Propagation guided in weakly disomogenei means
1) atmospheric Culvert:
If the refractive index is not monotone with the quota but it introduces a maximum for h = h0 , the beams that enter in the culvert with small angle regarding its axis, when they catch up the quota correspondent to the flexed advanced of the refractive index come bent towards the bottom while they come bent towards the high one when they catch up the quota correspondent to the flexed inferior, is had therefore that the beams remain confine to you in around of quota h0 .
2) guided Modes of propagation one structure to glide down:
Supposing of having a culvert with maximum refractive
index for h=h0 , we place to such
height z=0 that is the plan xy and assume moreover that the
cancellation propaghi only along x. Cerchiamo a solution of the
equation of the waves ![]() of the type to variable
separabili
of the type to variable
separabili ![]() , replacing
, replacing ![]() is
had and dividend for T(z)X(x) the two equations are obtained
is
had and dividend for T(z)X(x) the two equations are obtained
![]()
![]() .
.
Since the parameters of means do not vary then with x kx are independent from the
coordinates and 1ª the equation has solution ![]() while for 2ª the equation we have that the varied refractive index
with the coordinates z with parabolic course
while for 2ª the equation we have that the varied refractive index
with the coordinates z with parabolic course  therefore, inasmuch as for the separabilità condition is
therefore, inasmuch as for the separabilità condition is ![]() , the equation pu² to be rewritten
, the equation pu² to be rewritten  in which
in which ![]() and subsequently
and subsequently ![]() is replaced, collecting and becoming simpler place is
reached
is replaced, collecting and becoming simpler place is
reached 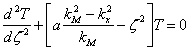 the
the ![]() che, turns
out to be the equation of Schroedinger for the unidimensionale
harmonic oscillator, for it is had gives quantistica theory that
to every autovalore
che, turns
out to be the equation of Schroedinger for the unidimensionale
harmonic oscillator, for it is had gives quantistica theory that
to every autovalore ![]() is associated a autofunction
of Gauss & Hermite
is associated a autofunction
of Gauss & Hermite ![]() (…where
(…where ![]() is the polynomial of Hermite of order m) that it is
solution of the same one. Replacing the value of
is the polynomial of Hermite of order m) that it is
solution of the same one. Replacing the value of ![]() , the solution tried for the equation of the waves is
, the solution tried for the equation of the waves is  where
where ![]() is obtained from the
definition of g that is
is obtained from the
definition of g that is 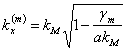 is observed in particular that if
is observed in particular that if ![]() complex roots are had that, replaced in the solution give place to
real esponenziali that therefore decay and not to complex esponenziali
which they are associated of the periodic oscillations.
complex roots are had that, replaced in the solution give place to
real esponenziali that therefore decay and not to complex esponenziali
which they are associated of the periodic oscillations.
3) Waves YOU, TM e TEM:
The solution of the equation of the waves relative to the
way of order m is ![]() , replacing it in
, replacing it in ![]() the and applying the vectorial relation
the and applying the vectorial relation ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() and finally simplifying and dividend for jwm0
and finally simplifying and dividend for jwm0 ![]() is obtained which extension that if and is
orthogonally polarized to the propagation direction (YOU) then H
possesses one member also in the propagation direction and viceversa,
such undesired behavior is cancelled if the derivative trasversa of
the member trasversa varies slowly. In the expression of H the
stiffness of wave can moreover be defined
is obtained which extension that if and is
orthogonally polarized to the propagation direction (YOU) then H
possesses one member also in the propagation direction and viceversa,
such undesired behavior is cancelled if the derivative trasversa of
the member trasversa varies slowly. In the expression of H the
stiffness of wave can moreover be defined ![]() that
characterizes the member of the carrier of Poynting in the propagation
direction, in particular for a way under cut-off has an imaginary
power that therefore propaga.
that
characterizes the member of the carrier of Poynting in the propagation
direction, in particular for a way under cut-off has an imaginary
power that therefore propaga.
