Acids and bases
1) What is an acid:
One whichever able chemical species to yield a proton (ione H ) to one base.
2) What is one base:
One whichever able chemical species to accept the proton yielded from an acid.
3) What is the meaning for conjugated brace:
One agrees that an acid for loss of the proton is transformed in a base and in analogous way the base for purchase of a proton is transformed in an acid. The conjugated brace therefore is constituted from a conjugated acid and one conjugated base.
4) What is the meaning for anfolita substance:
A substance like the water agrees or the ammonia that can react is like acids that like bases.
5) What is the meaning by force of an acid:
The force of an acid is one measure of its ability to yield a proton.
6) Thing by force agrees of one base:
The force of a base is one measure of its ability to tie a proton.
7) Like measure the force of an acid regarding that one of an other acid:
A brace is necessary to fix a reference that is acid/base
under dissolvent shape, normally the water and to calculate the
constant of ionization of the 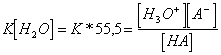 reaction where
exactly the concentration of the constant water has been supposed.
From this relation fà other that to confront IT HAS with H3Or in fact if the acid is more strongly of ione ossonio then
the equilibrium is not moved towards reagents and K is much small,
otherwise viceversa.
reaction where
exactly the concentration of the constant water has been supposed.
From this relation fà other that to confront IT HAS with H3Or in fact if the acid is more strongly of ione ossonio then
the equilibrium is not moved towards reagents and K is much small,
otherwise viceversa.
8) Why in the calculation of the KW the concentration of the constant water can be considered:
Why it dissociates least, a lot is true that KW is worth 10-14 that for an equilibrium it indicates that the dissosciation reaction is all moved towards reagents.
9) What is the meaning for levelling effect of the dissolvent and as it is resolved:
One agrees that it is not succeeded to create a priority between the acids that are stronger regarding H3Or . The problem is resolved choosing which dissolvent the water but acetic acid CH3COOH which which has a conjugated brace constituted from a base much weak person do not have one smaller ability to attract protons of acid forte.
An analogous behavior is had also for the measure of the force of a base when the base to measure is more strongly of base OH-.
10) In that categories subdivide compounds in which are contained one or more ossidrilici groups:
Ossiacidi E' this the case in which 3° the element last one is elettronegativo to the par of the oxygen therefore this will unload its elettronegatività in the attraction towards the H with which it will form therefore a strongly ionic tie that in water comes easily attacked, dissociates therefore H and the compound is therefore an acid. HClO.
Idrossidi Is this the case in which 3° the element it is less elettronegativo regarding hydrogen therefore between oxygen and 3° the element will form a strongly ionic tie that in water comes easily attacked, dissociates therefore the OH- and the compound is therefore one base. KOH.
Anfoliti E' this the case in which 3° the element oxygen has elettronegativà similar to that one of the H therefore will form ionic ties with both the elements and to second of the situation therefore the compound base will be able to be behaved like one or an acid.
11) To what the force of an acid is tied:
to) To the difference between the n° of atoms of Or and the n° of present atoms of H in the compound, in fact more atoms than Or are and with more force the acid will resist to the base that it it wants to embezzle a proton.
b) the force of an acid diminishes with growing of the dimensions of the atom centers them which to they time diminishes to growing of the n° of electrons on the more external orbit. Fact is that the many more electrons are far from the nucleus much more easy can be embezzled to the atom in issue.
c) In poliprotici acids the force of acid decreases passing from the first ionization n-esima to the ionization.
d) For the atoms that do not contain oxygen the force grows to growing of the dimensions of the atom legacy to the H
12) What is the ionic product of the water:
It is the constant tied to the reaction of ionization of acqua the KW = [ H3Or ][OH-] = 10-14 .
13) What is the cologaritmo of the ionic product of the water and what indicates:
The cologaritmo it is a way to express the numbers so as to to remove the negative powers, therefore for the water pKW = 14, but the interesting what is the fact that pH indicated pOH = 14 having with pH the cologaritmo of the concentration of Ionian [ H3Or ]. In the case of the pure water pH = pOH and the solution it comes said neutral.
