Elettrolitica dissosciation and Electrolysis
1) For which solutions the colligative property assume various values from those theorists:
For the solutions of solute that are dissociated, which know them, the bases and the acids, that sayings come electrolytes. The phenomenon exactly has had to the fact that dissociating itself of an element increases the n° of present particles in solution and therefore they must increase also the values of the colligative property that directly are connected to the n° of particles.
2) Which it is the cause of the dissosciation of the Ionian ones of the electrolyte in water:
There are 2 causes:
to) the water constant greater dielectric has one 80 times regarding the empty one, and siccome this is inversely proporziona them to the energy upgrades them of 2 loaded located electrical workers at a distance r, follows that the energy necessary in order to break off the tie when this is in water he is remarkablly inferior regarding the force that would be necessary if the tie were in the empty one.
b) the solvation involves that around to every ione forms a water molecule cloud which exposes the negative part of their dipole, that is oxygen, their attraction is such to break off the tie that in water has become weak person and to create of Ionian the solvata one to you.
3) What is the meaning with the formula Na * 5H2Or:
One agrees that one ione of sodio is had solvatato, that is hydrated with 5 water molecules.
4) As the validity of the formulas for the colligative property is restored:
It is necessary to tie them to the ionization degree
being multiplied them for the binomial of Van' t Hoff ![]() where v are the n° of wharves of Ionian that they
form " size of solute.
where v are the n° of wharves of Ionian that they
form " size of solute.
5) That what ¨ the dilution of one solution:
When one is in many and stà tight one says that one is concentrates to you while when is in wide little and stà, one says that it has been become diluted.
6) Enounce the law of dilution of Ostwald in terms di concentration and degree of dissosciation:
![]() Constant = of ionization to one given temperature.
Constant = of ionization to one given temperature.
7) Like varied the constant of ionization with the concentration:
The ionization constant is expressed in terms of concentration, while the true thermodynamic constant is expressed in terms of activity. The 2 constants only coincide for solutions a lot diluted this why when the concentration increases, the Ionian ones are found like in via of the course Sunday, that is make difficulty to move. This property is estrinsecata through the activity coefficient f which exactly it decreases with the concentration for via of the reduced electrostatic attractions.
8) What is the ionic force:
It is a measure of the density of loads with the solution and therefore with the electrostatic actions which a data ione is subordinate from part of all the others.
![]()
9) That relation is between the activity coefficient f and ionic force m :
For solutions characterized from the same ionic force, the activity coefficient is always the same one independently from the nature of other present electrolytes.
10) That relationship is between the dilution of one solution and the degree of ionization:
From the law of Ostwald it is observed that if c
decreases, as an example as a result of a volume increase, having to
remain constant K for one given temperature, then ![]() must grow, and this is obtained increasing the dissosciation degree.
must grow, and this is obtained increasing the dissosciation degree.
11) What is the solubility of one substance in a dissolvent data:
The phenomenon that the solubility means to describe is the fact that throws the idrolitina in the water and it does not melt itself completely but it remains a bottom body and the solution water-idrolitina is said saturates.
It is defined like the number of substance wharves that are melted in a liter of solution, that is the concentration molar of the solution saturates.
12) What is the product of solubility of a little soluble electrolyte:
It is obtained from Kc applied to the equilibrium of a solution of a little soluble electrolyte in equilibrium with its solution saturates. It is important why when the product of the concentrations of anions and the cationi exceeds the value of the solubility product shape of the hasty one sin when the concentrations do not verify the solubility product.
The much smallest one is the value of the solubility product the much less soluble one is knows them in issue.
13) As it can be calculated the solubility of knows them:
The dissosciation reaction is taken and the concentration is placed of knows them equal to s, dopodichè fà the solubility product multiplying itself for s the stoichiometric coefficient of the respective one ione, the such way is obtained tosX and it can be gained s through the root x-esima of the product of solubility divided to.
