null the sum of the
reattanze one is had that two elements must be condensers and
inductance or viceversa.
13) Colpitts Oscillator:
It is an oscillator to 3 points with two condensers and an
inductance while the amplifier element is a FET, from the condition on
fasi ![]() the obtains the pulsation of
the obtains the pulsation of ![]() resonance where
resonance where ![]() while replacing the
circuit equivalent of the FET it finds that a resistance in 2
parallel to X is had and
therefore making reference to the formulas found for the oscillator to
3 aims the condition at the
while replacing the
circuit equivalent of the FET it finds that a resistance in 2
parallel to X is had and
therefore making reference to the formulas found for the oscillator to
3 aims the condition at the ![]() modules writes
modules writes ![]() therefore is had that varying L the condition
can be changed to the resonance pulsation leaving unchanged on the
modules. This outline comes preferred to the Hartley in the
oscillating ones to fixed frequency in how much is present a single
inductance that is an element that very increases the imprecisione of
the analysis since it introduces many you adorned to you.
therefore is had that varying L the condition
can be changed to the resonance pulsation leaving unchanged on the
modules. This outline comes preferred to the Hartley in the
oscillating ones to fixed frequency in how much is present a single
inductance that is an element that very increases the imprecisione of
the analysis since it introduces many you adorned to you.
14) Hartley Oscillator:
It is an oscillator to 3 points with two condensers and an
inductance while the amplifier element is a BJT of which the model to
p is replaced - hybrid
in which they are neglected rbb' , rb' c , rce , from the condition on fasi ![]() the obtains the pulsation of
the obtains the pulsation of ![]() resonance where L = L1 L2 is observed
moreover that
resonance where L = L1 L2 is observed
moreover that ![]() is had therefore making
reference to the formulas for the oscillator to 3 aims the condition
at the modules
is had therefore making
reference to the formulas for the oscillator to 3 aims the condition
at the modules ![]() is written
is written ![]() therefore varying C can be changed to the resonance pulsation leaving
unchanged the condition on the modules and since the variable
condensers are preciser regarding the variable inducers, the Hartley
oscillator is from preferring to the Colpitts in the realization of
oscillating to variable frequency.
therefore varying C can be changed to the resonance pulsation leaving
unchanged the condition on the modules and since the variable
condensers are preciser regarding the variable inducers, the Hartley
oscillator is from preferring to the Colpitts in the realization of
oscillating to variable frequency.
15) Realization alternative of an oscillator to 3 points:
A BJT polarized through R 1 is used and R2 and stabilized thermally through Rand and Cand , the collector is connected to VCC through the head physician of a transformer having in parallel one condenser C that turns out determining in the selection of the oscillation frequency, remembering that the escape taken on the collector sfasata of 180° and that the condition of Barckausen on is made previews that the phase-difference total is of 360°, secondary of the transformer the place between base and mass has the windings is inverted regarding the head physician moreover is a condenser in series that in continuous it separates the base from mass, is observed that the resonant circuit place on the collector to the resonance frequency sfasa in how much behaves like one resistance. One obtains that the resonance frequency is function beyond that of real the elements reatti to you and adorned to you, also of the cargo RL therefore it is necessary to put in front a buffer.
16) Characteristics of the quartz:
Subordinate to an electric field, it becomes deformed
itself while if he comes applied a mechanical deformation to it, he
generates to its heads an electric field. Its equivalent circuit
previews the series of an inductance associated to the mass, an
ability associated to the elastic constant and a resistance associated
to the frictions of the crystal, the all in parallel to an ability due
to the fact that the quartz is frapposto between two metallic slabs.
It is characterized is from a resonance frequency series ![]() that give to a resonance frequency
that give to a resonance frequency 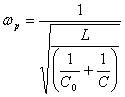 parallel, is had that wp>ws in how much the ability in parallel is
much greater one of the ability in series. The course of the
reattanza in function of the frequency extension that it negative
therefore capacitiva for w is
comprised between 0 and ws , is positive between ws and wp in correspondence
of which it becomes infinite (…therefore they can realize
large inductances varying little the frequency) finally for w>wp the reattanza is of new capacitiva.
parallel, is had that wp>ws in how much the ability in parallel is
much greater one of the ability in series. The course of the
reattanza in function of the frequency extension that it negative
therefore capacitiva for w is
comprised between 0 and ws , is positive between ws and wp in correspondence
of which it becomes infinite (…therefore they can realize
large inductances varying little the frequency) finally for w>wp the reattanza is of new capacitiva.
