Polarization transistor
1) Problematic relative to the determination of the job point:
The straight one of cargo in continuous determines the point of job in continuous, then to varying of marks them of income has the oscillation of marks them of escape in the escape characteristic, in all this but attention must be made that it is always remained in the active zone and that they are respects the following limits to you:
to) Current maximum it is tied to the dimension of the threads that they join reoforo and semiconductor
b) Tension massima is tied to the break-down and to the reach-through therefore it depends also on the logon
c) Power massima is tied to the adopted method of dissipation
d) VBE the maximum
in a generalized manner the job point is chosen so as to to halve the straight one of cargo in continuous, after which it is looked at which it would have to be the slope of the straight one of alternated cargo in, passing for the job point and trasla sin when the new point of job does not divide it in two equal parts. It is observed that the two straight ones have various slopes in how much in continuous consider RC and Rand while in alternated they consider RC and RL .
2) Problematic relative to the common emettitore with fixed polarization:
It is come true with a npn whose current of basethe B is obtained through one resistance RB connected to the VCC . Fixed RB determinesthe B however the job point can vary is with the temperature that replacing the transistor, in order to obviate to this disadvantage is necessary thatthe B can vary as it happens in the circuit for the automatic polarization.
3) Sources that determine the instability ofthe C :
to) the current of inverse saturationthe CO doubles every increase of 10° of the temperature
b) Vthe BE diminishes of 2,5mV/°C
c) b increases with the temperature
4) Difference between stabilization and thermal compensation:
The stabilization is come true with elements resists to you and is time to render minimums the effects of the temperature on the job point while the compensation is time to cancel such effects, has the only disadvantage that is more expensive.
5) Describe the circuit for the automatic polarization:
One places on the base a resistivo partitore and a R resistanceand on the emettitore, through it current slides one that is equal to the sum ofthe B andthe C which depends on the current of inverse saturationthe CO that varies with the temperature.
If the B increases the C diminishesthe current which pilot the amplification and therefore the C diminishes .
6) Factors of sensibility:
The C depends on the
temperature tramite b, VBE e ICO , its variation can be written ![]() in which the
in which the
![]()
![]()
![]()
One finds that these factors of sensibility come diminish if the resistance is increased to you on the emettitore, which cannot but to be much elevating in how much otherwise is necessary one feeding tension much elevating for having one current of decent intensity.
Often a condenser in parallel to the R is placedand in order to make that the stabilization only happens for the variations due to the temperature which have frequency much lowland and for the variations of it does not mark them of income, is had therefore that in presence of marks them of income, the Rand comes bypassata from condenser Cand , often in parallel to this last one that is much large one it places a smaller condenser which has the task of bypassarlo to the elevated frequencies more where the electrolytic one does not answer adequately.
7) Sensibility ofthe C to the variations ofthe CO :
With reference to the circuit to automatic polarization
the equation of the mesh of income ![]() is
written and the obtained B from the equationof the transistor is replaced in
it
is
written and the obtained B from the equationof the transistor is replaced in
it ![]() , carrying b to the numerator obtains
, carrying b to the numerator obtains ![]() , rewrites it
considering the variations ofthe CO and consequently ofthe C and placing
, rewrites it
considering the variations ofthe CO and consequently ofthe C and placing ![]() ha
ha ![]() , such factor of sensibility is considered mostly for the
transistors to the germanium.
, such factor of sensibility is considered mostly for the
transistors to the germanium.
8) Sensibility ofthe C to the variations of Vthe BE :
Writing it ![]() it is for Vthe BE1 that for Vthe BE2 that the C1 and one
determinerespective onethe C2 , considering the single terms
that varies and embezzling member to member have
it is for Vthe BE1 that for Vthe BE2 that the C1 and one
determinerespective onethe C2 , considering the single terms
that varies and embezzling member to member have 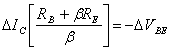 and therefore
and therefore ![]() , such factor of
sensibility is considered mostly for the transistors to the silicon.
, such factor of
sensibility is considered mostly for the transistors to the silicon.
9) Sensibility ofthe C to the variations of b :
The equation of the mesh of income ![]() is written and is replaced
is written and is replaced ![]() in it,
collecting, considering the sun variations and being
in it,
collecting, considering the sun variations and being ![]()
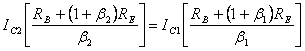 , embezzling 1 to both is had the
members obtains
, embezzling 1 to both is had the
members obtains ![]() that being b > > 1 he is negligible.
that being b > > 1 he is negligible.
10) Describe the circuit that executes the thermal compensation regardingthe CO :
A diode valve polarized between base and emettitore is
placed inversely, in it therefore the current of saturation Or
the slides that is
function of the temperature therefore likethe CO in the transistor whose current of base is
therefore IB= II0 that replaced in the equation of the
transistor ![]() and thereforethe C turns out independent from the
variations ofthe CO with the
temperature.
and thereforethe C turns out independent from the
variations ofthe CO with the
temperature.
11) Describe the circuit that executes the thermal compensation regarding VBE :
A transistor with collector and base cortocircuita to you
is placed between the base and the emettitore of the transistor to
compensate, in this way is had ![]() , that determines
that if the transistors are identical as pure the resistances on their
collectors, hasthe C1 =the C2 but of the restthe C1 can is rendered constant in fact
has
, that determines
that if the transistors are identical as pure the resistances on their
collectors, hasthe C1 =the C2 but of the restthe C1 can is rendered constant in fact
has ![]() with obvious conditions. The circuit
however works better if they are the currentsthe B of the transistors to being equal and Vthe BE therefore on the bases do not
become part the resistances 2R and 3R= R2 , in such a way if the
transistors is equal hasthe C1=the C2 and of the
restthe C1 can be deducted from
the equation to the external mesh
with obvious conditions. The circuit
however works better if they are the currentsthe B of the transistors to being equal and Vthe BE therefore on the bases do not
become part the resistances 2R and 3R= R2 , in such a way if the
transistors is equal hasthe C1=the C2 and of the
restthe C1 can be deducted from
the equation to the external mesh ![]() is had in
fact
is had in
fact 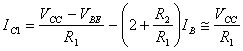 is observed moreover that
is observed moreover that ![]() therefore if
therefore if ![]()
![]() is had and therefore the transistor is polarized
to the center of the characteristic.
is had and therefore the transistor is polarized
to the center of the characteristic.
