Variable aleatory
1) Variable aleatory :
Draft of a function that it has as dominion the S entirety of turns out you of a experiment and like codominio with of the real numbers.
2) Function of cumulative distribution :
It allows to quantify the probability that variable aleatory the X assume smaller or equal values to a data value x
3) Property of the distribution function :
to) FX(-¥) = 0 FX( ¥) = 1
b) FX is one not decreasing function monotonous , that is if x1 £ x2 > FX(x1) £ FX(x2)
c) P{X>x} = 1 - FX(x)
d) the distribution function is
continuous from destra ![]()
and) P{x1 < X 2 £x } = FX(x2) - FX(x1)
f) the jump of the function of distribution in correspondence of a point of discontinuity x0 is equal to the probability that the variable one assumes value x0
4) Variable aleatory of continuous type :
One variable aleatory x say of continuous type if its function of distribution is continuous.
5) Variable aleatory of discreet type :
One variable aleatory x say of discreet type if its function of distribution is one function to steps.
6) Variable aleatory of mixed type :
One variable aleatory x say of mixed type if its function of distribution is batch processing line but not to steps.
7) Distribution empiricist :
A distribution empiricist is a function to steps having like points of the dominion the values of variable the aleatory correspondent to the outcome of the test, to everyone of they the function empiricist associates a height step 1/n.
8) Percentile :
The percentile u (or percentile n-esimo) of variable aleatory the X is that such valuex u that P{X £ xu} = u. The function percentile is therefore the inverse one of the distribution function. In other the 10 words percentile indicates the value of x for which the area that goes from -subtended ¥ to x and from the distribution function is equal to 10%.
9) Median of variable aleatory the X :
Draft of the value 0,5 percentile and has been indicated with the letter m..
10) Function probability density :
The density of probability fX(x) is defined like the derivative of the distribution
function ![]() .
.
11) Property of the probability density :
to) the density function (x) is not negativefX ³ 0
b) FX(x2) - FX(x1) = ![]()
c) FX(x) = ![]()
d) ![]()
and) P{x1 < X £ x2 } = ![]()
12) Function of mass of variable probabilities for aleatory :
Draft of the function pk = P {X = xk}.
13) Expected value :
Variable the expected value of one aleatoria X is the center of gravity of the density or the masses of probability in the cases continuous or discreet respective. In other words it is the medium value of the distribution.
14) variable Expected value of an aleatory one continues :
![]()
15) Expected value of one variable aleatory discreet :
![]()
16) Property of medium statistics :
to) E[a*X ] = a*E[X ]
b) E[a*X b*Y] = a*E[X ] b*E[Y ]
17) Variance :
The aleatory variable variance of one X expresses one measure of the âconcentrazioneâ? of the values assumed from one variable aleatory around its medium value.
![]()
18) Shunting line standard :
It is the root of the variance
![]()
19) variable Variance of an aleatory one continues:
![]()
20) Variance of one variable aleatory discreet:
![]()
21) quadratic Relation between average and variance:
![]()
22) Moment of order n of one variable aleatory X:
mn = E[Xn]
23) Moment centers them of order n of one variable aleatory X:
![]()
24) Inequality of Chebyschev:
![]()
25) Inequality of Markov:
![]()
26) Variable statistically independent :
Two variable aleatory X and Y says statistically
independent if, given 2 sets arbitrary and to B of values of X and
Y respective, it is had ![]() .
.
27) Variable aleatory uniform :
Variable an aleatory one continues X says uniform between ![]() e
e ![]() if its density is constant in the null
if its density is constant in the null ![]() interval and
elsewhere.
interval and
elsewhere.
28) Variable aleatory Gaussian :
Variable an aleatory one continues X is said Gaussian if its function of density is of the shape
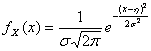
29) Variable Gaussian standard :
Null draft of one variable Gaussian with valor medium and unitary variance.
30) Function of density of one variable aleatory exponential :
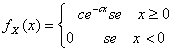
31) Function of density of one variable iperexponential :
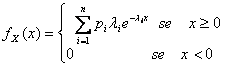
32) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed Rayleigh second :
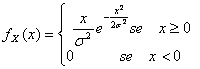
33) Function of density of one variable lognormale :
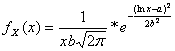
34) Function of density of one variable distributed according to the range model :
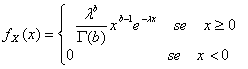
35) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the model who-picture :
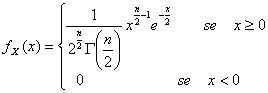
36) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the model of Erlang :

37) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed Student second :
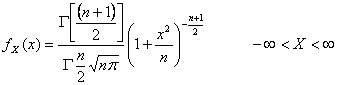
38) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the K model :
![]()
39) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the model beta :

40) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the model of Cauchy :
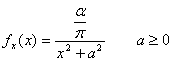
41) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the binomial model :
![]()
42) Function of density of one variable aleatory distributed according to the geometric model :
![]()
43) Variable aleatory Poissoniana :
If l it is one parameter and X one variable aleatory entire and positive.
![]()
44) Law of the great numbers :
In a series of n repeated tests, in which the
probability of succeeding of a single test is equal to p, the
relationship between the number of successes k and the number of tests
n stretches to p when n ® ¥ , ![]()
45) theorem centers them of the limit for binomial functions :
In a series of n repeated tests, indicating with X the number of successes, constructs variable the aleatory Y
![]()
The distribution of probability FY(y) is such that 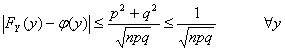
46) Function of distribution of one variable function of aleatory :
The function of distribution FY(y) supplies probability P{Y £ y}
47) fundamental Theorem of the probability density :
For a specific value y of the density fY(y) is given da 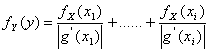
48) Expected value of one variable aleatory Y = g(X):
![]()