17) Factor of sensibility of an oscillator:
If in an oscillating circuit one of the members alters, a
frequency variation is had due to the fact that the phase-difference
of the ring is not more zero tuttavia if in the circuit is present a
having element a high Q, is had that also the factor of ![]() sensibility is the much elevated therefore phase-difference
comes compensated varying the frequency of least. In particular
for an oscillator to 3 points it is
sensibility is the much elevated therefore phase-difference
comes compensated varying the frequency of least. In particular
for an oscillator to 3 points it is ![]() therefore
realizing a Colpitts with a quartz in place of the inductance obtains
an optimal oscillator (PIERCE) for frequencies comprised between the
frequency of resonance series and the frequency of resonance parallel.
The problem is that the stability is increased but the circuit
has become much critic therefore or oscillates to a precise frequency
or does not oscillate at all.
therefore
realizing a Colpitts with a quartz in place of the inductance obtains
an optimal oscillator (PIERCE) for frequencies comprised between the
frequency of resonance series and the frequency of resonance parallel.
The problem is that the stability is increased but the circuit
has become much critic therefore or oscillates to a precise frequency
or does not oscillate at all.
18) Realization of an oscillation not distorted:
So that the oscillation is primed is necessary that it is Tob> 1 that involves that the amplitude grows sin when is limited from not the linearity of the devices active you, otherwise can be acted dynamically on To or on b so as to to have the ring gain |Tob|= 1 once that the oscillation has been established.
Automatic control of b
With reference to the bridge oscillator of Wien the resistance relative R 2 to the negative feedback with a FET can be replaced whose resistance between drain and source is function of the negative tension on the gate ones that it is obtained straightening the negative semiwave through a diode valve and a condenser and attenuating it so as to to render the present tensions in escape with V the GSof the FET that must be comprised between 0 and the tension of Pinch-Off compatible that is worth approximately â?"2V.
Automatic control of To
A Colpitts realized with a BJT stabilized through C is had thermallyand and Rand while the oscillating circuit is placed on the collector where also is fed to VCC through an inductance of Choke much large one which leaves to only pass the continuous one but dynamically it is behaved as a circuit opened in analogous way comes place one condenser C3 much large between resonant the circuit and base of the BJT in order to avoid that dynamically it finds itself to mass. On the collector it comes captured marks them from a buffer on whose emettitore has a condenser that blocks the continuous one and a diode valve that ago to pass only the negative semiwave that is gone to embezzle to the present tension on an initially loaded condenser to the tension it sets up from a zener through a resistance, the tension on the condenser is captured through a variable resistance and goes to vary the polarization of the BJT that initially introduced the b maximum and that therefore with growing of the amplitude of the oscillations it must diminish until to that |Tob| = 1.
Graphical analysis of not linear circuits
19) dynamic Effect of condenser and inducer in presence of a jump of tension:
The condenser stretches to being a short circuit, while the inducer an open circuit.
20) Analizzare the circuit constituted from the series of one inductance and a diode valve with in parallel one R resistance:
The point of job of the diode valve is initially
in the origin, a tension impulse, tramuta immediately in one current
in how much the inductance does not produce an equal tension and
opposite, the job point therefore remains in the origin but once that
the transitory ones are get exaustedded it moves stretching to the
intersection between the straight one of cargo and the segment that
corresponds to the dynamics resistance of the diode valve which is in
conduction. Applying to hour a negative tension it is had that
the inductance does not leave to immediately pass to the permane
current therefore the diode valve in conduction and the job point
stretches to the intersection of the straight cargo new with the
extension of the branch of the linearizzata characteristic of the
diode valve, joints in the origin this interdice and the point of job
is stretched to the intersection between straight of cargo and the R
branch of the linearizzata
characteristic of the diode valve. The
course of the tension to the heads of the diode valve obtains for via
diagram ribaltando the characteristic of the diode valve on which it
has been overlapped the job cycle and connecting with the esponenziali
the topical moments of it marks them of income, in particular when the
diode valve leads the time constant is ![]() while when is interdetto it is
while when is interdetto it is ![]() that is
smaller of the previous one and therefore the exponential will more
fastly arrive to the value limit.
that is
smaller of the previous one and therefore the exponential will more
fastly arrive to the value limit.
21) Analizzare the circuit constituted from a transistor having on the collector a relay with in parallel a diode valve:
Initially the transistor is interdetto like also the diode
valve therefore the job point is to the straight intersection between
of forebody andb =bl when the current on the base of the
BJT becomesthe bk the point of
job stretches to the straight intersection between of forebody andb=bk but the ago muovendosi ones instantaneously along
the straight one of dynamic load that since to the jump the inductance
is behaved like a opened circuit, coincides with the inverse
characteristic of the diode valve opportunely ribaltata and traslata.
