Theorems of Vectorial Analysis
1) First criterion of integrabilità of the 1_forme :
If w it is continuous on a connected open D of "3 then
w is esatta
>
taken to, b pertaining to D is had that ![]() with g1 , g2 ? camm(a, b).
with g1 , g2 ? camm(a, b).
For definition of integral of 1_forma has ![]() del
rest if w it is exact exists a
function upgrades them U, primitiva of w ossia F = `U
= Ux Uy Uz will be had therefore
del
rest if w it is exact exists a
function upgrades them U, primitiva of w ossia F = `U
= Ux Uy Uz will be had therefore ![]() and
therefore it looks at that the integral value della does not depend
dal covered but dal point only begins them and dal final point.
and
therefore it looks at that the integral value della does not depend
dal covered but dal point only begins them and dal final point.
?
Sappiamo that ![]() is independent from the way, but
from the point only begins them and from that end therefore it is
is independent from the way, but
from the point only begins them and from that end therefore it is ![]() = U(b)-U(a), we will try that the derivative
respect to x is equal to F1 ,
in analogous way for Uy and Uz and therefore w is exact. Are chosen
therefore to move itself of Dx through parametrizzazione x(t) = x tDx y(t) = y z(t)
= z with t?[ 0.1 ]
= U(b)-U(a), we will try that the derivative
respect to x is equal to F1 ,
in analogous way for Uy and Uz and therefore w is exact. Are chosen
therefore to move itself of Dx through parametrizzazione x(t) = x tDx y(t) = y z(t)
= z with t?[ 0.1 ] ![]() for the theorem of the
average for integrals will be had that the same value is assumed in an
intermediate point =
for the theorem of the
average for integrals will be had that the same value is assumed in an
intermediate point = ![]() , is had after all that
, is had after all that ![]() and therefore passing to the limit for Dx®0 it is had that Ux = F1.
and therefore passing to the limit for Dx®0 it is had that Ux = F1.
2) Corollario of 1° the criterion of integrabilità of the 1_forme:
If w it is continuous on a connected open D of "3 then
w support in D is exact
> for every having
circuit is had ![]()
w is exact therefore ![]() does not depend on the way but they only give to and b
therefore if we take a circuit closed and on it we characterize 2
points to and b we have che
does not depend on the way but they only give to and b
therefore if we take a circuit closed and on it we characterize 2
points to and b we have che ![]() along a side of
the circuit is equal but of opposite sign to
along a side of
the circuit is equal but of opposite sign to ![]() and therefore their sum is null.
and therefore their sum is null.
? If all the circuitazioni are null, finds that subdividing a cycle in 2 circuits g1 and g2 , the integral along g1 is equal to the integral along g2 and therefore for 1° the criterion of integrabilità of the 1_forme, w it is exact.
3) According to criterion of integrabilità of the 1_forme:
If w he is derivabile on a simply connected entirety then
w it is esatta > w is sluice
Dimostro for n = 2, analogous for n > 2.
If w it is exact then for definition a function exists upgrades them such U that Ux = F1 and Uy = 2F deriving 1ª the respect to y and 2ª the respect to x obtains F1y = F2x that is just the condition so that w it is sluice.
? the demonstration consists
essentially in the calculation of upgrades them by means of the
customary ![]() formula. It is observed
that :
formula. It is observed
that :
to) deriving U regarding z F 3(x is obtained, y, z)
b) deriving regarding y and
using che ![]() F
2(x is obtained, y, z)
F
2(x is obtained, y, z)
c) deriving regarding x and
using that ![]() and
che
and
che ![]() ottiene F1(x, y, z)
ottiene F1(x, y, z)
after all therefore F = ` U is hadche that is the definition di wexact .
4) Theorem of Gauss - Green in the plan :
to) If D is a dominion of "2 with to < x < b e j1(x) < y < j2(x) with j1(x), j2(x) regular at times, is had :
![]()
b) If D is a dominion of "2 with c < y < d e y1(x) < x < y2(x) with y1(x), y2(x) regular at times, is had :
![]()
I demonstrate to), in analogous way can be demonstrated the b).
For 1° the member taking advantage of the formula of reduction for double integrals on simple dominions respect to an axis is had :
![]()
For 2° the member instead the circuitazione is estimated observing that in the rectilinear features dx=0 and therefore also the integral :
![]()
and therefore the 2 integrals are equal less of the sign.
