Fields in the dominion of the frequency
1) Transformed of Fourier:
![]()
2) Antitrasformata di Fourier and meant its:
![]()
that is in every point the A(r, t) is given from the superimposition of obtained harmonic vectorial fields taking the part real of carriers represented to you complex multiplies to you for andjwt .
3) polarized Carrier circularly:
It is had that |Andr| = |Andj| and the two carriers are between orthogonal they that is their product to climb are null.
4) linearly polarized Carrier:
Andr and andj they are parallels that is their vectorial product is null.
5) Rake:
It is the angle y comprised between the greater axis of the polarization ellipse and as an example the horizontal axis of the plan in which the ellipse is found.
6) Angle of ellitticità:
It is angle c comprised between the greater axis of the ellipse and the
segment that leave in the center of the ellipse and end in the
intersection of the orthogonal projections of the greater axle shaft
and the smaller axle shaft, it is worth ![]() .
.
7) analytical Carriers us:
They are carriers that are introduced in order to evidence the fact that to one sinusoide is not combinable some information and moreover it marks them that they carry information are to tight band and therefore it can be thought that the module and the anomaly are variable in the time but appreciably constant in around of a generic moment.
8) Means non-polar:
Is constituted from an aggregate of charges of opposite sign whose disposition spaces them, in electric field absence is such that the barycentre of the positive charges coincides with the barycentre of the negative charges.
9) Coefficient of damping:
![]()
where m are the mass associated to loads and s it is the relative constant to the damping force that acts on the charges of means to apolare which they are put in motion from a field and but they are hindered from hits with other particles.
10) Pulsation of resonance w0 :
![]()
where c is the relative constant to the callback force which the charges of means are subject to apolare that they move for effect of an electric field applied.
11) dielectric Constant in means non-polar with bound charges:
The expression of the dielectric constant in function of the polarization to volume unit is used in order to find which is associated a mass to loads electrical worker, and therefore a callback force is had, a viscous friction and an inertia force, writes the equation differentiates them and from it P is extracted according to w from which it is obtained and according to w. It is obtained:
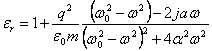
from which it is had that for frequencies many inferiors or the much advanced to the resonance frequency dielectric constant are pure real and substantially independent from the frequency, for next frequencies to the resonance pulsation is had that the real part from place before to a sovraelongazione and then to a sottoeleongazione while the imaginary part that is always negative for the average ones passes to you, gives place to the âLorenzianeâ? that is of the Gaussian bells centered on the resonance.
12) dielectric Constant in means I composed (atmosphere to you):
For the means I composed to you must be kept in mind that are possible various types of deformation of molecules in presence of an electric field and sure they change from molecule to molecule, well for these means the dielectric constant must hold account for every member of means of all the possible ways and also of the ways that are independent from the frequency, this is for the real part that for the imaginary part. The course that obtains is the same one that it was had for means I did not compose to you, repeated on for every way contraddistinto from one various frequency of resonance.
13) Polarization for guideline:
In polar means as the liquid water permanent electrical workers have themselves of dipoles which are orient to you to case, only in presence of an external electric field they orient themselves as the field.
14) Time of relaxation of a material:
![]()
where s it is the coefficient associated at the moment of the damping force that is opposed to the dipole spin i while c is the coefficient associated at the moment of the force of collision due to the thermal energy which stretches to disordinare dipoles.
15) dielectric Constant in polar means:
In order to find P it is necessary to hold account stavolta of the moments of the forces, one obtains that the dielectric constant is constituted from a which had contribution to the polarization for deformation and from a which had contribution to the polarization for guideline. One finds that the dielectric constant is almost constant to the vlves while for greater frequencies of the resonance frequency the contribution is only that one of the polarization for deformation because that one for guideline is too much fast for being continuation from molecules.
16) dielectric Constant in the conductors:
![]()
17) Conductivity in the dominion of the frequency:
In order to find the conductivity the equation is used differentiates them written for the conductors, stavolta but with incognito the speed u and not the movement l in function of the time, is obtained:
![]()
Such expression is simplified remarkablly to âbassa frequenzaâ? that is in the case in which it is had w< <to, than then is the case of the more common conductors uses you in radio frequency.
18) Relation between conductivity and dielectric constant:
It is had that the real part of the conductivity is tied to the imaginary part of the dielectric constant through the relation:
![]()
therefore it is and'' that g they describe of the phenomena dissipated to you.
19) equivalent Conductivity in means:
In the case of the materials not conductors for which
therefore the conductivity stretches to zero, can be defined one
equivalent conductivity through the imaginary part of the constant
dielettrica ![]() .
.
20) dielectric Constant in watery dielectrics:
It is the real part that the imaginary part is tied to all and the 3 ways of polarization that is deformation, guideline and movement of free charges, have the two following expressions:
![]()
![]()
famous in particular that to the vlves it prevails the effect of knows them which for higher frequencies introduces mobility much lowland, such effect is hardly visible for the real part while he is much obvious one for the imaginary part.
Watery dielectric examples are the cellular water of sea and membranes.
21) Ionosphere:
2 are found turn out different to you in function of the frequency:
to) for frequencies many lowlands the ionosphere is behaved as a conductor therefore the cancellation propaga guided between the earth and this conductor.
b) For frequencies in the range hf the ionosphere becomes a dielectric with dielectric constant varying with the altitude, that it determines the phenomenon of the diffraction that ago to have the electromagnetic field until making it to return to earth.
22) plasma Frequency:
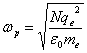
for advanced frequencies to it the ionosphere is behaved like a dielectric.
