Alternating currents
1) periodic Largenesses, alternated, alternated sinusoidali :
A largeness says periodic if it assumes equal values and courses to regular intervals, is said instead alternated if it is periodic and medium its valor on a period is 0, says then alternated sinusoidale if it is of the I(t) type =0sin(wt j).
2) effective Valuethe EFF :
It is the medium quadratic value of the largeness, ![]() in the case of sinusoidali largenesses is reduced to
in the case of sinusoidali largenesses is reduced to ![]() .
.
3) Law of Galileo Ferraris :
It describes to the real medium power in a circuit ![]() being j the
phase-difference between tension and current in the circuit electrical
worker.
being j the
phase-difference between tension and current in the circuit electrical
worker.
4) Conditions of Dirichlet :
They are the conditions for the convergence of the series of Fourier, in short it is demanded that the function f(t) and its derivative are generally continuous that is admit an ended number of ended discontinuity.
5) Theorem of Fourier :
Every periodic largeness that satisfies the conditions of Dirichlet can be expressed like series of sinusoidali functions.
6) Series of Fourier :
![]()
with ![]() e
e ![]()
7) Equality of Parseval:
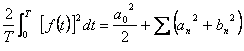
8) Identity of Euler :
![]()
![]()
![]()
9) exponential Series :
![]() with
with ![]()
10) Stiffness of the simple members :
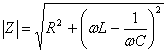
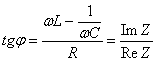
resistance has the dimensions of one and its module measure in Ohm.
11) Reattanza :
Draft of the pure imaginary part of the stiffness.
12) Fasore :
It is a carrier that wheel in the plan of Argand Gauss, with equal angular velocity to the pulsation of the alternated largeness.
13) Pulsation of resonance :
It is the pulsation to which the stiffness is pure
resistiva and a maximum of the current in the case of circuits RLC is
had therefore series and instead a minimum in the case of circuits RLC
parallel. The pulsation always is given from the relation ![]()
14) Factor of merit :
It indicates how much is tightened the bell that describes
the current that slides in a circuit RLC in function of the pulsation
of the pulsation of forcing.
![]()
being w0 the pulsation of resonance and Dw the variation of pulsation in
correspondence of which it is had ![]() .
.
15) real Power and reactive power :
On a period the reactive power has valor medium always null while the real power has value given from the law of Galileo Ferraris.
![]() is the real power and measure in Watt.
is the real power and measure in Watt.
![]() is the reactive power
and measure in Volt-ampere.
is the reactive power
and measure in Volt-ampere.
16) appearing Power :
![]() Is the power effectively measured from
the contatori.
Is the power effectively measured from
the contatori.
17) Fasatura :
The fasatura is understanding to the aim to render j = 0 in the relation of Galileo Ferraris and therefore to render the real power and the appearing power equal.
18) Coefficient of connection :
![]() in short expresses the phenomenon for which one
circulating current in a circuit produces a field of magnetic
induction B which concatena with an other circuit. are worth
in the case the winding senses are agree and - in the case they are
disagrees.
in short expresses the phenomenon for which one
circulating current in a circuit produces a field of magnetic
induction B which concatena with an other circuit. are worth
in the case the winding senses are agree and - in the case they are
disagrees.
19) Relationship of transformation:
![]()
![]()