5) Corollario of the theorem of Gauss Green in the plan:
If D is a dominion limited in
"2 the whose frontier is a curve
of regular Jordan at times and that it is simple respect to both the
aces. If f = Pi Qj is
worth the formula ![]() .
.
One is obtained from the theorem of Gauss Green embezzling formula from the other member to member.
6) Demonstration by means of Gauss Green of 1° the criterion of integrabilità of the 1_forme:
They are g1 and g2 two delimiting curves a D. entirety If F(x, y) is a
derivabile and irrotational vectorial field (rot F = 0) that is Px = Qy in D. ![]() .
.
For the equality of the theorem of Gauss Green it is had
that ![]() = 0 being Qx = Py of the
rest the frontier of the entirety is constituted from g1 covered in
counter-clockwise sense and g2 covered in hour sense in how much
inner one to gthe 1 pertanto equality is verified.
= 0 being Qx = Py of the
rest the frontier of the entirety is constituted from g1 covered in
counter-clockwise sense and g2 covered in hour sense in how much
inner one to gthe 1 pertanto equality is verified.
7) Theorem of Stokes in the space :
If S is one
contained regular surface to pieces in an open To ? "3 and F = Devout Qj Rk a derivabile vectorial field ![]()
It is r(u, v) = x(u, v)i y(u, v)j z(u,
v)k one parametrizzazione of the surface ![]()
Leaving instead from the circuitazione
is written as the correspondent 1_forma therefore considers for
semplicità ![]() the solo,
the solo, ![]() being,writing it for extensive
and applying to the theorem of Gauss Green us filler to a double
semplificabile integral for means of the theorem on the mixed
derivatives of Schwarz
being,writing it for extensive
and applying to the theorem of Gauss Green us filler to a double
semplificabile integral for means of the theorem on the mixed
derivatives of Schwarz ![]() being itself hour
being itself hour ![]() a composed function, its derivatives is
a composed function, its derivatives is ![]() and
and ![]() replacing, developing the
products and becoming simpler
replacing, developing the
products and becoming simpler ![]() is obtained in
which the terms between parenthesis are deteminanti jacobiani.
is obtained in
which the terms between parenthesis are deteminanti jacobiani.
Operating in the same way also for the others members and adding the thesis is obtained.
8) Theorem of Ostrogradsky:
It is D ? "3 a limited dominion the whose frontier is one surface sluice, regular and adjustable one :
If D is simple respect to one of the aces it is worth one of following :
![]()
![]()
![]()
If the dominion is simple regarding all and the three aces then adding member to member are had :
![]()
I only demonstrate third in the case of a simple dominion regarding the axis z :
Leaving from the triple integral, it can be decomposed for via of the semplicità of the dominion, has itself :
![]()
Leaving hour instead from 2° the member it will be arrived
to the same result, account must in fact be held that the frontier of
the dominion is constituted from a advanced cap, an inferior cap and a
sidewall parallel to the axis z on which the integral is null in how
much ![]() is a flow and the normal carrier to the
surface is orthogonal to the carrier k.
is a flow and the normal carrier to the
surface is orthogonal to the carrier k.
Carrying out a change of parametrizzazione and observing that the advanced surface is oriented positively while that inferior is oriented negatively of it follows that the same obtained result is found leaving from the triple integral.
![]() being the jacobiani in equal issue to 1.
being the jacobiani in equal issue to 1.
9) Theorem of the divergence in the space:
It is D ?
"3 a limited dominion the whose
frontier is a surface sluice, regular and adjustable one moreover are D a simple dominion regarding all and the 3
cartesian aces, F = devout Qj Rk is then a vectorial field class C1
![]()
It is obtained adding turns out to you contained in the theorem of Ostrogradsky.
10) If F = To Bj Ck is of class C2(t), T ? "3 superficialally connected open
F is a rotor > F is solenoidale
F is a rotor that is exists upgrades them such U carrier that rotU = F therefore div F = div rot U = 0 and therefore F is solenoidale in how much has null divergence.