To this point the inductance begins to make to pass current that
on the characteristicb =the bk it corresponds to an
increase of Vthe CE and the
time constant is initially ![]() while when is
exited from the saturation becomes
while when is
exited from the saturation becomes 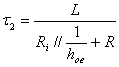 and with it
the job point stretches to the intersection betweenb =bk and the straight one of forebody, point that will catch up
sufficiently after a time along. When it marks them of income
passes to the low state, the job point stretches to the intersection
between the straight one of forebody andb =the bL ago
initially moving itself along the straight one of dynamic load that
once again coincides with the inverse characteristic of the diode
valve opportunely ribaltata and traslata, instantaneously along it it
reaches in VCE = VCC and to this point the diode valve
begins to lead and the straight one of dynamic load becomes the
characteristic direct of the diode valve therefore the time constant
is
and with it
the job point stretches to the intersection betweenb =bk and the straight one of forebody, point that will catch up
sufficiently after a time along. When it marks them of income
passes to the low state, the job point stretches to the intersection
between the straight one of forebody andb =the bL ago
initially moving itself along the straight one of dynamic load that
once again coincides with the inverse characteristic of the diode
valve opportunely ribaltata and traslata, instantaneously along it it
reaches in VCE = VCC and to this point the diode valve
begins to lead and the straight one of dynamic load becomes the
characteristic direct of the diode valve therefore the time constant
is 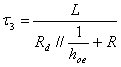 with which it catches up tension VCE= VCC for which the interdice diode valve newly and is reached
the job point with constant
with which it catches up tension VCE= VCC for which the interdice diode valve newly and is reached
the job point with constant 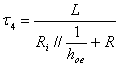
22) Diode valve of "Free-wheeling":
It is a diode valve that is placed in parallel to a relais to the aim to avoid that the strong present overstrains in the inductance to the action of the commutation introduce the heads of the transistor facendogli to catch up the zone of breakdown with consequent breach.
23) Analizzare the circuit constituted from a transistor having on the collector a condenser and a diode valve towards mass:
Initially the job point is in the intersection between the
straight one of forebody andb =the bL , to the positive jump of
tension in income a tension jump is had negative on the collector, the
condenser is behaved initially as short circuito therefore a
interdice diode valve therefore the job point is moved instantaneously
onb=the bK following straight of dynamic load with R slopethe //r in order then to move itself alongb=the bK stretching to the point of intersection of the same one
with the straight one of cargo, the time constant is 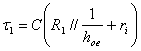 . To the tension jump negative in income a positive
jump of tension is had on the collector, the condenser is behaved as a
short circuit therefore the diode valve conduce cos¬ the job point
is moved instantaneously onb =the bL following the straight
one of dynamic load with slope R1//rd in order then
to move itself alongb =bL the stretching to the point of
intersection of the same one with the straight one of cargo, the time
constant is
. To the tension jump negative in income a positive
jump of tension is had on the collector, the condenser is behaved as a
short circuit therefore the diode valve conduce cos¬ the job point
is moved instantaneously onb =the bL following the straight
one of dynamic load with slope R1//rd in order then
to move itself alongb =bL the stretching to the point of
intersection of the same one with the straight one of cargo, the time
constant is 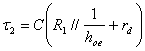 .
.
Oscillating not sinusoidali (multishakers)
24) monostable Behavior for a device to negative resistance of type n:
The diode valve Tunnel goes inserted in series to a resistance and an inductance, to varying of the R resistance and the tension of feeding, varies the straight one of cargo and the following cases can be introduced:
Intersection of the straight one of cargo with the branch to resistance R1
The equation is had differentiates them ![]() where they give a graphical point of view v' is
obtained projecting in the direction of R the generic point of the
characteristic of coordinated iD , vD . Leaving
from the origin it is observed graphically that VCC > v' therefore
where they give a graphical point of view v' is
obtained projecting in the direction of R the generic point of the
characteristic of coordinated iD , vD . Leaving
from the origin it is observed graphically that VCC > v' therefore ![]() and therefore the job point are moved finche do not
catch up the point of K equilibrium.
and therefore the job point are moved finche do not
catch up the point of K equilibrium.
Intersection of the straight one of cargo with the branch to resistance R3
Leaving from the origin the point of K equilibrium it comes caught up covering the branch R1 and then with a jump to constant current for the presence of the inducer it is moved to us on the branch R3 and therefore on the point of K equilibrium. The monostable behavior is demonstrated applying to an impulse negative of amplitude and such duration to exceed the breach point, with a jump to constant current the job point is moved on the feature to resistance R1 and from it evolve until bringing back itself on the feature to resistance R3 in the point of K equilibrium.