14) What is the effect of the ione common:
It is the ulterior diminuizione of the solubility of a little soluble electrolyte (than it is melted little) to continuation of the insertion in the solution of one of Ionian the coming from ones from the dissosciation of the same electrolyte. That is explained with the fact that the reaction happens so as to to consume all the other ione and therefore it will be produced greater hasty.
15) As it can be increased the solubility of a data knows them, which as an example the limestone of the washing machines:
It is necessary to facilitate the reaction embezzling the products, that it does not happen with small tweezers but with acids and opportune bases that are arranged with single the Ionian ones and in such a way create substances that in order to give sense to all do not have to be to the solid state.
16) That relationship is between the solubility and the temperature:
The same relationship that there is between whichever equilibrium and the temperature, which for the note moves the equilibrium towards reagents, therefore knows them not disciolto, is melted partially increasing the temperature.
17) What is the current electrical worker:
It is a tidy flow of charges that pu² to before have place in conductors and of second species. In first it is due to the motion of electrons, in the second ones is instead due to the motion of the Ionian ones.
18) Which è the mechanism for which passage of current in the conductors of 1ª species is had:
The conductors of 1ª species are the metals and the liquids and in they the current is transported exclusively from electrons. Such behavior very is defined from the metallic tie that a reticulum of Ionian previews positi to you and around to they one electron cloud.
19) Which è the mechanism for which passage of current in the conductors of 2ª species is had:
The conductors of 2ª species are know them solid and liquids and the electrolyte solutions, constituted that is from know them, bases or acids disciolti in acqua. the tidy motion are generated to continuation of the application of a potential difference them electrical worker, in 3 are made:
to) the generator it embezzles electrons to a elettrodo(anodo) and it supplies them to altro(catodo) therefore the anode is loaded positively while the cathode is loaded negatively.
b) the cathode attracts Ionian positi you that they are you form you from the dissosciation of the solute electrolyte in water, such Ionian ones positi to you comes calls cationi to you, around to the cathode ce will be a great number.
the anode attracts Ionian denied you that they are you form you from the dissosciation of the solute electrolyte in water, such Ionian ones denied to you comes calls anions to you, around to the anode ce will be a great number.
c) We have to contact 2 distributions of charges that are attracted, but us the of transfer of the current cannot be passage in how much modalità electrical worker is various in the 2 conductors, this instead flows in how much is established of the reactions of riduzione(la solution acquires electrons) to the cathode and of ossidazione(la solution cede electrons) to the anode.
20) What is a cathode:
It is the electrode or metallic sheet to upgrades them negative towards which migrano the present cationi in solution.
21) What is the resistance of a conductor:
It is the factor that alloy the effect that is the current electrical worker to the cause that is the potential difference them, it he is characteristic of every various material, and is tied to its section, its length and its resistività second 2ª the law of Ohm:
![]()
22) What is the constant for one elettrolitica cell:
It is the ![]() relationship that are
exactly one constant for one elettrolitica cell and measure in cm-1.
relationship that are
exactly one constant for one elettrolitica cell and measure in cm-1.
23) What is the K conductance of a conductor:
It is the inverse one of the resistance and indicates how much exactly a conductor is lend to being crossed from current electrical worker
![]() where c is
the inverse one of the resistività and is called conductivity or
specific conductivity.
where c is
the inverse one of the resistività and is called conductivity or
specific conductivity.
24) Which are the factors that influence the K conductance of one solution:
The conductance sure is tied to n° of cationi and present anions in water, and this we have seen grows with the dilution that is with the volume. Then it is tied to mobility of these Ionian ones.
25) How much is worth the K conductance of 2 processes of conduction that happen parallel:
It is the sum of the conductances of the single processes.
26) specific conductivity c of a watery solution is influenced from specific conductivity c of the water:
In how much the c of the water is not much lowland, however for measures of extreme precision embezzled và it to the measured c.
27) What is the weight equivalent for an electrolyte:
It is the relationship between its molecular weight and the product of the n° of wharves of cationi that are formed for the n° of associated positive charges to every size, as an example for Cu(SO4) taking as reference Cu2 we have that PE = PM/(1*2). Such value identical if is calculated regarding the anion (KNOWS4)2- .