14) If the pH how much is 2,35 is worth the concentration of Ionian [ H3Or ]:
[ H3Or ] = 10 - 2,35
15) When a watery solution is acida and when basic or alkaline:
A solution is acida when it has a pH smaller of 7 or analogous a pOH greater of 7. This why an acid in solution increases the concentration of Ionian [ H3Or ] and therefore the cologaritmo is smaller. The solution is instead basic in the complementary case.
16) That relation is between the force of acido a KTo and the force KB of its conjugated base:
The product of the constant of dissosciation of an acid and of the constant of dissosciation of its conjugated base is equal to the ionic product of the water or in a generalized manner he is equal to the ionic product of the dissolvent. KTo * KB = KW .
17) Itemize some strong acids:
Perchloric acid HClO4 , hydrochlorate HCl, nitric HNO3 , sulfuric H2I KNOW4 , bromidrico Hbr, iodidrico HI, selenico H2SeO4 , HSCN, HIO3
18) How much is worth pH of watery solutions of acids and the strong bases with concentration > 10-6 :
The dissosciation of the water can be neglected and therefore the concentration of Ionian [ H3Or ] is equal to the concentration of acid or, in the case of a base, the concentration of Ionian [ the OH-] he is equal to the concentration of the base.
19) How much is worth pH of watery solutions of acids and the strong bases with concentration < 10-6 :
The dissosciation of the water cannot be neglected and therefore for an acid the concentration of Ionian [ H3Or ] is gained from:
[ H3Or ]- c [ 2 H3Or ] - KW = 0.
In the case of a base instead the concentration of Ionian [ the OH-] OH is gained dalla [-]- 2 c [ OH-] - KW = 0.
20) How much is worth pH of one the watery solution of an acid weak person:
It is necessary to neglect Ionian [ H3Orcoming from ] from the dissosciation of the water, applying the
law of action of mass are reached ![]()
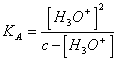 the , from this
it is necessary to resolve [ H3Or ]2 KTo * [ H3Or ] - c * KA = 0 or in the case that 10K To <-3 e c > 10-3 H 3 Or ]tothe denominator can be
neglected [ obtaining
the , from this
it is necessary to resolve [ H3Or ]2 KTo * [ H3Or ] - c * KA = 0 or in the case that 10K To <-3 e c > 10-3 H 3 Or ]tothe denominator can be
neglected [ obtaining ![]() .
.
21) Which law alloy the degree of dissosciation to to the concentration of an acid weak person and to the concentration of [ H3Or ]:
[ H3Or ] = c * to
22) Itemize some strong bases:
The idrossidi of the alkaline metals NaOH, KOH, LiOH and alkaline terrosi Ca(OH)2 , Ba(OH)2 , 2Sr(OH) , etc....
23) Which law alloy the degree of dissosciation to to the concentration of one base weak person and to the concentration of [ OH-]:
[ OH-] = c * to
24) How much is worth pH of one the watery solution of one base weak person:
It is necessary to neglect Ionian [ the OH-] coming from from the dissosciation
of the water, applying the law of action of mass is reached to ![]()
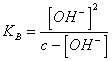 the , from this it is necessary to resolve [ the OH-]2 KB * [ OH-] - c * KB = 0 or in the case that K10 B <-3 e c > 10-3 can be neglected [ OH-] to the denominator obtaining
the , from this it is necessary to resolve [ the OH-]2 KB * [ OH-] - c * KB = 0 or in the case that K10 B <-3 e c > 10-3 can be neglected [ OH-] to the denominator obtaining ![]() .
.
25) As the pH is estimated of the poliprotici acid solutions:
The calculation of the pH is much complex in how much is necessary to hold account of the successive ionizations but in practical it is strongly acida only 1ª the ionization therefore pu² to only consider the concentration begins them of Ionian [ H3Or ].
26) As the concentrations of the Ionian ones are estimated that take origin from the successive ionizations of a poliprotico acid?
