Analysis of Fourier
1) Series of Fourier associated to one periodic function :
![]()
essendo ![]() e
e ![]()
such series is convergent > the periodic function integranda is limited
2) exponential Shape of the series of Fourier :
![]() con
con
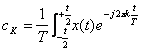
3) Theorem of Parseval :
For the energy of it marks them periodic in a T period, that is for its medium power it is worth the equality
![]()
4) Write the function envelope of the coefficients of Fourier of a pulse train :
![]()
5) Meant of the transformed one of Fourier :
It concurs to write the series of Fourier also for functions that are not periodic considering the limit for the T period that stretches to ¥ .
![]()
6) It marks them of energy :
Draft of marks them x(t) such that ![]()
7) Convoluzione and its property:
A convoluzione is the function turning out from the product of 2 functions g(t) = f(t)*h(t)
to) f(t)*h(t) = h(t)*f(t)
b) [ f(t)*h(t)]*k(t) = f(t)*[h(t)*k(t) ]
8) Property of the integral of Fourier :
to) Translation
b) Convoluzione
c) Symmetry
d) Linearity
and) Dualità
f) Scalatura
g) Coniugio
h) Derivation
i) Integration
9) characteristic Function:
The characteristic function j(w) of one variable aleatory X whose density of probability is fX(x), is defined like
![]()
alternatively like the variable expected value of aleatory andjwXthe , it assumes the its equal maximum value to 1 in the origin.
10) Function generatrix of moments of one variable aleatory X:
![]()
11) Second characteristic function of one variable aleatory X:
![]()
12) Second function generatrix of moments of one variable aleatory X:
![]()
13) Cumulante ln of one variable aleatory X:
Draft of the derivative n_esima of the second function generatrix of the moments estimated in point s = 0.