28) What is the constant of Faraday:
It is loads positive total or negative that can be obtained from the complete dissosciation of 1 g-equivalent of a whichever electrolyte, it is equal to the product of the n° of Avogadro for loads with the single electron. ? and = F.
1 Faraday = 96487 Coulomb = 26,8 Ah
29) What is the equivalent conductivity L:
It proposes itself to tie the conductance of a solution to
its ![]() concentration where N is normality that is
equal to the product of the molarità for the n° of charges of the
ione. Es: H2 is
necessary to multiply for 2 the molarità.
concentration where N is normality that is
equal to the product of the molarità for the n° of charges of the
ione. Es: H2 is
necessary to multiply for 2 the molarità.
It comes defined like the conductance of that volume of solution that contains disciolto 1 electrolyte equivalent, measured between 2 electrodes parallels to the distance of 1 cm.
30) What is the equivalent conductivity limit L¥ :
It is observed that for solutions weak people, also increasing the dilution, does not have more increase of the equivalent conductivity, therefore the maximum value from caught up it comes defined limit, it is legacy to the fact that increasing the dilution is increased also the dissosciation until to the maximum value to = 1 which it corresponds L¥ exactly therefore is useful why it uncouples the conductivity from the concentration and therefore it only remains tied to mobility of the ione.
31) That relationship is between the equivalent conductivity and the equivalent conductivity limit:
![]()
32) Enounce the law of dilution of Ostwald in terms of L and L¥ :
![]()
33) Enounce the law of Kohlraush:
Every ione it contributes in characteristic and constant measure to the equivalent conductivity limit of an electrolyte, and its contribution is independent from the nature of the coming from other ione from the dissosciation of the electrolyte.
![]()
34) Why L¥ of Ionian (H3Or ) ed (OH- ) in water much more is elevated respect to other Ionian ones:
The elevated conductivity is not due to particular mobility of these Ionian ones but to the fact that in water they form and create in continuity a great number of ties O-H under the infuence of an electric field, therefore the protons moves from one molecule to the other catching up the opportune electrode.
35) What is electrolysis:
It is the phenomenon for which a chemical transformation of a solution by means of ossidoriduzioni is had when this is crossed from current electrical worker. The phenomenon has had to unloading itself of the Ionian presents in solution on the respective electrode. The substance amount is tied to the amount of electricity that crosses the solution and to the weight equivalent of the considered substance.
36) Origin of the name electrolysis:
Lisi = breach, therefore agrees the breach of the ties for via electrical worker.
37) Relation between the battery and electrolysis:
They are 2 complementary processes, the 1° it is spontaneous and it has the scope to produce to electric power through of the ossidoriduzione reactions, while the 2° it is not spontaneous and necessity of the energy supplied from one battery in order to realize of the reactions of ossidoriduzione to the aim to separate to substances to the pure state presents in solution as Ionian.
38) In the process of electrolysis which electrode is the cathode, which the anode and that it upgrades they have them:
The cathode is for definition the electrode where the reduction happens and therefore the substance to the pure state is formed, for happening the reduction, demands electrons to supply to the solution which this time is supplied from the battery and therefore the cathode is the electrode more negative. The positive pole of the battery connected to the electrode anode, of ciuccia via electrons concurring therefore the formation of Ionian positi to you that they get rid in water, and is gone to recombine on the cathode with coming from electrons from the battery.
39) Having in solution n ossidoriduttive braces, which it will be unloaded to the anode:
Remembering that to the anode the oxidation happens, the ossidoriduttiva brace will be oxidized having upgrades them elettrodico more bottom while to the cathode happening the reduction, will unload the having brace upgrades them elettrodico more positive.
40) It is possible to obtain the decomposition of the alkaline metals and alkaline terrosi in watery solutions:
Not, in how much they have upgrades them elettrodico inferior regarding the brace H3Or / H2 and therefore it is this to ridursi.
