Magnetism in the matter
1) Equations generate them of the magnetostatica in matter presence :
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
2) girometrico Factor g:
It is the relationship between the magnetic moment ![]() and the angular moment L of a whichever system.
and the angular moment L of a whichever system.
3) Principle of exclusion of Pauli :
It asserts that on every energetic level 2 electrons can be found single and provided that with spin opposite.
4) Carrier intensity of magnetic polarization M and its unit of measure :
It indicates the magnetic dipole moment ![]() to unit of volume
to unit of volume 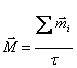 measure in A/m.
measure in A/m.
5) Density of superficial amperiana current and its unit of measure :
Every atom possesses an electron that turns around to it,
the system is assimilable to a coil and therefore for the theorem of
equivalence of Ampere it is characterized from a dipole moment, if
magnetization M is uniform inner to the material these currents is
totally neutral while on the surface of the material not. The
density of superficial amperiana current is called ![]() and measure in A/m.
and measure in A/m.
6) Density of volumica amperiana current and its unit of measure :
Every atom possesses an electron that turns around to it,
the system is assimilable to a coil and therefore for the theorem of
equivalence of Ampere it is characterized from a dipole moment, if
magnetization M is not uniform inner to the material these currents is
not totally neutral and their density of volumica amperiana current is
called ![]() and measure in A/m2 .
and measure in A/m2 .
7) fundamental Relations between magnetization M and microscopical currents :
![]()
![]()
8) Carrier magnetic field H and its unit of measure :
The magnetic field H comes introduced with the scope to
place to 2° the member of 4ª the equation of maxwell in matter
presence the sun running macrocospic and not also the amperiane
microscopical currents. It is defined ![]() and
measure in Amperes-turn/meter.
and
measure in Amperes-turn/meter.
9) fundamental Equations of electrostatics in matter presence :
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
10) Theorem of the circuitazione of relative Ampere to H :
![]()
The flow is obtained from ![]() the
calculating some and applying to 1° the member the Theorem of Stokes.
the
calculating some and applying to 1° the member the Theorem of Stokes.
11) magnetic Field inner to an infinite solenoid :
![]() being n the coil number
to length unit
being n the coil number
to length unit
12) Conditions of connection for B and H :
To the passage from means to an other conserve the normal member of B and the tangential member of H. For B enough to naturally calculate the flow on cilindretto, while for H the circuitazione must be calculated, both on distances that contain the separation surface.
13) Relation between B and H in the empty one and means :
![]()
14) magnetic Permeability m :
is one characteristic of means m =m 0mr. In the empty one m are hadr = 1.
15) Law of refraction of the lines of force of B and H :
![]() being q1 e q2 the angle forms you from
B with the normal school to the separation surface.
being q1 e q2 the angle forms you from
B with the normal school to the separation surface.
16) magnetic Suscettività :
cm = 1 - mr
Indica is parallels or antiparallels of B and H,
has in fact the ![]() relation.
relation.
17) diamagnetic Substances :
They are substances with smaller magnetic suscettività c of 1, therefore
their magnetic moment is antiparallel to H therefore ![]() is repulsiva. For diamagneti the magnetic
suscettività he is independent from the temperature.
is repulsiva. For diamagneti the magnetic
suscettività he is independent from the temperature.
18) paramagnetic Substances :
For they c ~ 1 and weakly is attracted from a magnetic field.
The magnetic suscettività is inversely proporziona them to the
temperature through the law of Curie![]() where r it is the density of material and C
one constant.
where r it is the density of material and C
one constant.
19) ferromagnetic Substances :
For they the magnetic suscettività is much greater one of 1 therefore strongly is attracted from a magnetic field, to advanced temperatures to the temperature of Curie becomes paramagnetic.
20) residual magnetic Induction :
The cycle of hysteresis of a ferromagnetic material is the value of long B when H = 0.
21) magnetic Field of coercion :
The cycle of hysteresis of a ferromagnetic material is the value of long H when B = 0.
22) Cycle of hysteresis :
It means to describe the relation not univoca and
proporziona sussiste them that between B and H in the ferromagnetic
materials. Customarily B according to H is arranged. It is
observed that in the ferromagnetic materials being ![]() the contribution of the magnetization is the much
highest one regarding the contribution of H therefore has B ~ m0 M, are therefore many frequent also diagrams of M according
to H.
the contribution of the magnetization is the much
highest one regarding the contribution of H therefore has B ~ m0 M, are therefore many frequent also diagrams of M according
to H.
23) Law of Curie - Weiss :
It is the temperature to of over of which the
ferromagnetic material is behaved second like paramagnetic with
variable suscettività the law of Curie Weiss ![]()
24) Dominions of Weiss:
They are introduced to the aim to explain the behavior of the ferromagnetic materials, in particular is supported that in they there are of the dominions spontaneously magnetizes to you, but the total magnetization of the material is null but as a result of the application of a weak person field of magnetic induction external B, these dominions are oriented consequently.
25) Precession of Larmor :
It describes the fact for which the angular moment of the electron it carries out a motion of precession around to the direction of the field localB applied. Such phenomenon is present in all the materials but it is noticeable single in the diamagneti.
26) Function of Langevin:
It expresses the medium magnetic moment of the material 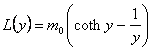
essendo ![]() 0
andm the magnetic moment of
the atom.
0
andm the magnetic moment of
the atom.
27) microscopical Interpretation of the diamagnetismo:
Every atom through the precession of Larmor orients its angular moment so as to to precede around to the field BL
28) magnetic Circuit :
Draft of a circuit constituted from ferromagnetic materials, windings of excitation and eventually from traferri.
29) Law of Hopkinson :
![]() where " it is the reluctance
where " it is the reluctance ![]() e j is the flow through one coil of the circuit. It is
obtained applying to the theorem of the circuitazione of Ampere for H
to one inner line to the magnetic circuit.
e j is the flow through one coil of the circuit. It is
obtained applying to the theorem of the circuitazione of Ampere for H
to one inner line to the magnetic circuit.
30) magnetomotrice Force :
![]() measure in AmpereSpire
measure in AmpereSpire
31) Reluctance :
![]() is the opposition that the circuit offers to
the passage of the magnetic flow. Measure in AmpereSpire/Weber
is the opposition that the circuit offers to
the passage of the magnetic flow. Measure in AmpereSpire/Weber
32) Electromagnet :
It is an equipped magnetic circuit of traferro.
33) permanent Magnets :
Draft of a material in the which permane magnetization also to continuation of the elimination of the excitation, draft customarily of ferromagnetic materials with high residual magnetization, therefore with hysteresis cycle much wide one.