? In order to demonstrate that F is a rotor of it we try upgrades them carrier U = xi yj zk, it must it are such that
rotU = F ossia 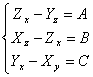 in order to become simpler is attempted upgrades them
carrier with the third null member that is U = xi yj 0k therefore
the simplified system is
in order to become simpler is attempted upgrades them
carrier with the third null member that is U = xi yj 0k therefore
the simplified system is 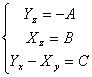 must hour to
elaborate the first 2 and to replace them in the 3ª, integrating
them regarding z has
must hour to
elaborate the first 2 and to replace them in the 3ª, integrating
them regarding z has 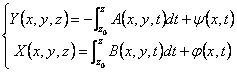
for semplicità we will suppose j(x,t) = 0. Deriving 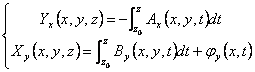 from which replacing it is had :
from which replacing it is had : ![]() and taking advantage of the hypothesis of divergence
nulla therefore Cz = -
Tox - By has
and taking advantage of the hypothesis of divergence
nulla therefore Cz = -
Tox - By has ![]() that is
that is ![]() and integrating respect to y it is
had :
and integrating respect to y it is
had : ![]() supposing to(x) = 0 and replacing in the
first equations obtains the thesis.
supposing to(x) = 0 and replacing in the
first equations obtains the thesis.
11) Theorem of upgrades them carrier :
If To it is a simply connected open of "3 and V are a vectorial field derivabile solenoidale (div F = 0)
Esiste a vectorial field such F che rot F = V in To every Inoltre other upgrades them carrier is given from the shape
F gradj where j ? C2(a) is one to climb.
The F is written rot considering null the member along
axis i, from the equation vettoriale rot F = V obtains three
scalari equations, satisfied in terms of integrals, they must to this
point to only characterize the constants that gush from the
integration, what that are possible replacing in ![]() the and taking advantage of the fact that
the and taking advantage of the fact that
div F = 0 is obtained upgrades them carrier F =
F2j F3k where ![]() e
e ![]()
12) Characteristic of the solenoidali fields :
Superficial ones are had 2 that they are frontier of a limited open, and are D the dominion constituted from the interstice between the two superficial ones, well if in this dominion the divergence of a vectorial field F is 0 the flow through one of the superficial ones is equal to the flow through the other.
13) Theorem of Gauss :
A surface is S sluice and is r the carrier position that
designates the distance of a whichever point (x, y, z) from origin 0.
Then 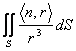 is worth :
is worth :
to) 0 if the origin is external to the surface sluice
b) 4p if the origin is inner to the surface sluice.
to) the divergence of r/r3 a result is null second classic, therefore this flow is null also.
b) the divergence is null also this time but to pact to eliminate a sferetta of infinitesimal beam whose surface goes parimenti considered for the calculation of the flow.
14) geometric Interpretation of the theorem of Gauss :
It is dS a surface element and we combine all the
points of the contour of dS with the origin Or coming in such a way to
form a cone. The intersection betweena
center sphere is hour d W Or and
beam r and the previous cone the solid angle dw is characterized from the relationship between this area
and the square of the distance from the origin ![]() being
being ![]() therefore the solid angle is
therefore the solid angle is ![]() .
.
In short if the source is external to the surface sluice then to every positive contribution when the flow enters in the surface a contribution will correspond negative when the flow exits some. If instead the source it is inner then the 2 contributions are added and the solid angle total is equal to the area of the unitary sphere that is 4p.
15) Meant of the divergence :
The divergence of a vectorial field F in the P point is
given from 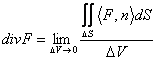 the being DV the volume enclosed from the surface dS, such
volume to the limit is reduced to the P point.
the being DV the volume enclosed from the surface dS, such
volume to the limit is reduced to the P point.
It is obtained to leave from the theorem of the divergence being applied the theorem of the average for integrals and isolating therefore to 1° the member the divergence, making then the limit obtains the thesis whose meant physicist it is the flow clearly through the surface dS which had to the F field, if such flow is positive, wants to say that there is an inner source while if the flow is negative wants to say that the source is external. If the divergence is 0 it means that in the region not sources are of pools of and therefore the field is solenoidale.
16) Meant of the rotor :
A derivabile field F is F : T® "3 and is Sr a having disc center in P, beam r and guideline characterized from the
external normal payer n. 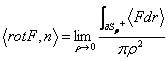 .
.
One obtains to leave from the theorem of Stokes being applied the theorem of the average for integrals and isolating therefore to 1° the member the product of the rotor for the normal payer to the surface, making then the limit obtains the thesis whose meant physicist it is that the rotor characterizes the direction in which the superficial density of circuitazione of F in P is maximum.