41) Enounce the 2 laws of Faraday on electrolysis:
to) the amounts of substances that are formed to the electrodes they are proporziona them to the electricity amount that has crossed the solution.
b) the weights of 2 various substances produced from the same amount of electricity are proporziona them to the weights equivalents of the same substances.
42) Enounce the formula of Faraday in order to gain the amount of substance produced through electrolysis:
![]() where F is the constant of Faraday, the equivalent
weight like for the ossidoriduzioni is estimated dividend the
molecular weight of the substance for the n° of electrons exchanges to
you. In terms of wharves the proportion can instead be set up:
where F is the constant of Faraday, the equivalent
weight like for the ossidoriduzioni is estimated dividend the
molecular weight of the substance for the n° of electrons exchanges to
you. In terms of wharves the proportion can instead be set up:
1 Faraday : 1 mole = x_moli Q :
in fact 1 Faraday is the amount of loads associated to one electron size.
43) Estrinsecare the consequences of the passage of current in one solution:
Al cathode happens the reduction with formation of substances allo be not ionic, the generator supplies affinchà electrons that happens, alla anode happens the run oxidation nel della which the electrons come yielded al generating closing in such way the circuit.
44) What is the meaning for faradico rendering:
The amount of substance produced in practical is inferior regarding that calculating for via of insturarsi of numerous processes of ossidoriduzione, between which unloading itself of Ionian H3Or therefore it comes defined a faradico rendering of electrolysis
![]() equivalent to the current rendering
equivalent to the current rendering
![]()
45) What is upgrades them of decomposition of one solution:
It is upgrades them andD beyond which the solution has one directed proportionality between the potential difference applied them and the intensity of current that crosses the solution. Before that it comes caught up this upgrades them to growing of the applied tension the current increases in insignificant way.
46) Enounce the law of Ohm for the conductors of 2ª species:
![]()
47) To which causes the phenomenon described is legacy from upgrades them of decomposition:
It is the sum of 2 factors;
to) As soon as they begin the reduction and the oxidation, an inner battery to the solution is generated that is opposed to fem the external like in a potenziometrico circuit, increasing to the external tension the fem of the inner battery grows in way specular until reaching to a value andsaid R upgrades them reversible of ionization, beyond which the external battery has the windward.
b) the process in truth is not reversible and the processes that compose electrolysis must happen to adapted speed, if one of they is slower, become necessary one overstrain that compensations this slow stage.
48) As it is estimated it upgrades them of decomposition for one given elettrolitica cell:
AndD = AndANODO - AndCATHODE
where and ANODE is upgrades associated them to the oxidation reaction that happens to the anode which is that one to more low upgrades them of Nernst between all. And CATHODE instead is upgrades associated them to the reduction reaction that happens to the cathode which is that one to upgrades them of higher Nernst between all.
49) Knowing that the overstrain of discharge of hydrogen on nickel is worth 0,21v determining the reaction and it upgrades them to associated it:
2 H3Or 2e ® H2 (g) 2 H2Or

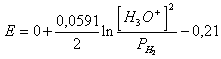
50) Knowing that the overstrain of oxygen on platinum is worth 0,48v determining the reaction and it upgrades them to associated it:
6 H2O ® Or2 (g) 4 H3Or 4e
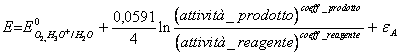
![]()
51) Which processes are generated in the course of electrolysis:
to) New Ionian in solution they must diffuse in the pressed ones of the anode in order to replace those that are unloaded.
b) the Ionian ones in truth are solvata to you and are therefore necessary of the additional energy in order to dehydrate them.
c) the Ionian ones that is unloads to you must join in order to create a stable crystal, that it demands energy.
d) If the substance generated for reduction is to the state of gas, this must be separated from the anode.
52) What is a voltametro to silver:
It is an instrument in a position to measuring the electricity amount that crosses a data simply circuit using the law of Faraday that is measuring the substance amounts that they are deposited on the cathode. It is constituted from two silver electrodes dipped in one solution of Ag(NO)3 .