25) astabile Behavior for a device to negative resistance of type n:
The straight one of cargo must intersect the single branch R2 of the type tunnel n, to such aim imagines that he is almost vertical like also is in vertical the projection on the axis of the tensions of the generic point of the characteristic, reached 1° the point of breach VCC > V' therefore the current must still increase, becomes therefore a jump to constant current necessary on the branch R3 where per² VCC < V' therefore the current must diminish therefore the job point cover this branch sin when in correspondence of 2° the point of breach a jump happens to constant current that us filler on the branch R1, follows some that the circuit is behaved as an oscillator in how much the point of K equilibrium never does not come caught up.
As escape largenesses can be taken are the tension that
the current to the heads of the diode valve, the wave shapes are
obtained tracing of the parallels to the time to leave from the
estremali points of the job cycle and joining them between they by
means of esponenziali with constants of time ![]() while when is interdetto it is
while when is interdetto it is ![]() while it knows to
you that they happen to constant current they are instantaneous in the
diagram of the vd , observes
that they are possible only for the presence of an ability parasite in
parallel to the tunnel, it absorbs the effective variation of current
that would concur with the cycle of job of permanere on the
characteristic of the tunnel.
while it knows to
you that they happen to constant current they are instantaneous in the
diagram of the vd , observes
that they are possible only for the presence of an ability parasite in
parallel to the tunnel, it absorbs the effective variation of current
that would concur with the cycle of job of permanere on the
characteristic of the tunnel.
26) bistable Behavior:
It is obtained making that the straight one of cargo intersects all and three coppers of the characteristic of the Tunnel, is had that the point of equilibrium on the feature to negative resistance is unstable in how much once that goes away to us from it, the job point becomes, to second of the applied sollicitation, one of the others two points of intersection between the characteristic and the straight one of cargo. In particular if it is found to us on the point of equilibrium of the branch R1 , a positive impulse of opportune amplitude and duration us door on the point of equilibrium of the branch 3R and here an impulse negative of opportune amplitude and duration us door to the equilibrium point on the branch R1 .
27) Realization of one negative resistance of S type:
A mounted transistor to common emettitore with the base to mass through a R resistance is hadb , is had that the effect avalanche initially stretches to being like for the common base, in order then to flatten on the characteristic effect avalanche of the common emettitore in how much when it increases the current that slides in the emettitore, increases also the fall of upgrades them on the resistance of base. In order to tilt the characteristic after the ginocchio one resistance r Cis put on the collector who limits the current avoiding the breach of the transistor.
28) Realization of astabili, monostable and bistable multishakers with the negative resistance of S type :
The circuit to which reference is made previews the
negative resistance of S type with in parallel one condenser C, the
all fed from tension VCC through one R resistance. For the analysis the
equation is written differentiates them ![]() and
then it is proceeded analogous to how much fact for the negative
resistance of N type, in particular has a astabile if the job point is
found on the branch to negative resistance, has a monostable one if
the job point is found on one of two coppers to positive resistance
and finally a bistable one is had if the job point intersects all and
the three coppers of the characteristic. It is only observed
that for the presence of the condenser it knows to you happen to
constant tension, possible for the presence of parasitic inductances
in the connection threads, the sign of
and
then it is proceeded analogous to how much fact for the negative
resistance of N type, in particular has a astabile if the job point is
found on the branch to negative resistance, has a monostable one if
the job point is found on one of two coppers to positive resistance
and finally a bistable one is had if the job point intersects all and
the three coppers of the characteristic. It is only observed
that for the presence of the condenser it knows to you happen to
constant tension, possible for the presence of parasitic inductances
in the connection threads, the sign of ![]() is
considered and not di
is
considered and not di ![]() .
.
29) Conditions of oscillation for the negative resistances of type n and type s:
If the straight one of cargo is parallel to the branch of the characteristic to negative resistance (…it is of S type that of S type) has a sinusoidale oscillator, if the straight one of cargo is characterized from a resistance much high to the infinite limit if (…open circuit) becomes vertical and in the case of the devices you S has a bistable one (does not oscillate) while for the devices you N has a astabile (oscillates) therefore for knowing if a device is of type S or N enough to leave it open, if it oscillates is S otherwise is N.
Analogous if the straight one of cargo is characterized from a resistance much lowland to the null limit (short circuit) it becomes horizontal and in the case of the devices you S has a astabile (oscillates) while for the devices you N has a bistable one (does not oscillate) therefore for knowing if a device is S or N enough to close it in short circuit, if it oscillates is of S type otherwise of N type.
In short if we have a device to negative resistance Rn to whose clips a circuit to positive resistance R shows oneselfp so that permanga the oscillation must be had Rn Rp = 0 or analogous Gn Gp = 0 and also in vhf g1g2= 1. In the phase of foundation of the oscillation it must but to be Re[Ab]>1 and must be kept in mind who Rn Rp > 0 corresponds to Gn Gp < 0.