4) Fiber optic to continuous variation of refractive index:
One supposes that the cylindrical fiber is characterized
from a refractive index that is maximum nM on the axis and decreases with a parabolic course until to
the minimal value nm task on the
edge, the dielectric constant has a parabolic course that is 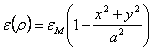 . The solution of the equation of the
. The solution of the equation of the ![]() waves is assumed of the type to variable separabili that is
waves is assumed of the type to variable separabili that is ![]() , replacing it has
, replacing it has  ,
dividend for ZT ottenegono the
,
dividend for ZT ottenegono the ![]() equations, having
like solution
equations, having
like solution ![]() and
and ![]() where
where ![]() replacing therefore
replacing therefore ![]() and the value of and obtains
and the value of and obtains 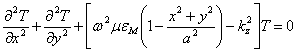 where
where ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() ottenendo
ottenendo 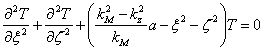 can be placed which after to have place
can be placed which after to have place ![]() necessity one factorization of
necessity one factorization of ![]() the
that it gives back
the
that it gives back ![]() the from
which extracting equazioni
the from
which extracting equazioni ![]() the e
the e ![]() ciascuna di.le which have the shape of the equation
of Schroedinger for the harmonic oscillator, to every autovalore
ciascuna di.le which have the shape of the equation
of Schroedinger for the harmonic oscillator, to every autovalore ![]() corresponds one autofunction solution of
corresponds one autofunction solution of ![]() . Multiplying for Z(z) the solution of the equation
of the waves
. Multiplying for Z(z) the solution of the equation
of the waves 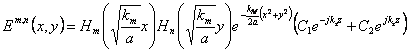 dove
dove ![]() is obtained is obtained that is from the definition of g
is obtained is obtained that is from the definition of g 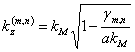 which
gives place to propagation se
which
gives place to propagation se ![]() .
.
5) Speed of phase and group velocity in one fiber optic:
For the speed of phase ha 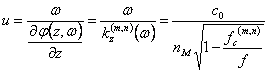 , it is
observed that if the denominator is smaller of 1, to the way (n,m) in
issue competes one speed of greater phase of c0 . For the group velocity instead
, it is
observed that if the denominator is smaller of 1, to the way (n,m) in
issue competes one speed of greater phase of c0 . For the group velocity instead
 is had that is different from the speed of
phase to confirmation that the refractive index depends on the
frequency.
is had that is different from the speed of
phase to confirmation that the refractive index depends on the
frequency.
6) Typology of dispersion in one fiber:
Modale dispersion:
The condition affinchè the means introduces dispersion is ![]() , in this case has
, in this case has ![]() therefore the means is dispersive because of the not linear dependency
of the constant of propagation from the frequency.
therefore the means is dispersive because of the not linear dependency
of the constant of propagation from the frequency.
Dispersion of the material:
It is due to the fact that the maximum refractive index that is had on the axis of the fiber, is not constant but varied with the frequency, a minimum of the dependency for l 0 =1,3 m is hadm.
Intermodal dispersion:
Everyone of which can be had that for one given operating frequency they are active more than a mode of propagation, is characterized from a various one ug that it can give place to increases of the impulses of approximately 10ns/Km. Standard of the fibers (a=30 m m , n M would have to be tried to activate a singlewaybut to the constructivevalues = 1,5) corresponds l0 = 150mm, for which one is had attenuation to the Km much high one.
7) usable Wavelengths in one fiber optic:
The attenuation is inferior to 1dB/km for wavelengths only comprised between 1,2mm and 1,7mm, in fact for greater wavelengths the scattering is had reticular while for advanced wavelengths absorption which had to the polarization of the material is had.
8) monomodali Fibers:
Fiber draft in which the refractive index introduces a discontinuity in fact it is leggermente greater in the inner cylinder (..core) that not in the cape (..cladder), in such a way is succeeded to obtain a frequency of cut of the equal dominant way to approximately 100Thz, which wavelength corresponds one subject to low attenuation.
9) Fibers that take advantage of not the dielectric linearity of the material:
They take advantage of the fact that the dielectric constant depends on the amplitude of the field and therefore it is described from an equation of not linear Schroedinger from which it is deduced that the energy remains caught in a narrow zone and concurs the transport of impulses of short duration on long distances.