It is necessary to gain the concentrations inherent to 1ª the ionization, to observe that if is still H in produced acid, this will stretch in its turn to ionizzarsi, therefore the concentration previously found is not that end but it goes ulteriorly decrementata in function of the dissosciation degree.
27) What is one solution pad:
It is a solution that is opposed to abrupt variations of the pH even if come in it introduced strong acids or bases.
28) Which are the 3 fundamental types of solutions pad:
to) Solution of an acid weak person and its it knows them,
for it is worth la ![]()
b) Solution of a base weak person and its knows
them, for it is worth la ![]()
c) Mixture of knows them of a polibasico acid, for it is worth la
![]()
29) Which reactions carry to one of the 3 fundamental types of solutions pad:
to) they carry to the acid case weak person its knows them the reactions:
*) acid debole(in excess) strong base
*) strong acid knows them of acid debole(in excess)
b) they carry to the base case weak person its knows them the reactions:
*) base debole(in excess) strong acid
*) strong base knows them of base debole(in excess)
c) carries to the mixture case of knows them of poliprotico acid the reactions:
*) knows them acids poliprotici(in excess) strong acid
*) poliprotici acids or they sali(in excess) strong base.
30) When a solution pad has the maximum efficiency:
When the pH of the solution it is close to the value of pKTo that verification when the concentration of knows them is next to the concentration of acid or respective of the base.
31) How much is worth the pH of a watery solution of knows them deriving from one strong base and a strong acid:
It is worth 7, how much the pH of the water, in fact the strong base gives place to an anion that in water does not react, and analogous the catione deriving from the complete dissosciation of strong acid. This type of reaction is called of neutralization and to the term that that is obtained is a solution of un knows them. The heat yielded in the neutralization is constant and is worth -13680 cal.
32) How much is worth the pH for knows them deriving from one strong base and an acid weak person:
The catione deriving from the base strongly does not react in water while the anion deriving from acid weak person reacts with water forming Ionian OH- and giving therefore to place to one weakly alkaline solution. The considered constant of ionization of the ione as base weak person obtains from the KB = KW / KTo and the concentration is that one of knows them, the pH can therefore be calculated from [ the OH-]2 KB * [ OH-] - c * KB = 0.
The pH of the solution it is but also calculable directly
through ![]() .
.
It is thinkable as the sum of a reaction of neutralization and a reaction of ionization, to the term di.le which it is obtained knows them of an acid weak person and one strong base.
33) How much is worth the pH for knows them deriving from one base weak person and a strong acid:
The anion deriving from acid strongly does not react in water while the catione deriving from the base weak person reacts with the water forming Ionian H3Or and giving therefore to place to one solution weakly acida. The considered constant of ionization of the ione as acid weak person obtains from the relative base through the KTo = KW / KB and the concentration is that one of knows them, the pH it can therefore be calculated from [ H3Or ]2 KTo * [ H3Or ] - c * KA = 0.
The pH of the solution it is but also calculable directly
through ![]() .
.
It is thinkable as the sum of a reaction of neutralization and a reaction of ionization, to the term di.le which it is obtained knows them of one base weak person and a strong acid.
34) How much is worth the pH of a watery solution of knows them deriving from one base weak person and an acid weak person:
Both the Ionian ones react in water, will be able
therefore to be obtained basic solutions, acide or neutral in virtue
of the force of you respect to you Ionian and independently from the
concentration of it knows them. The pH he is determinable with: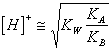 or directly
or directly ![]() .
.
It is thinkable as the sum of a reaction of neutralization and 2 reactions of ionization, to the term di.le which it is obtained knows them of acid weak person and base weak person.
35) How much is worth the pH of a watery solution of knows them deriving from an acid deriving from the ionization of a strongly poliprotico acid:
If the acid is strongly the ionization it is complete and the acid from deriving it is an acid weak person whose pH it is estimated from [ H3Or ]2 KTo * [ H3Or ] - c * KA = 0 considering like KA2 that relative one to 2ª the ionization of strongly poliprotico acid and as concentration that one of knows them of which acid weak person it is constituent.
36) How much is worth the pH of a watery solution of knows them deriving from an acid deriving from the ionization of an acid poliprotico weak person:
A solution acida, basic or neutral can be had whose pH it
is calculable through 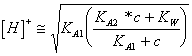
that it can be become simpler to ![]() the in the case that c is negligible regarding KA1 and Knegligible W regarding KA2 * c.
the in the case that c is negligible regarding KA1 and Knegligible W regarding KA2 * c.
37) What is the amino acids:
It is a category of anfoliti that they contain in the same molecule the group acid - COOH and the basic group - NH2 .
38) What is the iso-electric point:
It is that value of the pH for which the protonata shape and the anionic shape have the same concentration, it is gained from:
![]()
39) What is the meaning for tiration:
The determination agrees analytics of the incognito amount of one given sostanza making it to react in complete way with a famous amount of an other substance dictates titolante reagent.
40) Why the reaction of neutralization in the tiration is used:
It satisfies following 3 requirement:
to) almost complete reaction Is one.
b) the state of equilibrium is caught up in short time.
c) the complete reaction is marked from the fact that n° the equivalents of base = n° acid equivalents.
41) What is the meaning and what happens in the equivalence point:
In the point of equivalence the n° of base equivalents he is equal to the n° of acid equivalents, that it wants to say that they are neutralized completely giving place to knows them whose n° of wharves he is equal to the n° of wharves begins them of the substance from holder. To such point the acidity or basicity of the solution is tied to the characteristics of this only knows them.
42) Describe the tiration of a strong acid with one strong base:
To the equivalence point they are neutralized completely giving place to knows them whose Ionian in water they do not react and therefore the solution is totally neutral, pH = the 7. It is not necessary a particularly next pointer to 7 why the solution does not have property pads neither before neither after the equivalent point therefore pH=7 is a point to vertical tangent.
43) Describe the tiration of an acid weak person with one strong base:
To the equivalence point they are neutralized completely giving place to knows having them basic property. Before that the equivalent point is caught up, the varied solution slowly its pH in how much constituted from an acid weak person and its knows them, therefore is behaved like a pad.
44) Describe the tiration of one base weak person with a strong acid:
To the equivalence point they are neutralized completely giving place to knows having them property acide. Before that the equivalent point is caught up, the varied solution slowly its pH in how much constituted from a base weak person and its knows them, therefore is behaved like a pad.
45) Describe the tiration of a diprotico acid strongly with one strong base:
An ionization is had before that determines the loss of 1° the proton of acid, the pH to questo point is calculable as for a whichever acid weak person, continuing to introduce the base it is reached the equivalence point where acid and base are neutralized completely giving place to know having them the characteristic of a base weak person and which therefore before are estimated the KB from the IndianK A2 the pOH and finally the PH.
46) Describe the tiration of a diprotico acid weak person with one strong base:
An ionization is had before that determines the loss of 1°
the proton of acid, the pH to questo point it is calculable from 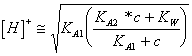 in how much acid deriving from 1ª the
dissosciation is anfolita, continuing to introduce the base it is
reached the equivalence point where acid and base are neutralized
completely giving place to know having them the characteristic of a
base weak person and which therefore before are estimated the KB from the IndianK A2 the pOH and then the PH.
in how much acid deriving from 1ª the
dissosciation is anfolita, continuing to introduce the base it is
reached the equivalence point where acid and base are neutralized
completely giving place to know having them the characteristic of a
base weak person and which therefore before are estimated the KB from the IndianK A2 the pOH and then the PH.
47) What is a pointer of pH:
It is an acid or organic base weak person, having the characteristic that the ionizzata molecule and its ione are not of various color. The pointer is characterized from a point of viraggio in correspondence of which the concentration of the ionizzata shape of the pointer is equal to the concentration of the shape not ionizzata. In solutions more acide regarding the viraggio point the pointer assumes the color of the shape not ionizzata while in basic solutions it assumes the color of the ionizzata shape, for pH intermediate it assumes a value that the colorimetria associates to the combination of the extreme colors a pointer example is the lemon that we throw in the thé and of it it changes the color.
48) Which molecules are used like pointers of pH and which principle takes advantage of:
The color of a substance is tied to its ability to absorb determined members of the phantom of the light and therefore we see only complementary the phantom non absorbed. The absorption of the light is legacy to the photon absorption when these invest an atom and supply their energy to an electron making to pass more it to an elevated energetic level. The aromatic molecules type the benzene thanks to the delocalizzazione of electrons introduce one smaller distance between the energetic levels and therefore attitude to absorb photons just of the phantom of the visible one.
49) Which formula alloy the difference between pH of the solution and the point of viraggio to the concentrations of the pointer not ionizzato and the ionizzato pointer:
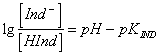 where pKIND is a
characteristic value of the determined pointer.
where pKIND is a
characteristic value of the determined pointer.
50) Which it is the criterion of chosen of the pointer for one determined solution:
It is necessary to choose the pointer that it has a point of possible the next viraggio to the value of the pH of the solution.
51) Describe the method of conduttometrico tiration:
It is a method that for the survey of the equivalent point is based on the ascertainment that the Ionian conductivity of H3Or and OH- it is maximum regarding the other Ionian ones, and that in the neutralization in correspondence of the equivalence point they catch up a minimal concentration in how much replaced from the Ionian ones of know them, therefore to the point equivalent the conductivity of the solution is minimal.
52) As the solubility for the idrossidi is estimated:
It is necessary to keep in mind that the idrossidi free OH- than they are gone to add to those of the water, the solubility is therefore equal to the single concentration of the catione and pu² to be estimated imposing that you respect the ionic product of the water.
53) As it is estimated the solubility of knows them coming from from acids weak people:
It is necessary to keep in mind that the anion deriving from the ionization of knows them is a strong base therefore in part is recombined with H of the water that it is equivalent to say that comes embezzled to the solution leaves of the anion, the Ks is canted and therefore having it to remain constant, the reaction is moved towards the ulterior issolution of knows them in the solution. After all in order to hold account of this effect it is necessary to multiply the solubility s of the anion for corrective factor R.
54) How much is worth corrective factor R for knows them of monoprotici acids weak people:
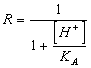 or directly the solubility through
or directly the solubility through 
55) How much is worth corrective factor R for knows them of diprotici acids weak people?
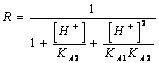 or directly the
solubility dalla
or directly the
solubility dalla 
56) How much is worth corrective factor R for knows them of triprotici acids weak people:
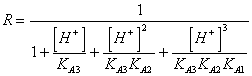
57) How much is worth the solubility in water of an acid little soluble weak person:
It is given from the sum of the concentration of indissociato acid and the anion, or, more easily:
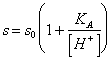 where s0 are the
solubility of the indissociata shape of acid.
where s0 are the
solubility of the indissociata shape of acid.
58) How much is worth the solubility in water of one base little soluble weak person:
It is given from the sum of the concentration of the indissociata base and the catione, or, more easily:
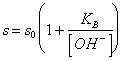 where s0 are the
solubility of the indissociata shape of the base.
where s0 are the
solubility of the indissociata shape of the base.
59) Which are the considerations that the Crociani method uses for the calculation of the concentrations of acids and bases:
to) Budget of the masses holding account that generally comes supplied the concentration of indissociato acid.
b) Budget of the charges holding account to multiply every concentration for the n° of charges of the single one ione.
c) Produced of Ks solubility.
d) Constant of ionization of acids
and) constant Kw
f) in solution acida the OH are negligible in the sums [-].
g) in basic solution they are negligible in the sums [ H3Or ].
h) in poliprotici acid solutions where 1ª the ionization is most substantial, it can be neglected the acid concentrations of the successive ionizations regarding the concentration of 1ª the ionization.
